SMTP Settings - CRM6.2P1US6.2
1. Problem Statement
User Roles Identified
- System Admin (IT Director): Responsible for IT infrastructure, security protocols, and system configurations
- Utility Administrator: Primary SMART360 system administrator managing system settings and configurations
Pain Points by User Role
System Admin (IT Director):
- Difficulty in managing email delivery configurations across multiple utility systems
- Lack of centralized SMTP configuration management causing security vulnerabilities
- Unable to implement consistent email authentication protocols across all systems
- Time-consuming manual configuration of email settings for each system component
- Insufficient visibility into email delivery performance and failure rates
Utility Administrator:
- Complex email configuration requirements that require IT expertise
- Inability to test email configurations before implementing in production
- Difficulty troubleshooting email delivery issues without technical knowledge
- Manual process to configure different email providers for various system notifications
- Risk of system downtime due to incorrect email configurations
Core Problem
The utility lacks a centralized, user-friendly interface for configuring and managing SMTP email settings across the SMART360 system, leading to inconsistent email delivery, security vulnerabilities, and operational inefficiencies.
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
System Admin (IT Director):
- Oversees all IT infrastructure and security protocols
- Manages system integrations and vendor configurations
- Ensures compliance with cybersecurity standards
- Should have full access to all SMTP configuration features
Utility Administrator:
- Primary system administrator for SMART360
- Manages system settings and business process configurations
- Coordinates between IT and business departments
- Should have access to basic SMTP configuration with IT approval for security-sensitive settings
3. Jobs To Be Done
For System Admin (IT Director): When I need to configure secure email delivery settings for the SMART360 system, But I currently manage multiple disconnected email configurations across different system components with limited visibility into delivery performance, Help me centralize SMTP configuration management with comprehensive security controls and monitoring capabilities, So that I can ensure reliable email delivery while maintaining cybersecurity standards and reducing administrative overhead.
For Utility Administrator: When I need to set up email notifications and system communications for business processes, But I struggle with complex technical email configurations that require IT expertise and cannot easily test settings before deployment, Help me configure email settings through an intuitive interface with guided setup and testing capabilities, So that I can ensure business-critical notifications are delivered reliably without depending on IT for routine configuration changes.
4. Solution
The SMTP Settings Configuration module provides a comprehensive email configuration management system that enables secure, reliable email delivery for all SMART360 system communications.
Key Capability Areas
1. SMTP Server Configuration
- Host server address configuration with validation
- Port number management with standard port suggestions
- Connection protocol selection (SMTP, SMTPS, SMTP with STARTTLS)
2. Authentication Management
- Multiple authentication protocol support (LOGIN, PLAIN, CRAM-MD5)
- Secure credential storage and management
- Email provider selection with pre-configured templates
3. Security and Encryption
- TLS/SSL encryption configuration
- Certificate verification settings
- Security protocol compliance validation
4. Connection Management
- Maximum concurrent connections control
- Connection timeout and retry configuration
- Idle timeout management for resource optimization
5. Email Delivery Controls
- Custom header configuration for email tracking
- HELO hostname specification for server identification
- Email provider integration templates
6. Testing and Validation
- Built-in connection testing functionality
- Email delivery test capabilities
- Configuration validation before deployment
7. Monitoring and Analytics
- Connection status monitoring
- Delivery performance tracking
- Failed delivery alerts and notifications
5. Major Steps Involved
Step 1: Access Configuration Interface
Step 2: Basic Server Configuration
- Click in "Host" field (currently showing placeholder "smtp.example.com")
- Enter email provider's SMTP server address (e.g., "smtp.gmail.com")
- System validates domain format in real-time
- Navigate to "Port" field (shows default "587")
- Use increment/decrement buttons or manually enter port number
- System highlights if non-standard port is selected
Step 3: Authentication Setup
- Click "Auth Protocol" dropdown (currently showing "LOGIN")
- Select appropriate protocol: LOGIN, PLAIN, or CRAM-MD5
- System displays protocol description tooltip
- Enter username in format "user@example.com" in Username field
- Click Password field and enter secure credentials
- System masks password input with dots
Step 4: Provider and Security Configuration
- Click "Email Provider" dropdown (showing "Select email provider")
- Choose from list: Gmail, Office 365, Yahoo, Custom, etc.
