User Story: Schedules Management (AX03US04)
1. Problem Statement
This user story addresses the foundational need to plan, create, manage, and analyze recurring Preventive Maintenance (PM) schedules. The primary user is the O&M Manager, who is responsible for implementing a proactive maintenance program to ensure asset reliability, prevent failures, and optimize workforce planning.
Primary User Role & Pain Points:
- Reliance on Manual Systems: Manages maintenance schedules using spreadsheets or calendars, which are prone to error, difficult to update, and lack automation.
- Inconsistent Maintenance: Without a centralized system, there is no guarantee that assets are being maintained at the correct intervals.
- Poor Workforce Planning: Struggles to forecast future workloads from recurring tasks.
- No Link to Procedures: Schedules are disconnected from Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), leading to inconsistent work.
- Lack of Visibility and Control: Has no central dashboard to see schedule status, history, or the specific assets included in a recurring job.
Core Problem:
For the O&M Manager, managing preventive maintenance without a dedicated scheduling system is inefficient, unreliable, and purely administrative. It prevents the implementation of a true, scalable PM program, leading to an over-reliance on reactive maintenance, increased risk of unexpected failures, and inefficient use of the field workforce.
2. Who Is the User Facing the Problem?
The O&M Manager is the most important user for this feature. They are tasked with shifting the organization from a reactive "fire-fighting" model to a proactive, planned maintenance culture. This "Schedules Management" module is their primary tool for building, automating, and overseeing the entire Preventive Maintenance program.
Access Control:
The O&M Manager and Utility Administrator should have full create, read, update, and activate/deactivate permissions. The Asset Manager would have read-only access. The Dispatcher may have read access and the ability to view generated work orders.
3. Jobs To Be Done
- For the O&M Manager: When I need to implement a reliable preventive maintenance program to reduce unexpected failures, but I am using manual spreadsheets and calendars that are inefficient and error-prone, help me by providing a system to create, manage, and analyze automated, recurring maintenance schedules, so that I can ensure critical assets are serviced on time, optimize my workforce planning, and systematically reduce operational risk.
4. Solution
The proposed solution is a comprehensive Schedules Management module. It allows the O&M Manager to create and manage automated schedules for generating Preventive Maintenance work orders. The solution consists of three main parts: a management dashboard for oversight, a detailed view for analyzing a single schedule, and a multi-step wizard for creation.
Key Capability Areas:
- Centralized Schedules Dashboard: High-level KPIs and a filterable list of all PM schedules.
- Guided, Multi-Step Schedule Creation: A wizard to define a schedule's details, trigger, linked SOP, and associated assets.
- Detailed Schedule View: A dedicated page for each schedule that provides a comprehensive overview, including its configuration, linked SOP, associated assets, and a complete history of all work orders it has generated.
- Flexible Trigger & Frequency Engine: Allows for defining various recurring schedules (Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Yearly).
- SOP-Driven Standardization: Mandates linking an SOP to every schedule, ensuring consistency in all generated work.
- Complete Generation History: The detail view includes a log of every time the schedule has run, providing full traceability and performance history for that specific recurring job.
