Bill Generation V2 (BX01US03)
1. Problem Statement
Pain Points:
For Billing Administrator:
- Lack of visibility into bill generation errors leading to confusion and a "black box" experience
- Inability to quickly fix data issues when errors are identified
- Fragmented workflow requiring switching between multiple screens to complete the billing process
- No clear view of consumer eligibility and data completeness before starting bill generation
- Difficulty tracking billing cycle status and completion rates
Core Problem:
The current bill generation process lacks transparency, error handling capabilities, and a cohesive workflow. This results in incomplete bill generation (e.g., only 600 of 1000 consumers receiving bills), no clear mechanism for resolving data issues, and fragmented information architecture across multiple screens. Users cannot effectively manage the end-to-end process or quickly resolve issues when they arise.
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
Billing Administrator
- Responsibilities: Day-to-day operation of the billing system including cycle setup, consumer data management, validation, bill generation, and error resolution
- Access Level: Full access to create, edit, and execute billing cycles
3. Jobs To Be Done
For Billing Administrator:
When I need to generate bills for the current billing cycle, But I lack visibility into data quality issues that could cause failed bills, Help me identify and resolve all data problems before starting bill generation, So that I can maximize billing success rates and minimize customer complaints.
For Billing Administrator:
When I need to review and approve bills before distribution, But I can't easily verify if all billing components have been correctly calculated, Help me validate billing data, consumer information, and meter readings in a structured checklist, So that I can confidently approve bills knowing they are accurate and complete.
For Billing Administrator:
When I need to monitor the progress of bill generation, But I have no visibility into the success rate or specific failures during processing, Help me track generation progress in real-time with detailed error reporting, So that I can quickly identify and address issues that prevent successful bill completion.
For Billing Administrator:
When I need to analyze billing performance across cycles, But I lack comprehensive metrics about billing success rates and issues, Help me visualize key metrics through intuitive dashboards and comparative reports, So that I can identify trends and address recurring problems that affect billing quality.
For Billing Administrator:
When I need to validate meter readings with anomalies before billing, But I can't easily identify problematic readings that might cause billing errors, Help me efficiently review and validate questionable consumption data, So that I can ensure billing accuracy and reduce customer disputes.
For Billing Administrator:
When I need to manage missing consumer data like plans or tariffs, But I don't have a streamlined way to identify and fix incomplete records, Help me quickly locate and update consumers with missing information, So that I can prevent billing failures due to incomplete consumer data.
4. Solution
The Bill Cycle Insight Nexus provides a comprehensive, step-by-step workflow that guides Billing Administrators through the entire billing cycle process from initial configuration to final bill approval. The solution addresses key pain points through the following capabilities:
Unified Billing Cycle Management
- Structured Workflow Process: Clear step-by-step navigation through the complete billing cycle
- Progress Tracking: Visual indicators showing completion status for each step
- Contextual Transitions: Intelligent navigation between related steps with data consistency
Proactive Data Quality Management
- Consumer Data Validation: Pre-validation of consumer records, plans, and tariffs
- Meter Reading Analysis: Comprehensive tools for identifying and resolving reading anomalies
- Missing Data Alerts: Early notification of data gaps that would cause billing failures
Real-time Bill Generation Monitoring
- Generation Progress Tracking: Live progress indicators during bill processing
- Detailed Error Reporting: Specific error codes and messages for failed bills
- Retry Capabilities: Targeted reprocessing of failed bills after corrections
Comprehensive Billing Analytics
- Cycle Comparison: Performance metrics compared to previous billing cycles
- Consumption Pattern Analysis: Distribution of consumption across customer segments
- Error Trend Identification: Analytics on recurring issues affecting billing quality
Verification and Approval Workflow
- Structured Verification Checklist: Guided process for verifying billing components
- Approval Documentation: Audit trail of verification and approval steps
- Final Review Summary: Comprehensive overview before bill distribution
Exception Management
- Failed Bill Handling: Tools for investigating and resolving generation failures
- Anomaly Resolution: Workflows for addressing consumption anomalies
- Missing Data Resolution: Streamlined processes for completing missing consumer information
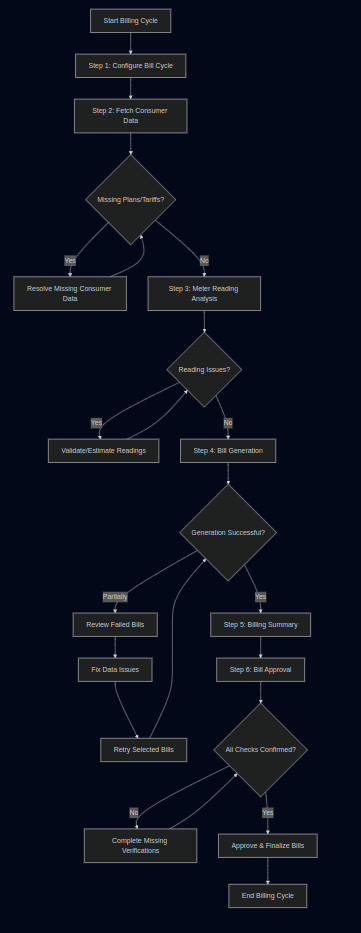
5. Major Steps Involved
Step 1: Bill Cycle Configuration
Step 2: Fetch Consumer Data
Step 3: Meter Readings Analysis
