System Settings Configuration Management : User Story ( WX04US04 )
1. Problem Statement
Core Problem:
The current system lacks a centralized configuration management interface that provides comprehensive visibility, control, and analytics over all system parameters. This results in fragmented configuration management, potential inconsistencies across modules, and inability to make data-driven decisions about system optimization.
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
O&M Manager :
- Requires visibility into work order types, safety requirements, and their operational effectiveness
- Uses configuration data to optimize maintenance and operational processes
3. Jobs To Be Done
For O&M Manager:
- When I need to ensure that field teams follow consistent procedures for tasks like installation, maintenance, and repair, But I notice inconsistencies in how tasks are labeled or handled in the field, Help me define and manage clear, standardized work order types that align with operational workflows,So that service execution is more predictable, measurable, and compliant across all teams.
- When I need to ensure safety protocols are followed during field operations,But I see that safety requirements are often missed or inconsistently applied across work orders,Help me enforce safety compliance by linking clear safety requirements to each work order type,So that field staff are better prepared and risks are minimized during service delivery.
- When I need to launch a new type of field service or process change,But I’m unable to quickly reflect that in the system due to rigid or outdated configurations,Help me easily add and configure new work order types and link them to SLAs and safety requirements,So that new services can go live smoothly without disrupting operational flow.
4. Solution
The System Configuration Management solution provides a comprehensive interface for managing and analyzing all system configurations:
Key Capability Areas:
- Configuration Dashboard
- Unified view of all configuration categories (Work Order, Field Force, Billing)
- Status indicators showing active/inactive configurations
- Search and filter capabilities across all configuration types
- Work Order Configuration Management
- Comprehensive management of work order types, sub-types, and categories
- SLA rules configuration
- Tax rate settings
- Safety requirement management
- Field Force Configuration
- Certification management
- Rate configuration
- Skills matrix management
- Bulk Operations
- Mass configuration updates with validation
- Template-based configuration creation
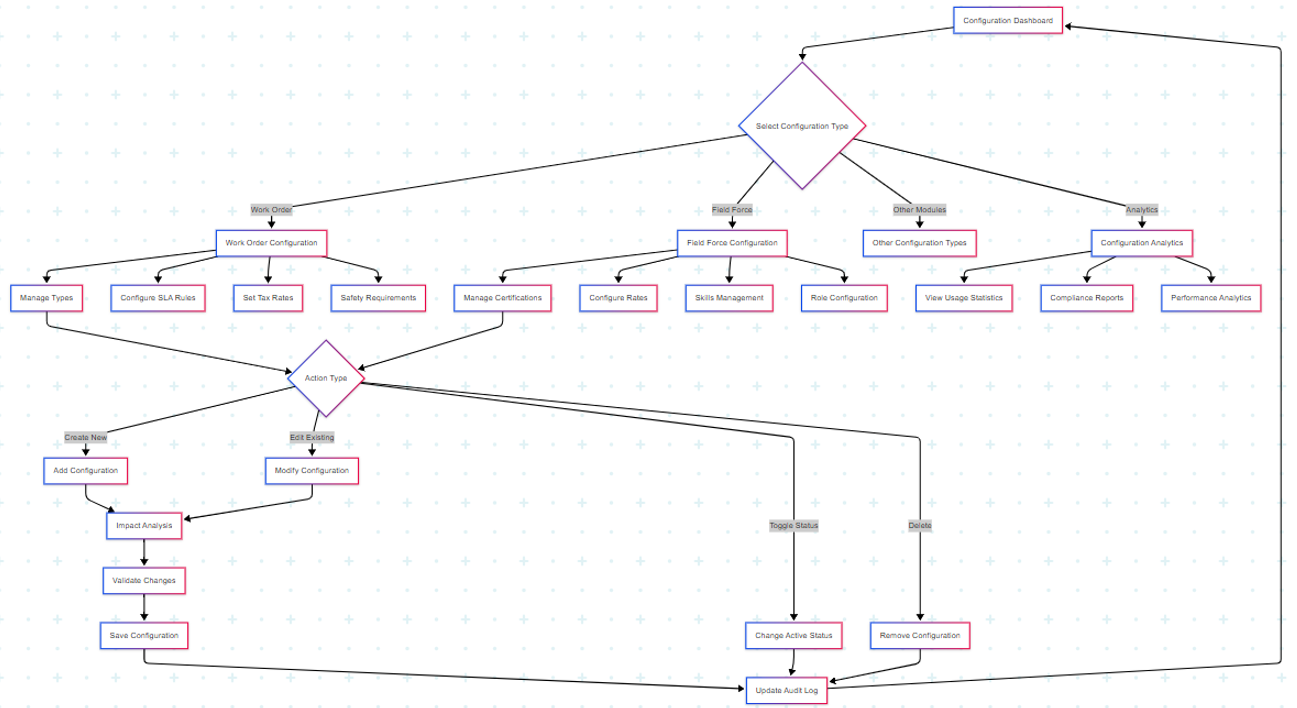
5. Major Steps Involved
For using the Configuration Management feature:
- Access Configuration Dashboard
- Navigate to Settings in the main SMART360 navigation
- View unified dashboard showing all configuration categories
- Review configuration status indicators and metrics
- Identify areas requiring attention based on usage analytics
- Manage Work Order Configuration
- Select "Work Order" tab to access work order configurations
- View existing work order types
- Click "Add New" to create additional work order types
- Configure SLA rules, tax rates, and safety requirements for each type
- Configure Field Force Parameters
- Switch to "Field Force" tab for field personnel configurations
- Manage certifications with status toggles (Active/Inactive)
- Set up rates
- Configure skills matrix
- Modify Configuration Settings
- Select specific configuration item to edit
- Review current settings and usage
- Make necessary changes with impact preview
- Validate changes against system dependencies
6. Flow Diagram
7. Business Rules
General Configuration Rules:
- All configuration changes must be logged with user identification, timestamp, and change details
- Configuration names must be unique within their respective categories
Work Order Configuration Rules:
- Work order types must include mandatory fields: creator name, description, creation date
- Must have active inactive toggles