5. Major Steps Involved
User Role: O&M Manager
Flow 1: Creating a Monthly Inspection Schedule
(This flow remains the same as the previous version)
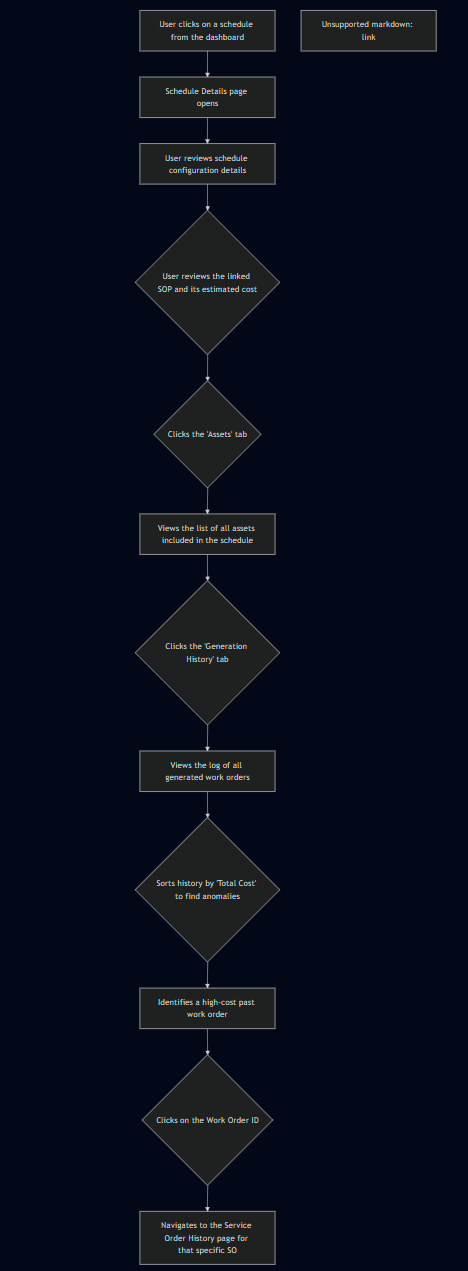
Flow 2: Reviewing the Performance of a Specific Schedule
6. Flow Diagram
7. Business Rules
This section provides an exhaustive, granular breakdown of rules for every single visible element across all three screens (Dashboard, Details, and Wizard).
A. Schedules Management (Dashboard View)
- Page Title/Subtitle: Static descriptive text.
- KPI Card 1: "Total Schedules"
- Formula:
COUNT(Schedules)regardless of status.
- Formula:
- KPI Card 2: "Active Schedules"
- Formula:
COUNT(Schedules)whereStatus= 'Active'.
- Formula:
- KPI Card 3: "Avg. Cost per Schedule"
- Formula:
AVG(SOP.TotalCost)for all schedules whereStatus= 'Active'. This reflects the average estimated cost of the work planned, not executed.
- Formula:
- KPI Card 4: "Work Orders Generated"
- Formula:
COUNT(Service Orders)whereServiceOrder.Source= 'Schedule' andCreationDateis within the "Last 30 days".
- Formula:
- Search Bar: Must search across
Schedule ID,Schedule Name, andSOP Name. - Filters Button: Must open a dropdown/modal with filtering options for
StatusandFrequency. - Table: "Schedules"
Schedule ID: Unique, system-generated ID (e.g., SCH-001).Schedule Name: The user-defined name of the schedule.SOP Name: The name of the linked Standard Operating Procedure.Frequency: A text description of the trigger (e.g., "Monthly on the 15th").Status: A colored tag: 'Active' (Green) or 'Inactive' (Gray).Last Generated: The date the schedule last ran and created work orders. Displays "N/A" if it has never run.Next Due Date: The calculated date the schedule is set to run next.Actions("..."): A menu button that must reveal:View Details: Navigates to a detailed view of the schedule.Edit: Opens the creation wizard pre-filled with the schedule's data.Deactivate/Activate: Toggles the schedule's status.Run Now: Manually triggers the schedule to generate work orders, ignoring theNext Due Date. Prompts for confirmation.
B. Create Schedule (Wizard View)
- Step 1: Schedule Details
Schedule Name: Mandatory text field. Must be unique.Description: Optional multi-line text area.Trigger Type: Mandatory dropdown with options: 'Daily', 'Weekly', 'Monthly', 'Yearly'.FrequencyControls (Dynamic):- If
Trigger Type= 'Weekly', a multi-select checkbox group for days (Sun-Sat) must appear. At least one day must be selected. - If
Trigger Type= 'Monthly', a dropdown to select the day of the month (1-31, Last Day) must appear. - If
Trigger Type= 'Yearly', a month and day selector must appear.
- If
Start Date: Mandatory date field. Defaults to the current date.End Date: Optional date field. If blank, the schedule runs indefinitely. Must be after theStart Dateif filled.
- Step 2: Select SOP
- Rule: The user must select exactly one SOP using the radio buttons.
- Rule: The table must be searchable and filterable by
SOP ID,SOP Name,Service Association, andOperation Type.
- Step 3: Select [Assets/Systems/etc.]
- Rule: The title and the list displayed are dynamic based on the
Service Associationof the selected SOP. - Rule: The user must select at least one entity from the list using the checkboxes.
- Rule: The list must be searchable and filterable.