Step 4: Bill Generation
Step 5: Billing Summary
Step 6: Bill Approval
6. Flow Diagram
Main Billing Cycle Process Flow
7. Business Rules
General System Rules
- A users must have appropriate permissions to access the Bill Generation
- Each billing cycle must have a unique identifier and defined billing period
- Each cycle should have at least one parameter different
- The system must maintain a complete audit trail of all actions taken during the billing cycle
- Approved bills cannot be modified after final approval is complete
- Users must confirm all verification items before bill approval can be completed
- The system must enforce data validation rules at each step of the process
Bill Generation Rules
- Bill generation must process all eligible consumers in the billing cycle
- Failed bills must have specific error codes and descriptions
- Bills cannot be generated for consumers with missing critical data
- Bill generation can be retried for specific failed accounts after error resolution
- Generation logs must capture detailed processing information for audit purposes
- System must prevent duplicate bill generation for the same consumer and period
- Bill generation progress must be trackable in real-time
- Maximum processing time for bill generation is determined by system capacity
Bill Approval Rules
- All verification checklist items must be confirmed before approval
- Approver name must be recorded for audit purposes
- Optional approval comments can be added for documentation
- Approval cannot be completed if unresolved critical errors exist
- Bill distribution channels must be configured before approval
- Once approved, bills are locked for editing and ready for distribution
- Approval can be revoked only by authorized users and before distribution begins
Error Handling Rules
- Each error must have a unique error code and descriptive message
- Critical errors must block process progression until resolved
- Warning-level issues should be highlighted but not block progression
- Resolution actions must be logged for audit purposes
- Repeated errors of the same type must be grouped for efficient resolution
- System must suggest resolution actions for common error types
- Error notifications must be sent to appropriate users based on error type
Field Specific Rules
Cycle Selection Section
1. Select Billing Cycle
- Rule 1: If a billing cycle is selected from the dropdown, the form auto-populates based on the selected cycle’s saved parameters.
- Rule 2: If "Create New" is selected, all input fields must be manually filled.
- Rule 3: Only one cycle can be selected at a time.
2. Create New / Creating New Toggle
- Rule 5: Switching to “Create New” resets any selected cycle configuration.
- Rule 6: When toggled, the “Cycle Name” field becomes mandatory.
3. Cycle Name
- Rule 7: Must be unique and not duplicate an existing billing cycle name.
- Rule 8: Minimum 3 and maximum 50 characters
- Rule 9: Required field when creating a new cycle.
4. Previous Period (Derived)
- Rule 10: Auto-filled based on the last billing cycle's end date.
- Rule 11: Used to calculate “Days Since Last Billing.”
5. Days Since Last Billing (Derived)
- Rule 12: Calculated as the difference between today’s date and the previous billing period end date.
Cycle Parameters Section
6. Area
- Rule 16: Mandatory field.
- Rule 17: Selection filters the list of premises available in the Premises dropdown.
7. Premises
- Rule 19: At least one premise must be selected.
- Rule 20: Multi-select allowed; only premises from the selected Area are shown.
- Rule 22: Premises already included in another active or ongoing billing cycle should not be selectable.
8. Consumer Category
- Rule 26: Mandatory field.
- Rule 27: Filters consumer data for billing—e.g., Residential, Commercial, Industrial.
9. Consumer Subcategory
- Rule 28: Optional field unless system requires subcategory-level billing rules.
- Rule 29: Options dependent on the selected Consumer Category.
- Rule 30: If subcategory exists for the selected category, field becomes mandatory.
10. Billing Period Start / End
- Rule 31: Both fields are mandatory.
- Rule 32: End date must be later than Start date.
- Rule 34: Start date must be after the end date of the previous billing cycle for the same premises.
Billing Cycle Summary Section
13. Name
- Rule 37: Derived from the selected billing cycle or the manually entered name.
15. Areas
- Rule 39: Auto-filled from the Area field.
17. Consumer Categories
- Rule 41: Derived from selected categories and subcategories.
18. Premises
- Rule 42: Derived from selected premises in the Cycle Parameters section.
19. Last Billing Period
- Rule 43: Auto-filled from the last billing period for selected premises.
- NA if new cycle is created of if cycle is scheduled first time
21. Bill Template
- Rule 46: Mandatory before proceeding to the next step.
- Rule 48: If no bill template is selected, "Next" button should remain disabled.
Bill Template Preview Section
22. Preview for [Template Name]
- Rule 49: Template preview should render based on the selected bill template.
- Rule 50: Preview may be an image, PDF embed, or HTML view, depending on system design.
Other Functional Elements
23. Save as Draft
- Rule 51: Saves all filled values as a draft cycle without validation errors (except date format and required fields).