- System auto-populates recommended settings if provider template selected
- Configure "HELO Hostname" (defaults to "localhost")
- Click "TLS" dropdown and select "STARTTLS" (recommended option shown)
- System displays encryption description: "TLS/SSL encryption; STARTTLS is commonly used"
Step 5: Connection Management
- Review "Max Connections" field (default "10")
- Use increment/decrement or enter custom value based on email volume needs
- Set "Retries" count (default "3") for failed delivery attempts
- Configure "Idle Timeout" (default "30s") for connection cleanup
- Set "Wait Timeout" (default "30s") for response waiting
Step 6: Advanced Configuration
- Click in "Custom Headers" text area
- Add custom headers in format "X-Custom-Header: value"
- Example entries: ---
X-Mailer: SMART360-System
X-Priority: 1
X-Source: UtilityNotifications- Each header on separate line following RFC 2822 format
Step 7: Configuration Testing
- Click "Test Connection" button at bottom of form
- System displays loading indicator "Testing connection..."
- Wait for test results (typically 5-15 seconds)
- Success Path: Green checkmark with "Connection successful" message
- Failure Path: Red error icon with specific error message like:
- "Authentication failed - check credentials"
- "Connection timeout - verify host and port"
- "TLS handshake failed - check encryption settings"
Step 8: Error Resolution (if test fails)
- Review error message for specific issue
- Common fixes:
- Verify host server address spelling
- Check if port is blocked by firewall
- Confirm username/password accuracy
- Validate authentication protocol compatibility
- Modify configuration based on error type
- Re-run "Test Connection" until successful
Step 9: Configuration Activation
- Once test passes, click "Save" button
- System validates all required fields are completed
- Configuration is saved with current timestamp
- Toggle "Active" switch to ON position (top right)
- System displays confirmation: "SMTP configuration activated successfully"
Step 10: Verification and Monitoring
- System sends test email to admin's email address
- Check inbox for delivery confirmation
- Monitor system notifications for any delivery issues
- Access email delivery logs from monitoring dashboard
- Set up alerts for authentication failures or connection issues
Alternative Flows:
Modify Existing Configuration:
- If configuration exists, form pre-populates with current values
- User can modify any field while maintaining others
- System highlights changed fields for review
- Test connection validates only modified components
- Save updates existing configuration rather than creating new
Multiple Provider Setup:
- Click "Add New" button to create additional SMTP configuration
- System opens new configuration panel
- Complete same steps for secondary provider (backup/failover)
- Only one configuration can be active at a time
- Switch between configurations using provider dropdown
Error Handling:
- Network Issues: Display "Connection timeout" with retry option
- Invalid Credentials: Show "Authentication failed" with credential reset link
- Port Blocking: Alert "Port may be blocked" with alternative port suggestions
- Invalid Format: Highlight fields with format errors in red
- Unsaved Changes: Warn user before leaving page with unsaved modifications
Post-Conditions:
- SMTP configuration is successfully saved and activated
- Test email delivery confirms functionality
- System can send notifications and alerts via configured SMTP
- Admin receives confirmation of successful setup
- Configuration is logged in system audit trail
Success Metrics:
- Configuration completed without IT support ticket
- Test connection passes on first or second attempt
- Email delivery begins working immediately after activation
- No configuration-related errors in first 24 hours
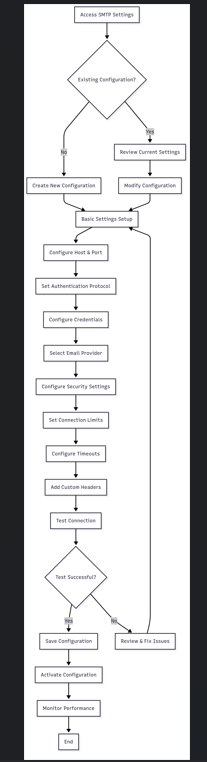
6. Flow Diagram
flowchart TD
A[Access SMTP Settings] --> B{Existing Configuration?}
B -->|Yes| C[Review Current Settings]
B -->|No| D[Create New Configuration]
C --> E[Modify Configuration]
D --> F[Basic Settings Setup]
E --> F
F --> G[Configure Host & Port]
G --> H[Set Authentication Protocol]
H --> I[Configure Credentials]
I --> J[Select Email Provider]
J --> K[Configure Security Settings]
K --> L[Set Connection Limits]
L --> M[Configure Timeouts]
M --> N[Add Custom Headers]
N --> O[Test Connection]
O --> P{Test Successful?}
P -->|Yes| Q[Save Configuration]
P -->|No| R[Review & Fix Issues]
R --> F
Q --> S[Activate Configuration]
S --> T[Monitor Performance]
T --> U[End]7. Business Rules
Header and Navigation Elements
General Configuration Rules
- SMTP Settings Page Title
- Must display "SMTP Settings" as main page header
- Header must be non-editable static text
- Must remain visible during page scrolling
- Text content cannot be modified by user actions
