User Story: System Alerts & Proactive Recommendations (AX03US03)
1. Problem Statement
This user story addresses the need to move beyond scheduled maintenance and reactively fixing failures by proactively identifying at-risk assets before they fail. The primary user is the Asset Manager, who is responsible for managing the long-term health and risk profile of the utility's entire asset base.
Primary User Role & Pain Points:
- Asset Manager:
- Blind to Emerging Risks: Relies on fixed schedules (Preventive Maintenance) or waiting for failures (Corrective Maintenance), leaving them blind to assets that are degrading faster than expected between cycles.
- Inability to Act Proactively: Lacks a system that can synthesize complex data (e.g., condition, criticality, operational data) to flag specific, high-risk assets that need immediate attention.
- Difficulty Prioritizing "Hidden" Work: Struggles to decide which non-urgent work to perform. Without data-driven recommendations, they may service a low-risk asset while a high-risk one is silently approaching failure.
- Missed Cost-Saving Opportunities: Cannot quantify the potential savings of performing proactive maintenance, making it difficult to justify the allocation of resources away from scheduled tasks.
- Overwhelmed by Data: Has access to vast amounts of asset and operational data but lacks the tools to automatically analyze it and surface actionable insights.
Core Problem:
For the Asset Manager, traditional maintenance strategies are insufficient to prevent all critical failures. Without an intelligent system to analyze data and predict potential issues, they are perpetually one step behind, unable to identify and mitigate emerging risks proactively. This leads to preventable failures, higher emergency repair costs, and an inability to optimize maintenance spending effectively.
2. Who Is the User Facing the Problem?
The Asset Manager is the most important user for this feature. Their core mandate is to manage and mitigate risk across the asset lifecycle. This "System Alerts" module acts as their early-warning system, directly feeding them the data-driven, prioritized insights needed to make strategic decisions about where to intervene. While an O&M Manager would execute the resulting work, the Asset Manager is the one who reviews, validates, and approves these proactive recommendations as part of their overall risk management strategy.
Access Control:
The Asset Manager should have full access to review, action, and dismiss recommendations. The O&M Manager would also have full access to convert recommendations into Service Orders. The Utility Administrator would have configuration access.
3. Jobs To Be Done
- For the Asset Manager: When I need to prevent critical asset failures and optimize my maintenance budget, but I cannot see which assets are silently becoming high-risk between scheduled inspections, help me by providing an AI-powered system that analyzes asset data to generate prioritized maintenance recommendations, so that I can intervene before failures occur, reduce emergency repair costs, and allocate my resources to the most significant risks.
4. Solution
The proposed solution is a System Alerts module that functions as an AI-powered recommendation engine. It analyzes assets with low condition scores and high risk scores to generate "Proactive Maintenance Insights." This provides a prioritized list of potential interventions, complete with context and actions to convert insights into work.
Key Capability Areas:
- Proactive Insights Dashboard:
- High-level KPIs summarizing the state of proactive maintenance:
Total Active Recommendations,High-Risk Assets Identified,Potential Cost Savings, andRecommendations Overdue.
- High-level KPIs summarizing the state of proactive maintenance:
- Prioritized Recommendation List:
- A central table listing all system-generated recommendations.
- Each recommendation includes an ID, the associated Asset, Location, Condition Score, Risk Score, a description of the
Potential Impact, and its currentStatus.
- Risk-Based Prioritization:
- The core logic of the feature is to identify assets with a combination of a low
Condition Score(high probability of failure) and a highRisk Score(high consequence of failure). - This ensures the most important and vulnerable assets are surfaced first.
- The core logic of the feature is to identify assets with a combination of a low
- Actionable Workflow:
- Each recommendation has a clear status (e.g., New, Reviewed, Action Taken, Overdue, Dismissed).
- A simple "Actions" menu allows the Asset Manager to:
View Detailsfor deeper analysis.+ Create Service Orderto directly convert the recommendation into a work order.Mark as Reviewedto acknowledge the insight.Dismiss Recommendationto close it out with a justification.
- Quantified Business Value:
- The
Potential Cost SavingsKPI estimates the financial benefit of acting on these recommendations over a given period, providing a clear ROI for the feature. - The
Potential Impactcolumn for each recommendation describes the specific negative outcome that the proactive work would prevent.