- Rule 52: Drafts are not considered active and can be resumed later.
24. Previous / Next Buttons
- Rule 53: “Previous” is disabled on Step 1.
- Rule 54: “Next” becomes active only when all mandatory fields are correctly filled and bill template is selected.
- Rule 55: "Next" validates the current step but does not trigger bill generation.
Fetch Consumer Data
Consumer Overview
- Display count of total consumers fetched in this billing cycle based on the filters set on the first step
- % change should indicate the percentage change of consumers compared to last run of same cycle
- formula ( current count - previous count / previous count ) * 100 this formula will be same for all the percentage change in the complete flow
Missing Plan Details
- Should display the count of consumer without a plan attached
- NA is all consumers have a plan attached
Missing Tariff Details
- It should display the number of plans without a tariff attached to it and the plans should be the plans of the consumers fetched
- NA if all the plans have tariff attached
- A plan should definitely have usage tariff if the utility service is metered
Consumer Breakdown
Consumers by Category
- Display consumer count and distribution of consumer count by category of the consumers
- % change should be displayed beside all the count numbers
- Cycle comparison should include consumer count in the previous cycle and the number of consumers increased from the previous cycle
Consumer Status
- Should show the distribution of consumers by the status of the consumer
- Active, Inactive, Pause and Temporary Disconnected
- % Change should be displayed below every number
🔹Missing Data Table
Tabs:
- Missing Plan Details Tab
- Rule: Shows consumers with no plan ID associated
- Missing Tariff Details Tab
- Rule: Shows consumers whose plan is associated with a missing or inactive tariff
Fields in Table:
Field Name | Rule |
|---|---|
Account Number | Unique account ID of the consumer; fetched from master consumer table |
Consumer Name | Fetched from consumer profile; display only |
Service | Utility associated with consumer (e.g., Water, Electricity); must be pulled from assigned plan or meter |
Category | Consumer category (Residential, Commercial, etc.); must match allowed categories in tariff |
Action | “Assign Plan” shown if plan is missing; opens plan assignment flow when clicked On click should open a dropdown with all the plans from which user can select plan and attach it to the consumer |
🔹Recent Changes Table
Field Name | Rule |
|---|---|
Type | Values: Plan / Tariff; denotes which configuration changed |
Name | Name of the plan or tariff changed since last cycle |
Field | Field within the plan/tariff that was modified (e.g., Rate, Fixed Charge, Rebate) |
Old Value | Value used in the last billing cycle |
New Value | Updated value for current cycle; value used in bill computation this run |
🔹Missing Data Tab: "Missing Tariff Details" View
Table Fields:
Field Name | Rule |
|---|---|
Plan Name | Name of the plan that lacks a tariff mapping for the current utility |
Service | Utility service the plan is intended for (Water, Electricity, etc.) |
Consumers Affected | Count of consumers assigned to this plan for whom tariff is not configured |
Action | Shows “Assign Tariff” if tariff ID is null or expired/inactive on click should open a dropdown with all tariffs and select and add to add tariff to the plan |
- Important:
- Only active plans will be listed here
- Tariff assignment is mandatory for metered billing
Payment Summary
Total Amount
- Sum of all billed amounts (Paid + Outstanding) of the previous run of selected cycle.
- NA if it is new cycle and same for all the fields.
Paid
- Sum of payments successfully received.
- Displayed in green with % of total amount.
Usage Charges
- Sum of amount charges based on the usage
- Displayed in Purple with % of total amount.
Outstanding
- Amount still unpaid as of current date.
- Displayed in orange, and excludes any future-dated payments.
Service Charges
- Subset of total amount that comes from non-tariff fees (e.g., connection charges, late fees).
- Displayed in blue with % of total.
Late Fees
- Amount received through late fee.
- Displayed in red with % of total.
Billing Period
- Shows the active billing period date range and duration (in days).
- Pulled from selected bill cycle metadata.