Configuration
StatusDescription Text:- Must
Systemdisplaymaintains"ConfigureActive/Inactiveyour SMTP server settings for email delivery" as subtitle - Text must be informational and non-interactive
- Cannot be edited or modified by users
- Must appear below main header consistently
Action Buttons
Save Button
- Must validate all required fields contain valid data before enabling
- Cannot execute save operation if mandatory fields are empty
- Must perform complete field validation including format checking
- Should display loading state during save operation
- Must create audit log entry with timestamp and user identification
- Cannot save configuration if connection test has not been performed successfully
- Must display confirmation message upon successful save
- Should show specific error messages if save operation fails
- Must update last modified timestamp in configuration record
Add New Button
- Must be available regardless of existing configuration status
- Cannot
togglebe disabled based on current configuration state - Must open clean configuration form without pre-populated values
- Should allow creation of unlimited configurations within system limits
- Must maintain existing configurations when creating new ones
- Cannot overwrite or modify existing configurations
- Must provide unique identification for each
SMTPnew configuration created
HostTestFieldConnectionValidationButton:- Cannot
Hostbefieldclickedmustuntil all required fields contain valid data - Must validate host, port, username, and password fields before execution
- Should display loading indicator during connection test process
- Must attempt actual connection to specified SMTP server
- Cannot exceed 60-second timeout for connection testing
- Must verify authentication credentials during test
- Should test TLS/encryption negotiation if encryption is enabled
- Must display specific error messages for different failure types
- Cannot allow configuration save if connection test fails
- Must log all test attempts with results and timestamps
Configuration Status Controls
Active/Inactive Toggle Switch
- Must default to inactive state for all new configurations
- Cannot be activated until configuration passes connection test
- Must immediately disable email sending when toggled to inactive
- Should display current state visually (active/inactive indication)
- Cannot have multiple configurations active simultaneously
- Must require confirmation before deactivating if emails are queued
- Should log all state changes with user and timestamp
- Must prevent activation if required fields are incomplete
Configuration Delete Button (Trash Icon)
- Must display confirmation dialog before deletion
- Cannot delete configuration if it is currently active
- Must require toggle to inactive before allowing deletion
- Should warn about impact on email delivery functionality
- Cannot be undone once deletion is confirmed
- Must remove all associated configuration data permanently
- Should create audit trail entry for deletion action
- Cannot delete if it's the only existing configuration
Server Connection Fields
Host Input Field
- Must accept only valid domain
namenames or IPaddressaddresses - Cannot be empty - required field validation must enforce this
- Should validate domain format in real-time during input
- Must accept IPv4 addresses in dotted decimal notation (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx)
- Should support IPv6 addresses in bracket notation
- Cannot accept localhost or 127.0.0.1 in production environments
- Must trim leading and trailing whitespace automatically
- Should validate DNS resolution during connection test
- Cannot exceed 253 characters maximum length
- Must reject input containing invalid characters for domain names
Port Number
RangeField:- Must
Portacceptnumberonlymustnumericbevalues between1-65535, with increment/decrement controls providing ±1adjustmentand 65535 DefaultShouldPort Assignment: System defaultsdefault toport587 for new configurations- Cannot accept negative numbers, zero, or decimal values
- Must validate port is within valid TCP port range
- Should display warning for non-standard ports (
standardnotsubmission25,port)465, 587, 2525) - Cannot be empty - must contain valid port number
- Must update value immediately when increment/decrement controls are used
- Should revert to previous valid value if invalid input is detected
Port Increment/Decrement Controls
- Must increase/decrease port value by exactly 1 per click
- Cannot increase port value above 65535 maximum
- Cannot decrease port value below 1 minimum
- Should disable increment button when maximum value is reached
- Should disable decrement button when minimum value is reached
- Must update port field value in real-time
- Cannot function if port field contains invalid data
Authentication Fields
Authentication Protocol Dropdown