- Must have add new buttons
- must have edit buttons
- must have a search bar
- Work order sub-types must be associated with a parent work order type
- Active work order types cannot be deactivated if they have pending or in-progress work orders
- while deactivating a card show a message if it is already being used , you cant deactivate it
Field Force Configuration Rules:
- Inactive certifications cannot be assigned to new field personnel
- Rate configurations must specify base rates, overtime multipliers, and skill premiums
- Rate changes require effective date specification to prevent payroll disruptions
- Must have active inactive toggles
- Must have add new buttons
- must have edit buttons
- must have a search bar
Change Management Rules:
- when a setting is being deactivated with the toggle, it should open a modal telling where all it is being used and you cant delete it write now.
8. Sample Data
Work Order Configuration:
- Installation
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-10
- Status: Active
- Usage: 156 work orders (last 30 days)
- SLA: 4 hours response, 24 hours resolution
- Maintenance
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-09
- Status: Active
- Usage: 89 work orders (last 30 days)
- SLA: 8 hours response, 48 hours resolution
- Repair
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-08
- Status: Active
- Usage: 234 work orders (last 30 days)
- SLA: 2 hours response, 12 hours resolution
Field Force Configuration:
- Certifications
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-10
- Status: Active
- Rates
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-09
- Status: Active
- Skills
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-08
- Status: Inactive
- Last Usage: 2024-03-15
- Role
- Created by: Admin
- Created on: 2024-05-10
- Status: Active
Configuration Analytics:
- Most Used Work Order Type: Repair (45% of total)
9. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must display a unified page showing all configuration categories with current status
- The system must allow to create, edit, configuration items
- The system must provide toggle switches to activate/deactivate configuration items
- The system must prevent deletion of configuration items that are currently in use ( open a modal to display this message and where is it being used )
- The system must display usage statistics for each configuration item - in type & subtype & safety reqirements only
- The system must log all configuration changes with user identification and timestamp
- The system must provide search functionality across all configuration types
- The system must validate configuration dependencies before allowing changes ( open a modal to display this message and where is it being used )
10. Process Changes
| Current Process | New Process | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Navigate to separate screens for each configuration type | Unified dashboard with all configuration categories accessible from one interface | 70% reduction in navigation time; improved configuration visibility |
Manual tracking of configuration usage and effectiveness | Automated analytics dashboard showing usage patterns, compliance rates, and performance metrics | 85% improvement in configuration optimization decisions |
Ad-hoc configuration changes without impact analysis | Structured change process with dependency validation and impact preview | 60% reduction in configuration-related system issues |
Limited audit trail for configuration modifications | Comprehensive logging of all changes with user attribution and change details | 100% compliance with regulatory audit requirements |
Individual configuration updates requiring multiple screen visits | Bulk operations and template-based configuration management | 50% reduction in time spent on routine configuration maintenance |
Reactive approach to configuration problems | Proactive monitoring with automated alerts for configuration issues | 40% faster resolution of configuration-related problems |