🔹Top Outstanding Accounts
Field Name | Rule |
|---|---|
Account | Unique account number of the consumer with highest dues |
Consumer | Name of the consumer linked to the account |
Amount | Total outstanding dues for the billing period |
Last Payment | Date of the last recorded successful payment |
- Sorted by descending outstanding amount
- Limited to top 5 entries
Meter Readings Analysis
Total Meters
- Count of all meters registered in the current billing cycle
- Displayed with percentage change from previous cycle in parentheses (green or red)
- Represents the total meter base for billing calculations
Readings Collected
- Percentage of total meters with successful readings in current cycle
- Shows the completion progress of meter data collection
- Displayed with a progress bar to visualize completion percentage
Missing Readings
- Count of meters with no readings submitted for the current cycle
- Displayed with percentage of total meters in parentheses (red)
- Critical metric for identifying collection gaps
Pending Validation
- Count of readings that have been collected but not yet validated
- Displayed with percentage of total readings collected in parentheses (amber)
- Readings requiring verification before billing processing
Reading Collection Status
- Current Cycle: Percentage of readings collected in the active billing period
- Previous Cycle: Percentage of readings collected in the last completed cycle
- Comparison: Difference between current and previous cycles (with percentage)
- Displayed with progress bars for visual performance tracking
Reading Validation Status
- Current Cycle: Percentage of collected readings validated in active period
- Previous Cycle: Percentage of validated readings in last completed cycle
- Comparison: Difference between current and previous cycles (with percentage)
- Displayed with progress bars for visual quality tracking
Meter Types Breakdown
- Distribution of meters by technology type:
- Smart: Percentage of smart meters (automated digital readings)
- Photo: Percentage of photo-based readings (image capture)
- Manual: Percentage of manually read meters
- Displayed with horizontal bars showing proportion of each type
Reading Types Distribution
- Classification of readings by quality status:
- Normal: Percentage of readings within expected parameters
- RCNT: Percentage of readings requiring confirmation (unusual values)
- Faulty: Percentage of readings identified as erroneous
- Helps identify data quality issues for resolution
Reading Methods Comparison
- Current: Actual: Percentage of readings based on actual consumption
- Current: Estimated: Percentage of readings based on estimation
- Previous: Actual: Historical percentage of actual readings
- Comparison to monitor estimation vs. actual reading trends
- Higher actual readings percentage indicates better data quality
Meter Reading List
Meter ID
- Unique identifier for each metering device in the system
- Format follows utility's standard naming convention (letter prefix followed by numeric digits)
- Primary key for meter identification across all systems
Consumer
- Name of the account holder associated with the meter
- Can be individual customer or business entity
- Used for identification and communication purposes
Account
- Unique billing account number linked to the consumer
- May differ from Meter ID when multiple meters exist for one account
- Used to associate meters with billing entities
Meter Type
- Classification of meter by technology:
- Smart: Digital meters with automated reading capability
- Photo: Meters read via image capture technology
- Manual: Traditional meters requiring physical reading
- Determines reading method and data reliability
Service
- Type of utility service being measured:
- Electricity
- Water
- Gas
- Determines tariff structure and billing calculations
Last Reading
- Previous meter reading value from the prior billing cycle
- Used as baseline for consumption calculation
- Displayed in service-specific units (kWh, gallons, cubic feet)
Current Reading
- Latest meter reading value for the current billing cycle
- Used to calculate consumption since last reading
- May be highlighted if anomalies detected
Consumption
- Calculated difference between current and last readings
- Represents usage for the billing period
- Used for bill calculation and consumption analysis
Status
- Current validation state of the meter reading:
- Validated (green): Reading verified and approved for billing
- Pending Validation (amber): Reading received but requires verification
- Determines whether reading can proceed to billing
Action
- Available operations for the specific meter reading
- Eye icon indicates "View Details" functionality
Missing Readings
Section Header
- Displays the title "Missing Readings" to identify the section
- Shows the total count of missing readings in parentheses (5)
- Provides a subtitle explaining these are "Meters with no reading collected in the current cycle"
Select All Checkbox
- Control to select all missing reading records at once
- Used for batch operations (estimate or exclude multiple readings)
- Unchecked by default
Meter ID
- Unique identifier for each meter without a reading
- Format follows standard naming convention (letter prefix followed by numeric digits)
- Used for precise meter identification
Consumer
- Name of the business entity associated with the meter
- No individual consumers shown in this view (focused on commercial accounts)
- Used for customer identification and communication
Account
- Unique billing account number linked to the consumer
- Used to associate meters with billing entities
- Numeric format following utility's account numbering system
Meter Type
- Classification of meter by technology:
- Manual: Traditional meters requiring physical reading
- Smart: Digital meters with automated reading capability
- Photo: Meters read via image capture technology
- Determines reading method and helps diagnose missing reading causes
Service
- Type of utility service being measured:
- Water
- Gas
- Electricity
- Determines tariff structure and consumption estimation factors
Last Reading
- Most recent valid reading value received from the meter
- Displayed in service-specific units (kWh, gallons, cubic feet)
- Used as baseline for estimation if needed
Last Reading Date
- Date when the previous reading was collected
- Formatted as Onboarding
- Used to calculate the duration since last valid reading
- Helps identify pattern of reading failures
Action
- Available operations for handling missing readings:
- Exclude: Remove meter from current billing cycle
- Estimate: Generate estimated reading based on historical data
- Controls for resolving missing readings before bill generation
- Exclude Selected: Remove multiple selected meters from billing cycle
- Estimate Readings: Generate estimated readings for multiple selected meters
- Located at top-right of the table for batch processing
Pending Validation
Section Header
- Displays the title "Pending Validation" to identify the section
- Shows the total count of readings pending validation in parentheses (5)
- Provides a subtitle describing these as "Readings that require validation"
Select All Checkbox
- Control to select all pending validation records at once
- Used for batch operations (estimate or exclude multiple readings)
- Unchecked by default
Meter ID
- Unique identifier for each meter with a reading requiring validation
- Format follows standard naming convention (letter prefix followed by numeric digits)
- Used for precise meter identification
Consumer
- Name of the account holder associated with the meter
- Can be individual customer or business entity
- Used for customer identification and communication
Account
- Unique billing account number linked to the consumer
- Used to associate meters with billing entities
- Numeric format following utility's account numbering system
Meter Type
- Classification of meter by technology:
- Smart: Digital meters with automated reading capability
- Photo: Meters read via image capture technology
- Manual: Traditional meters requiring physical reading
- Helps determine validation protocols based on meter technology
Service
- Type of utility service being measured:
- Electricity
- Gas
- Water
- Determines tariff structure and validation parameters
Last Reading
- Previous meter reading value from the prior billing cycle
- Used as baseline for consumption calculation and validation
- Displayed in service-specific units (kWh, gallons, cubic feet)
Current Reading
- Latest meter reading value for the current billing cycle
- Reading that requires validation before bill generation
- Used to calculate consumption and evaluate for anomalies
Consumption
- Calculated difference between current and last readings
- Represents usage for the billing period
- May trigger validation flags if outside expected ranges
Validator
- Name of the validator that read cycle is assigned to.