- The
5. Major Steps Involved
User Role: Asset Manager
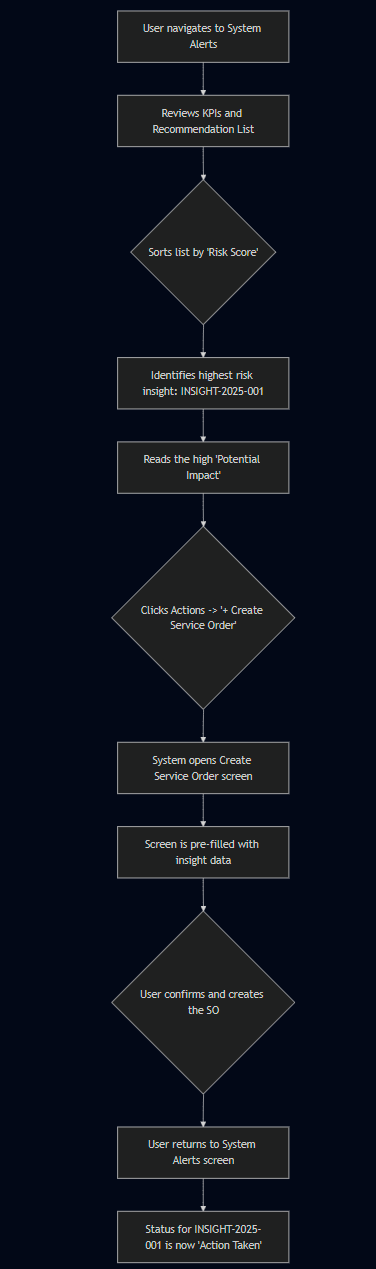
Flow 1: Reviewing and Actioning a High-Risk Recommendation
6. Flow Diagram
7. Business Rules
This section provides a detailed breakdown of rules for every visible element on the screen.
A. System Alerts (Dashboard View)
- Page Title/Subtitle: Static text explaining the feature's purpose.
- KPI Card: "Total Active Recommendations"
- Formula:
COUNT(Recommendations)whereStatusIN ('New', 'Reviewed', 'Overdue').
- Formula:
- KPI Card: "High-Risk Assets Identified"
- Formula:
COUNT(Recommendations)whereRisk Score>= 7.0 (or another defined threshold) ANDStatusIN ('New', 'Reviewed', 'Overdue').
- Formula:
- KPI Card: "Potential Cost Savings"
- Formula:
SUM(EstimatedCostOfFailure - EstimatedCostOfProactiveRepair)for all recommendations whereStatus= 'Action Taken' within the "last 30 days". This is a complex metric requiring predefined cost estimates.
- Formula:
- KPI Card: "Recommendations Overdue"
- Formula:
COUNT(Recommendations)whereStatus= 'Overdue'. A recommendation becomes overdue ifAction Datehas passed and status is still 'New' or 'Reviewed'.
- Formula:
- Search Bar: Must search across
Recommendation ID,Asset ID/Name, and keywords in thePotential Impactdescription. - Refresh/Filters Buttons: Standard controls to refresh the data and apply advanced filters (e.g., by Status, by Risk Score range).
- Table: "Proactive Maintenance Insights"
- Recommendation ID: Unique, system-generated ID for the insight.
- Asset ID / Name: The specific asset identified.
- Location: The location of the asset.
- Condition Score: The asset's current condition score. Must be color-coded (e.g., red for < 3.0).
- Risk Score: The asset's current risk score. Must be color-coded (e.g., red for > 7.0).
- Action Date: The suggested date by which action should be taken.
- Potential Impact: A text description of the business consequence of failure.
- Status: A colored tag indicating the recommendation's state (New, Reviewed, Overdue, Action Taken, Dismissed).
- Reviewed By / Reviewed On: If status is 'Reviewed' or later, these fields are populated with the user's name and the timestamp.
- Actions ("..."): A menu button that must reveal:
View Details: Opens a detailed view of the insight and the underlying data.+ Create Service Order: Initiates the workflow to create a new SO, pre-populating it with data.Mark as Reviewed: Changes the status to 'Reviewed' and populates the 'Reviewed By/On' fields.Dismiss Recommendation: Opens a prompt asking for a reason, then changes the status to 'Dismissed'.