- Rule: The title and the list displayed are dynamic based on the
- Wizard Buttons:
Cancel: Discards all progress and returns to the dashboard.Previous Step: Navigates to the previous step in the wizard, preserving the user's inputs.Next Step: Navigates to the next step, enabled only after the current step's mandatory fields are filled.Create Schedule: Appears only on the last step. Enabled only after at least one entity is selected. Creates the schedule record.
C. Schedule Details (Detailed View)
9. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must allow a user to navigate from the schedule dashboard to a detailed view for any schedule.
- The Schedule Details view must display all key configuration data, including ID, frequency, and dates.
- The details view must clearly display all information about the linked SOP, including its estimated cost.
- The "Assets" tab must correctly list all, and only, the assets associated with that schedule.
- The "Generation History" tab must correctly list all, and only, the service orders ever generated by that schedule.
- The counts in the tab titles (e.g., "Assets (5)") must be accurate.
- The user must be able to toggle the schedule's status between Active and Inactive from the details page.
- The user must be able to edit the schedule from the details page, which should open the pre-filled wizard.
- The user must be able to manually trigger a schedule run using the "Run Now" button.
- The "Delete" button must be disabled if the schedule has a generation history.
- All
SOP IDandSO IDfields in the details view must be hyperlinks to their respective detail pages. - The dashboard must allow creation of a new schedule via the 3-step wizard.
- The wizard must enforce all mandatory field selections on each step.
- The dashboard must display four correctly calculated KPI cards.
- The main schedules list on the dashboard must be searchable and filterable.
10. Process Changes
From: (Current Process) | To: (New Process) | Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
Preventive Maintenance is tracked on a shared calendar or spreadsheet, requiring manual creation of work orders each time. | PM schedules are created once in the system, which then automatically generates the required service orders at the specified frequency. | Justification: This is a fundamental shift from manual administration to full automation. It can save the O&M Manager and dispatchers dozens of hours per month, a 95%+ reduction in administrative overhead for PM planning. |
The tasks performed for a "monthly inspection" vary depending on which technician does the work. | Every work order generated from a schedule is linked to a specific SOP, ensuring every technician performs the exact same tasks every time. | Justification: This enforces standardization and quality control on all planned maintenance, leading to more reliable asset data and consistent work quality. |
The O&M Manager has no easy way to see the upcoming workload from planned maintenance. | The dashboard provides a clear view of all schedules and their | Justification: This provides the forward-looking visibility needed to manage a field workforce effectively, helping to balance planned work with anticipated corrective work and reduce overtime costs. |
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Metric | How it Improves |
|---|---|
:white_check_mark: Increased PM Compliance | Automating schedule execution ensures that planned maintenance is not missed or forgotten, dramatically increasing the PM compliance rate and reducing the risk of neglect. |
:white_check_mark: Reduced Administrative Overhead | Eliminates the manual, repetitive work of creating recurring work orders, freeing up the O&M Manager and staff to focus on more strategic, value-added activities. |
:white_check_mark: Improved Workforce Efficiency | By providing a predictable, long-term view of planned work, the O&M Manager can create more efficient routes and better balance the workload across their team. |
:white_check_mark: Foundation for Proactive Maintenance | A robust PM program is the foundation upon which more advanced strategies are built. This feature provides the stable base needed to reduce corrective maintenance and allow for the introduction of predictive, AI-driven maintenance. |
12. User Behavior Tracking
Primary User Role: O&M Manager
Metric/Event Name | Event Trigger | Properties Tracked | Question Answered for the O&M Manager |
|---|---|---|---|
Create Schedule | O&M Manager successfully creates a new schedule. |
| What types of schedules are being created most often? How large are these schedules? |
View Schedule Details | O&M Manager clicks on a schedule to view its detail page. |
| Which schedules are being reviewed most often? Are managers checking on schedules with many assets or long histories? |
Switch Detail Tab | On the details page, the user clicks a tab. |
| What is the primary information managers look for on the detail page? Are they checking the included assets or the performance history? |
Manual Run Schedule | O&M Manager uses the "Run Now" action. |
| Why are managers manually triggering schedules? Does this indicate a need for more flexible trigger options? |
Toggle Schedule Status | O&M Manager activates or deactivates a schedule. |
| Are schedules being actively managed and retired, or do they tend to run indefinitely? |

No Comments