- Exclude Selected: Remove multiple selected meters from billing cycle
- Estimate All: Estimate all selected readings at once
- Located at top-right of the table for batch processing
Bill Generation
Bill Generation Process
- Controls to initiate and monitor the bill generation workflow
- Shows current status of the generation process with visual progress indicator
- Three possible states:
- Not Started: Displays information message and "Start Bill Generation" button
- In Progress: Shows percentage complete with animated progress bar
- Completed: Displays success message with option to restart generation
Generation Progress
- Visual progress bar showing percentage of bills processed
- Percentage displayed as numeric value (e.g., 24%, 96%)
- Color coded (blue) to indicate active processing
- Updates in real-time as bills are generated
Notification Toggle
- Option to receive alerts when bill generation completes
- Toggle switch for enabling/disabling notifications
- Available before starting the generation process
- Helps users monitor long-running processes without watching the screen
Bill Generation Information
- Informational message about the bill generation process
- Provides estimation of process duration based on billing cycle size
- Displayed before generation starts to set user expectations
- Contains relevant context about the selected billing cycle
Generation Summary
- Statistics for the current or completed generation process
- Three possible states:
- Not Started: "No generation data available" message
- In Progress: "Bill generation in progress..." message
- Completed: Detailed statistics including:
- Total Bills: Count of all bills attempted for generation
- Generated: Successfully created bills (shown in green with percentage)
- Failed: Bills that couldn't be generated (shown in red with percentage)
- Processing Time: Duration taken to complete the process (MM
format)
Generation Log
- Chronological record of processing events with timestamps
- Shows system messages in real-time during generation
- Format: [HH:MM
] Event description - Color-coded entries:
- Standard log entries (gray)
- Success messages (green)
- Error/failure messages (red)
- Provides detailed insight into processing steps and progress
- Empty state shows "No log entries yet" when no generation has occurred
Failed Bills
- Table of bills that could not be generated due to errors
- Only displayed after generation completes with failures
- Includes:
- Select All: Checkbox to select all failed bills for bulk actions
- Consumer: Name of the account holder
- Account No: Unique account identifier
- Error Code: System error code (e.g., ERR-4001) in blue background
- Error Message: Human-readable description of the failure reason
- Action: Controls for resolving individual failed bills (retry icon)
- Helps identify and fix specific bill generation issues
- Start Bill Generation: Initiates the bill generation process (blue button)
- Restart Generation: Restarts the process after completion
- Retry Selected: Attempts to regenerate selected failed bills
- Export Failed List: Downloads list of failed bills for offline processing
- Next: Proceeds to the next step in the bill cycle workflow
Filter Logs
- Control to filter log entries based on specific criteria
- Helps focus on relevant information in large log files
- Located at the top-right of the Generation Log section
- Particularly useful for troubleshooting specific issues
Billing Summary
Bills Generated
- Count of successfully generated bills in the current billing cycle
- Displayed with percentage of total attempted bills (green)
- Shows cycle comparison with previous billing period:
- This cycle: Number and percentage of total
- Previous: Number and percentage for comparison
- Visual progress bar to illustrate generation completeness
Bills Not Generated
- Count of bills that failed to generate during processing
- Displayed with percentage of total attempted bills (red)
- Shows cycle comparison with previous billing period
- Includes primary failure reason for non-generated bills
- Critical metric for identifying billing process issues
Bill Types
- Breakdown of bills by generation method:
- Actual Bills: Based on actual meter readings
- Percentage of total bills (with progress bar)
- Comparison with previous cycle
- Estimated Bills: Based on estimated consumption
- Percentage of total bills (with progress bar)
- Comparison with previous cycle
- Actual Bills: Based on actual meter readings
- Helps track data quality and estimation reliance
Consumption Distribution
- Analysis of usage patterns across customer base
- Total Consumption: Aggregate usage across all meters
- Displayed in appropriate units (kWh, m³)
- Comparison with previous cycle (percentage change)
- Segmented into consumption categories:
- High Consumption: Number of accounts with usage significantly above average
- Shows this cycle count and comparison to last cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Low Consumption: Number of accounts with minimal usage
- Shows this cycle count and comparison to last cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Zero Consumption: Number of accounts with no recorded usage
- Shows this cycle count and comparison to last cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- High Consumption: Number of accounts with usage significantly above average
- Helps identify unusual consumption patterns and potential issues
Financial Summary
- Overview of billing financial metrics for the cycle
- Total Consumption: Aggregate usage across all services
- Displayed in appropriate units with comparison to last cycle
- Total Billed Amount: Sum of all generated bills
- Monetary value with comparison to previous cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Usage Charges: Current usage charges across all accounts
- Monetary value with comparison to previous cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Service Charges: Non-consumption charges included in bills
- Monetary value with comparison to previous cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Outstanding Amount: Current unpaid balance across all accounts