8. Sample Data
Recommendation Record (for INSIGHT-2025-001):
- Recommendation ID: INSIGHT-2025-001
- Asset ID / Name: PUMP-001, Primary Intake Pump
- Location: Main Treatment Plant
- Condition Score: 2.8
- Risk Score: 8.2
- Action Date: Jan 15, 2025
- Potential Impact: Service disruption affecting 12,500 consumers
- Status: New
- Reviewed By: N/A
- Reviewed On: N/A
9. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must generate recommendations for assets that cross a certain threshold (e.g., Condition Score < 4.0 AND Risk Score > 6.0).
- The system must display the four KPI cards with correctly calculated values.
- The system must display a searchable and filterable list of all active recommendations.
- The system must color-code the Condition and Risk scores to draw attention to poor values.
- The system must provide an "Actions" menu for each recommendation with four options: View Details, Create Service Order, Mark as Reviewed, Dismiss.
- Selecting
+ Create Service Ordermust launch the SO creation wizard and pre-populate relevant data. - After a service order is created from a recommendation, its status must automatically update to "Action Taken".
- Selecting
Mark as Reviewedmust update the status and log the user and timestamp. - Selecting
Dismiss Recommendationmust prompt for a reason before changing the status. - The
Recommendations OverdueKPI must accurately count recommendations that have passed theirAction Datewithout being actioned or dismissed. - The
Potential Cost SavingsKPI must correctly calculate the financial benefit based on its formula. - The system must allow filtering recommendations by their
Status. - The user must be able to sort the recommendation list by any column, especially
Condition ScoreandRisk Score. - The
High-Risk Assets IdentifiedKPI must use a configurable threshold (e.g., Risk Score >= 7.0). - Dismissed recommendations should be hidden from the default view but accessible via a filter.
10. Process Changes
From: (Current Process) | To: (New Process) | Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
Maintenance work is driven by calendar schedules (PM) or asset failure (CM). | Maintenance work is driven by data-driven, risk-based insights, allowing for targeted, proactive interventions. | Justification: This represents a fundamental shift from a traditional to a predictive maintenance model (Maintenance 4.0). It allows the utility to get ahead of failures, focusing resources with surgical precision. |
Asset risk is reviewed periodically during manual assessments. | Asset risk is monitored continuously by the system, which automatically flags assets whose risk profile has become unacceptable. | Justification: This automates a critical but labor-intensive part of the Asset Manager's job. It reduces the chance of human error and ensures emerging risks are caught instantly, not just during a quarterly review. |
The value of the maintenance department is measured by cost and budget adherence. | The value of maintenance is measured by its ability to reduce risk and generate cost savings by preventing expensive emergency repairs. | Justification: This changes the narrative around maintenance from being a "cost center" to a "value-creation center." The |
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Metric | How it Improves |
|---|---|
:white_check_mark: Reduced Critical Failures | By identifying and addressing high-risk assets before they fail, the system directly reduces the number of unplanned, critical failures that cause service disruptions and safety hazards. |
:white_check_mark: Optimized Maintenance Spend (OpEx) | Shifts spending from expensive, inefficient emergency repairs to lower-cost, planned proactive work. This lowers the total cost of maintenance over the asset's lifecycle. |
:white_check_mark: Improved Capital Deferral (CapEx) | By performing targeted proactive maintenance, the useful life of an asset can be extended, deferring the need for costly capital replacement. |
:white_check_mark: Enhanced Strategic Focus | Automates the "what should I worry about?" part of the Asset Manager's job, freeing them to focus on higher-level strategic planning, long-term investment strategies, and overall system improvement. |
12. User Behavior Tracking
Primary User Role: Asset Manager
Metric/Event Name | Event Trigger | Properties Tracked | Question Answered for the Asset Manager |
|---|---|---|---|
View Alerts Dashboard | Asset Manager lands on the System Alerts page. |
| How often is the Asset Manager checking for new proactive insights? What is the typical volume of recommendations they are dealing with? |
Action Recommendation | Asset Manager selects an option from the "Actions" menu. |
| What is the most common action taken? Are high-risk recommendations actioned more quickly or frequently than low-risk ones? |
Create SO from Insight | A service order is successfully created from a recommendation. |
| How many recommendations are being converted into actual work? What is the risk/condition profile of the assets that are getting proactive work orders? |
Dismiss Recommendation | Asset Manager dismisses a recommendation. |
| Why are recommendations being dismissed? Is the AI generating false positives? This helps tune the recommendation engine. |
Filter Recommendations | Asset Manager uses the filters. |
| How is the manager triaging the list? Are they focusing only on 'New' items or reviewing everything? |

No Comments