: Dropdown must- Must include LOGIN, PLAIN, and CRAM-MD5 options
asminimum - Should
minimumdefaultrequirementsto LOGIN for new configurations - Cannot be empty - must have a selected value
- Must validate selection matches email provider capabilities
- Should display authentication method description on selection
- Cannot allow custom/unlisted authentication methods
- Must log authentication method selection for security audit
- Should warn if less secure method (PLAIN) is selected over encrypted alternatives
SecurityEmail Provider Dropdown- Must include Gmail, Office 365, Yahoo, Outlook, Exchange, and
AuthenticationCustomRules- options
- Should auto-populate host, port, TLS settings when provider is selected
- Cannot override user's manually entered values when provider changes
- Must validate consistency between selected provider and manual host entry
- Should display "Select email provider" placeholder when no selection made
- Cannot be required field - Custom option allows manual configuration
- Must provide provider-specific configuration recommendations
- Should update available authentication methods based on provider capabilities
Username
FormatField: Username field must- Must accept email address format (user@domain.com)
- Should
asvalidateshownemailinformat if @ symbol is present - Cannot be empty - required field for authentication
- Must accept plain usernames without @ symbol for some providers
- Should trim leading and trailing whitespace
- Cannot contain line breaks or control characters
- Must store value securely with encryption
- Should display placeholder "your-email@example.com"
- Cannot exceed 320 characters (RFC 5321 email address limit)
Password
SecurityField:- Must
Passwordmask all input characters for security - Cannot display actual password value after initial entry
- Must be required field
must- cannot bemaskedempty - Should
andacceptencryptedall printable characters including special symbols - Cannot be stored in
storageplain text - must use strong encryption EmailMustProvidernotIntegration:appearEmailin any system logs or debugging output- Should provide show/hide toggle for password visibility during entry
- Cannot have maximum length restrictions that would prevent secure passwords
- Must validate password meets minimum complexity if provider
dropdownrequiresmustit
Advanced
includeConfigurationmajorFieldsHELO
providersHostname Field- Should default to "localhost" if left empty
- Must accept valid domain name format only
- Cannot contain spaces or invalid domain characters
- Should use organization's actual domain name for optimal deliverability
- Cannot be required field - system can function with
pre-configureddefaultsettingsvalue - Must validate domain format if value is entered
- Should not exceed 255 characters maximum length
- Cannot contain protocol prefixes (http://, https://)
TLS
ConfigurationEncryption Dropdown:- Must
TLSincludedropdownSTARTTLS, SSL/TLS, and None options - Should default to STARTTLS for new configurations
- Cannot be empty - must
includehaveSTARTTLSencryptionasselection - Must
recommendedvalidateoptioncompatibility withencryptionselected port number - Should enforce SSL/TLS for port 465 configurations
- Cannot allow unencrypted connections on standard secure ports
- Must display security level description for each option
CertificateShouldVerification:warnSystemusermustifvalidate"None"TLS(nocertificatesencryption)whenisenabledselected
Connection Management Rules- Maximum Connections Field
:- Must
Defaultdefaultvalue isto 10 concurrent connectionswith increment/decrement controls - Cannot accept values less than 1 or greater than 100
- Should accept only positive integer values
- Cannot contain decimal points or negative numbers
- Must validate against email provider connection limits
- Should warn if value exceeds recommended limits for provider
- Cannot be empty - must contain valid connection count
- Must enforce connection limit during actual email operations
ConnectionMaxLimitsConnections Increment/Decrement Controls:- Must
Maximumincrease/decrease connection count by exactly 1 per click - Cannot increase value above 100 maximum limit
- Cannot decrease value below 1 minimum limit
- Should disable buttons when respective limits are reached
- Must update connections field
acceptsvaluenumeric input with validation for reasonable limits (1-100)immediately RetryCannotLogic:functionRetriesif connections fielddefaultscontains invalid data
Retries Field
- Must default to 3 retry attempts
- Cannot accept negative values or exceed 10 maximum retries
- Should accept 0 retries for immediate failure handling
- Cannot contain decimal values - integers only
- Must be applied with
increment/decrementexponentialcontrolsbackoffforbetweenfailed deliveriesattempts - Should count original attempt plus retries in total attempts