- Monetary value with comparison to previous cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Late Fee: Current late fees across all accounts
- Monetary value with comparison to previous cycle
- Percentage change from last cycle
- Critical for financial tracking and revenue management
Consumer Bills
- Detailed tabular listing of all generated bills
- Includes search functionality and filtering options
- Table columns:
- Consumer: Name of account holder
- Account No: Unique account identifier
- Service: Utility service type (Electricity, Water, Gas)
- Consumption: Usage amount with unit and status indicator
- High: Orange tag for above-average usage
- Low: Yellow tag for below-average usage
- Zero: Red tag for no recorded usage
- Bill Amount: Monetary value of the current bill
- Outstanding: Previous unpaid balance, if any
- Total Due: Combined amount (current bill + outstanding)
- Actions: Controls for individual bill operations
- View details icon
- Download bill icon
- Supports bulk operations through "Select All" and "Download Selected"
- Comprehensive view of individual billing details
Export Summary
Bill Approval
Bill Verification Checklist
- Mandatory checklist of items requiring verification before bill cycle approval
- All items must be confirmed by checking the associated checkbox
- Sequential verification process with clear descriptions for each item
- Icons used to represent different verification categories
Data Verification Consent
- Confirmation that all meter and consumer data has been reviewed
- Verifies accuracy and completeness of all provided and modified information
- First step in the verification process
- Essential for data integrity assurance
Bill Calculation Consent
- Confirmation that calculation methodology has been verified
- Ensures all calculations align with applicable tariffs and regulations
- Verifies mathematical accuracy of billing amounts
- Critical for financial compliance
Communication Consent
- Approval for automatic payment collection
- Applies only to consumers who have opted for auto-pay functionality
- Confirms understanding of financial transaction authorization
- Required for automated payment processing
Billing Data Accuracy
- Verification that all billing components have been checked:
- Meter readings
- Tariffs
- Service charges
- Ensures comprehensive review of all financial elements
- Prevents billing errors and disputes
Consumer Data Reviewed
- Confirmation that all consumer information is correct
- Verifies that consumption anomalies have been investigated:
- High consumption
- Low consumption
- Zero consumption
- Ensures unusual patterns have been validated
Approve Bill Distribution
Complete Billing Process
Approver Name
- Field for entering the full name of the authorizing individual
- Creates accountability record for the approval action
- Required for audit and compliance purposes
- Documents responsible party for the approval decision
Approval Requirements
- Warning message if any verification items remain unchecked
- Reminds user to complete all required verifications
- Prevents premature approval of incomplete verifications
- Important for compliance and process integrity
- Back to Summary: Returns to billing summary screen
- Approve & Finalize Bills: Completes the approval process
- Green button indicating positive completion action
- Only enabled when all required items are verified
- Controls for workflow navigation and completion
8. Sample Data
Billing Cycle Configuration
Cycle ID: BC-2025-03
Name: March 2025 Downtown Billing Cycle
Billing Period: March 1-31, 2025
Areas: Downtown, Westside
Consumer Categories: Residential, Commercial
Meter Types: Smart, Photo, Manual
Utility Services: Electricity, Water, Gas
Total Consumers: 15,680
Total Meters: 15,300Consumer Data Sample
Account No | Consumer Name | Category | Service | Status | Plan Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AC-2025-001 | John Smith | Residential | Electricity | Active | Residential Standard Electricity |
AC-2025-002 | ABC Corporation | Commercial | Water | Active | Commercial Water Standard |
AC-2025-003 | Smith Manufacturing | Industrial | Electricity | Active | Industrial Power Plan |
AC-2025-004 | Jane Wilson | Residential | Water | Inactive | Residential Water Basic |
AC-2025-005 | City Mall | Commercial | Electricity | Paused | Commercial Electricity Premium |
AC-2025-112 | Metro Shopping Center | Commercial | Electricity | Active | Commercial Electricity Premium |
Meter Reading Sample
Meter ID | Consumer | Account | Meter Type | Service | Last Reading | Current Reading | Consumption | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
D1029384 | John Smith | 1029384 | Smart | Electricity | 5400 | 5850 | 450 | Validated |
D2039485 | Jane Doe | 9283746 | Smart | Electricity | 3200 | 3500 | 300 | Pending Validation |
D3048596 | Acme Corp | 8372615 | Photo | Electricity | 8700 | 9300 | 600 | Validated |
D4058697 | Bob Johnson | 7465839 | Manual | Water | 1200 | 1350 | 150 | Validated |
D7089043 | ABC Enterprises | 7263545 | Manual | Water | 2800 | - | - | Missing |
D6078943 | XYZ Manufacturing | 8162534 | Photo | Electricity | 12500 | 13200 | 700 | Pending Validation |
Failed Bills Sample
Consumer | Account No | Error Code | Error Message | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
John Smith | 1029384 | ERR-4001 | Missing tariff configuration | Retry |
ABC Enterprises | 7263545 | ERR-4002 | Invalid reading data | Retry |
Jane Doe | 9283746 | ERR-4003 | Missing consumer plan | Retry |
Billing Summary Sample
Metric | Value | Comparison to Last Cycle |
|---|---|---|
Bills Generated | 12,497 | +1.6% |
Bills Not Generated | 3 | -0.02% |
Late Payments | 218 | -35% |
Total Consumption | 5,782,455 kWh | +2.2% |
Total Billed Amount | $8,750,000 | +2.9% |
Service Charges | $1,250,000 | +4.2% |
Outstanding Amount | $3,750,000 | +7.1% |
Service Charges Sample
Charge Type | Consumer Type | Amount | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
Base Electricity Connection Fee | Residential | $15.50 | Regulatory |