Manual documentation of configuration relationships | Automated dependency mapping and consistency validation | 90% reduction in configuration conflict incidents |
Separate backup processes for different configuration types | Centralized backup and restore capabilities for all configurations | 80% improvement in disaster recovery preparation time |
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
| Metric | Improvement Impact |
|---|---|
Configuration Management Efficiency | 65% reduction in time spent managing system configurations |
System Reliability | 45% decrease in configuration-related system errors and downtime |
Compliance Adherence | 95% improvement in regulatory compliance for configuration management |
Operational Consistency | 80% reduction in configuration inconsistencies across system modules |
Change Management Speed | 55% faster implementation of approved configuration changes |
Audit Preparation Time | 75% reduction in time required for compliance audit preparation |
Configuration Optimization | 40% improvement in configuration effectiveness through data-driven decisions |
Error Resolution Time | 60% faster identification and resolution of configuration issues |
User Productivity | 35% improvement in System Administrator productivity for configuration tasks |
System Performance | 25% improvement in overall system performance through optimized configurations |
12. User Behavior Tracking
| User Role | Metric | Event | Properties | Business Question Answered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
O&M Manager | # of logins to Configuration Module |
|
,
,
| How often is the O&M Manager engaging with configuration settings? |
O&M Manager | Work order types viewed |
|
,
,
| What types of work orders are most reviewed by the O&M Manager? |
O&M Manager | New work order type created |
|
,
,
,
,
| What types of configurations are being added, and by whom? |
O&M Manager | Work order type edited |
|
,
,
,
| What fields are commonly updated, and by which user? |
O&M Manager | Work order type deactivated |
|
,
,
,
| Are deactivation rules working as expected? Are users trying to deactivate in-use types? |
O&M Manager | Safety requirement added/updated |
|
,
,
,
| Are safety protocols being actively managed and linked to field operations? |
O&M Manager | Dependency modal triggered |
|
,
,
| How often do users attempt changes that conflict with system dependencies? |
O&M Manager | Field force config opened |
|
(certification/skills/rates),
| What areas of field force configurations are most reviewed? |
O&M Manager | Skill/certification toggled |
|
,
,
,
,
| Are users attempting to deactivate active skills/certifications? |
O&M Manager | Usage analytics viewed |
|
,
,
,
| What insights are O&M Managers extracting from usage analytics? |
O&M Manager | Search performed |
|
,
,
| What configuration items are most frequently searched? |
O&M Manager | Configuration change logged |
|
,
,
,
| Are all changes traceable? What is the volume of config updates? |
O&M Manager | Impact validation modal triggered |
|
,
,
,
| How often are users previewing change impacts before applying them? |
Questions answered by tracking:
- What is the average time spent managing configurations before and after implementing the unified dashboard?
- Which configuration types require the most administrative attention and why?
- How does configuration change frequency correlate with system performance and reliability?
- What is the effectiveness of impact analysis in preventing configuration-related issues?
- Which users are most active in configuration management and what training needs exist?
- How do configuration usage patterns change over time and what does this indicate about system evolution?
- What is the correlation between configuration optimization activities and operational efficiency improvements?
- How effective are bulk operations in reducing administrative workload for configuration management?
wireframe - Link

No Comments