- Cannot be empty - must contain valid retry count
- Must stop retry attempts when maximum count is reached
TimeoutRetriesConfigurationIncrement/Decrement Controls:- Must
Bothincrease/decrease retry count by exactly 1 per click - Cannot increase value above 10 maximum retries
- Cannot decrease value below 0 minimum
- Should disable buttons when limits are reached
- Must update retries field immediately
- Cannot operate if retries field has invalid data
Idle Timeout
and Wait TimeoutField- Must default to 30 seconds
with(displayed's'as "30s") - Cannot accept values less than 10 seconds or greater than 300 seconds
- Should display time unit
indicator"s" suffix automatically - Cannot accept non-numeric values or negative numbers
- Must close idle connections when timeout period expires
- Should validate timeout is reasonable for email operations
- Cannot be empty - must contain valid timeout value
- Must apply timeout consistently to all SMTP connections
Timeout Range:Wait Timeout Field- Must default to 30 seconds (displayed as "30s")
- Cannot accept values less than 5 seconds or greater than 120 seconds
- Should display time unit "s" suffix automatically
- Cannot exceed total connection timeout duration
- Must trigger timeout error if server response exceeds limit
- Should be configured appropriately for email provider response times
- Cannot be empty - must contain valid timeout value
- Must apply to all SMTP command-response cycles
Custom Headers Text Area
- Must accept multi-line input with one header per line
- Should validate RFC 2822 header format: "Header-Name: Header-Value"
- Cannot modify standard SMTP headers (From, To, Subject, Date)
- Must accept header names containing letters, numbers, and hyphens only
- Should allow header values with spaces and printable characters
- Cannot exceed 8KB total size for all custom headers combined
- Must preserve line breaks and formatting as entered
- Should validate header names don't conflict with system-generated headers
- Cannot contain malicious content or script injections
- Must be included in all outbound emails when configuration is active
Field Interdependencies and Validation Rules
Host and Port Compatibility
- Port 465 must be
betweenused1-300withsecondsSSL/TLSforencryptionpracticalonly - Port
operation587 should default to STARTTLS encryption - Port 25 should display warning about potential ISP blocking
- Gmail hosts must use ports 465 or 587 only
- Office 365 hosts must use port 587 with STARTTLS
Advanced Configuration RulesHELO Hostname: Optional field for server identification, defaults to 'localhost' if not specifiedCustom Headers: Multi-line text area for custom email headers with format "Header-Name: value"HeaderProvider-Specific Validation:- Gmail
Custom headersconfigurations mustfollowuseRFCOAuth22822orformatapp-specificfor email header specificationpasswords ConfigurationOfficeTesting:365"TestmustConnection"havebuttonmodern authentication enabled- Yahoo configurations should warn about less secure app access
- Custom providers must have all fields manually configured
- Provider selection must validate
allagainstsettingsenteredbeforehostallowing save operationfield
DataSecurityPersistenceRequirementRulesEnforcementConfigurationUnencryptedState: Systemconnections mustmaintaindisplayconfigurationsecuritystate between sessionswarningsMultipleProductionConfigurations:environmentsSystemcannotsupportsusemultiplelocalhostSMTPorconfigurationsinternal(indicated by "Add New" button)IPsConfigurationPasswordActivation:complexityOnlymustonemeetSMTPproviderconfigurationminimumcan be active at a time per systemrequirementsAuditAuthenticationTrail:failures must not expose credential details in error messages- All configuration changes must be logged
withfortimestampsecurityand user identificationaudit
Error Handling Rules- Connection
FailuresTesting Validation: System- Test must
displayverifyspecifichosterrorresolutionmessages forbefore connection attempt - Authentication test
failuresmust use provided credentials InvalidEncryptionConfiguration:testPreventmustsavingverifyconfigurationsTLSthathandshakefailifvalidationenabled- Timeout tests must respect configured timeout values
TimeoutFailedHandling:testsDisplaymustappropriatepreventerrorconfigurationmessagesactivation- Successful
fortests must be logged with connectiontimeouts during testing Authentication Failures: Provide clear feedback for credential authentication issuesPort Blocking: Alert users when specified ports may be blocked by firewall or ISPdetails
8. Sample Data
Sample SMTP Configuration - Gmail
Host: smtp.gmail.com Port: 587 Auth Protocol: LOGIN Username: system-notifications@utilitycompany.com Password: [app-specific-password] Email Provider: Gmail HELO Hostname: mail.utilitycompany.com TLS: STARTTLS Max Connections: 10 Retries: 3 Idle Timeout: 30s Wait Timeout: 30s Custom Headers: X-Mailer: SMART360-System X-Priority: 1Sample SMTP Configuration - Office 365