Commercial Base Connection Fee | Commercial | $35.00 | Regulatory |
Industrial Base Connection Fee | Industrial | $75.00 | Regulatory |
Smart Meter Rental | All | $3.25 | Included |
Grid Maintenance Fee | All | $5.75 | Changed |
Minimum Electricity Bill | Residential | $10.00 | Included |
9. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must display a clear step-by-step navigation bar showing all 6 stages of the billing cycle process
- The system must visually indicate the current step and completion status of each step in the billing cycle
- The system must allow users to configure billing cycle parameters including billing period, areas, and consumer categories
- The system must display consumer data summary showing total consumers with breakdown by category
- The system must identify and display consumers with missing plans or tariffs that would prevent successful billing
- The system must provide functionality to assign missing plans to consumers directly from the interface
- The system must display meter reading statistics including total meters, collection progress, and validation status
- The system must identify readings requiring validation with clear indicators for the type of issue (low consumption, out of trend, etc.)
- The system must allow users to view, validate, or correct readings with anomalies through a structured interface
- The system must provide tools to handle missing readings through estimation or exclusion
- The system must display real-time progress during bill generation with percentage completion and estimated time
- The system must log all bill generation activities with timestamps and user information
- The system must provide detailed error messages for failed bills with specific error codes and descriptions
- The system must allow users to filter and review failed bills by error type
- The system must enable retry functionality for failed bills after error resolution
- The system must present a comprehensive billing summary with metrics on generated bills, amounts, and comparison to previous cycles
- The system must provide consumption distribution insights (high, normal, zero consumption) with comparison to previous cycles
- The system must implement a structured verification checklist before bill approval
- The system must require confirmation of all verification items before allowing final approval
- The system must record approver information and comments for audit purposes
10. Process Changes
Current Process | New Process | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Billing configuration and execution are managed across multiple disconnected systems | End-to-end billing process managed through a single unified interface | Reduces process time by approximately 30% and eliminates system switching errors |
Bill generation is a "black box" with limited visibility into progress or errors | Real-time monitoring of generation progress with detailed logs and error reporting | Improves error resolution speed by approximately 50% and reduces failed bills by 25% |
Data issues are identified only after bill generation fails | Proactive identification of data quality issues before bill generation begins | Reduces billing cycle duration by 15% by addressing issues earlier in the process |
Meter reading validation is performed separately from billing process | Integrated meter reading validation within the billing cycle workflow | Increases reading validation accuracy by 20% and improves cross-department collaboration |
Manual tracking of billing performance across cycles | Automated comparative analytics between current and previous billing cycles | Enables data-driven process improvements through 40% better visibility into trends |
Bill approval is an informal process with limited verification | Structured verification checklist with documented approval process | Reduces post-billing corrections by 35% and improves audit compliance |
Consumer data issues addressed reactively when bills fail | Proactive identification and resolution of consumer data gaps | Increases first-time-right bill generation by 25% and improves data quality |
Error resolution requires specialized technical knowledge | Guided error resolution with clear error codes and suggested actions | Reduces dependency on technical specialists by 30% and improves team efficiency |
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Metric | Impact |
|---|---|
Billing Cycle Duration | Reduction from 5 days to 2 days (60% improvement) by streamlining workflow and reducing rework |
First-Time-Right Bills | Increase from 92% to 99.5% success rate by identifying and resolving issues earlier |
Error Resolution Time | Decrease from hours to minutes (85% improvement) through better error visibility and guided resolution |
Staff Productivity | 40% improvement by eliminating manual tracking, system switching, and process fragmentation |
Data Quality | 35% improvement in consumer and meter data quality through proactive validation |
Regulatory Compliance | Enhanced audit trails and verification processes reduce compliance risks by 50% |
Customer Satisfaction | 25% reduction in billing-related complaints through more accurate and timely bills |
Revenue Leakage | 15% reduction in unbilled consumption through improved meter reading validation |
Training Time | 60% reduction in time to train new billing staff through intuitive, guided processes |
Cross-Department Collaboration | 45% improvement in alignment between meter operations and billing through integrated workflow |
12. User Behavior Tracking
Billing Cycle Configuration Events
Event | Properties | Insights |
|---|---|---|
billing_cycle_created | cycle_id, user_id, timestamp, parameters | Track frequency and patterns of new cycle creation |
billing_cycle_modified | cycle_id, user_id, timestamp, fields_changed, previous_values, new_values | Monitor configuration changes and their frequency |
billing_cycle_template_selected | cycle_id, user_id, timestamp, template_id | Understand template usage patterns |
Questions Answered:
- How often are new billing cycles created? Who creates them?
- What parameters are most frequently modified? Are changes made mid-cycle?
- Which bill templates are most popular? Should we consolidate rarely used templates?
Consumer Data Management Events
Event | Properties | Insights |
|---|---|---|
missing_plan_identified | count, cycle_id, consumer_types | Track consumer data quality issues |
consumer_plan_assigned | user_id, timestamp, consumer_id, plan_id, previous_plan_id | Monitor plan assignment activities |
consumer_tariff_updated | user_id, timestamp, consumer_id, tariff_id, previous_tariff_id | Track tariff management |
service_charge_reviewed | user_id, timestamp, charge_id, action_taken | Understand service charge review patterns |
Questions Answered:
- How many consumers typically lack plans at cycle start? Is this improving over time?
- How many plans are assigned during the billing process? Who is doing the assignments?
- How often are tariffs updated during the billing cycle? Are certain tariffs problematic?
- Which service charges require most review? Are there regulatory charges that need attention?
Meter Reading Events
Event | Properties | Insights |
|---|---|---|
reading_validation_started | user_id, timestamp, batch_size, issue_types | Track validation workload |
reading_validated | user_id, timestamp, meter_id, reading_value, issue_type, resolution_action | Monitor reading validation actions |
reading_estimation_performed | user_id, timestamp, meter_id, estimation_method, confidence_score | Track estimation patterns |
reading_excluded | user_id, timestamp, meter_id, exclusion_reason | Monitor reading exclusions |
Questions Answered:
- How much time is spent on reading validation? What are the most common validation tasks?
- What percentage of readings require manual validation? Who is performing validations?
- How often are readings estimated? Which estimation methods are most effective?
- How many readings are excluded from billing? What are the main reasons?
Bill Generation Events
Event | Properties | Insights |
|---|---|---|
bill_generation_started | user_id, timestamp, cycle_id, consumer_count | Track generation initiation |
bill_generation_completed | cycle_id, timestamp, duration, success_count, fail_count | Monitor generation performance |
bill_generation_failed | cycle_id, timestamp, error_distribution, top_errors | Understand failure patterns |
failed_bill_retry | user_id, timestamp, consumer_id, error_type, retry_outcome | Track resolution efficiency |
Questions Answered:
- When do users typically start generation? Is it consistent across cycles?
- How long does bill generation take? Is performance improving over time?
- What are the most common bill generation errors? Are they decreasing over time?
- How successful are retry attempts? Which errors are hardest to resolve?
Bill Approval Events
Event | Properties | Insights |
|---|---|---|
verification_checklist_started | user_id, timestamp, cycle_id | Track verification initiation |
verification_item_checked | user_id, timestamp, item_id, confirmation_status | Monitor verification thoroughness |
approval_comments_added | user_id, timestamp, comment_length, sentiment | Understand approval documentation |
bills_approved | user_id, timestamp, cycle_id, bill_count, cycle_duration | Track approval completion |
Questions Answered:
- When in the cycle is verification typically performed?
- Which verification items take longest? Are any items frequently unchecked?
- How detailed are approval comments? Do they indicate process issues?
- How long does the entire cycle take from start to approval? Is this improving?
System Usage Patterns
Event | Properties | Insights |
|---|---|---|
page_view | user_id, timestamp, page_name, time_on_page | Track interface usage |
feature_interaction | user_id, timestamp, feature_id, interaction_duration | Monitor feature adoption |
filter_applied | user_id, timestamp, page_name, filter_criteria | Understand data exploration |
export_performed | user_id, timestamp, data_type, record_count | Track data extraction |
error_encountered | user_id, timestamp, error_code, context, resolution_path | Monitor system errors |
Questions Answered:
- Which pages are most frequently used? Where do users spend most time?
- Which features are most/least used? Are new features being adopted?
- How do users filter and sort data? Which filters are most valuable?
- What data is frequently exported? Should we create new report templates?
- What system errors do users encounter? How quickly are they resolved?
Wireframe
Wireframe: Link
Reference: Link

No Comments