Host: smtp.office365.com Port: 587 Auth Protocol: LOGIN Username: smart360@utilitycompany.onmicrosoft.com Password: [secure-password] Email Provider: Office 365 HELO Hostname: localhost TLS: STARTTLS Max Connections: 5 Retries: 2 Idle Timeout: 45s Wait Timeout: 60s Custom Headers: X-Source-System: SMART360 X-Environment: Production9. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must display SMTP Settings page with all configuration fields visible and properly labeled
- The system must provide an Active/Inactive toggle that controls SMTP configuration state
- The system must validate host field input to ensure proper domain name or IP address format
- The system must provide port number field with increment/decrement controls and default value of 587
- The system must offer authentication protocol dropdown with LOGIN, PLAIN, and CRAM-MD5 options
- The system must provide secure password field with masked input display
- The system must include email provider dropdown with major email service options
- The system must offer HELO hostname configuration with default 'localhost' value
- The system must provide TLS encryption dropdown with STARTTLS as recommended option
- The system must include maximum connections field with numeric validation and default value of 10
- The system must provide retries field with increment/decrement controls and default value of 3
- The system must offer timeout configuration fields with seconds unit indicator and 30s default
- The system must include multi-line custom headers text area for advanced configuration
- The system must provide "Test Connection" button that validates all configuration settings
- The system must display appropriate success/error messages for connection testing results
- The system must include "Save" button that persists configuration after successful validation
- The system must provide "Add New" button for creating additional SMTP configurations
- The system must prevent saving invalid configurations and display specific error messages
- The system must maintain configuration state across user sessions and system restarts
- The system must log all configuration changes with user identification and timestamp
10. Process Changes
ProcessAreaFromToImpactEmailAreaFrom
To
Impact
Email
ConfigurationManualConfigurationManual configuration of individual system components with separate SMTP
settingsCentralizedsettingsCentralized SMTP configuration management through unified
interface75%interface75% reduction in configuration time and 90% reduction in configuration
errorsSecurityerrorsSecurity
ManagementScatteredManagementScattered email authentication across multiple systems with inconsistent security
protocolsStandardizedprotocolsStandardized security protocols with centralized credential
management80%management80% improvement in security compliance and 60% reduction in credential management
overheadTestingoverheadTesting &
ValidationProductionValidationProduction deployment of untested email configurations leading to delivery
failuresBuilt-failuresBuilt-in testing capabilities before configuration
deployment95%deployment95% reduction in email delivery failures and 70% faster issue
resolutionProviderresolutionProvider
ManagementManualManagementManual configuration for each email provider requiring technical
expertisePre-expertisePre-configured templates for major email providers with guided
setup85%setup85% reduction in setup complexity and 50% faster provider
onboardingMonitoringonboardingMonitoring &
SupportReactiveSupportReactive troubleshooting of email delivery issues with limited
visibilityProactivevisibilityProactive monitoring with connection status and delivery performance
tracking60%tracking60% improvement in issue detection time and 40% reduction in support
ticketsMulti-ticketsMulti-Environment
SetupSeparateSetupSeparate configuration processes for development, staging, and production
environmentsConsistentenvironmentsConsistent configuration process with environment-specific
customization70%customization70% improvement in deployment consistency and 50% reduction in environment-specific
issuesDocumentationissuesDocumentation &
ComplianceManualComplianceManual documentation of email configurations for audit
purposesAutomatedpurposesAutomated audit trails with configuration change
logging90%logging90% improvement in compliance documentation and 80% reduction in audit preparation
timeBackuptimeBackup &
RecoveryNoRecoveryNo standardized backup process for email
configurationsBuilt-configurationsBuilt-in configuration backup and recovery
capabilities100%capabilities100% improvement in disaster recovery readiness and 85% reduction in recovery time
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
ImpactCategoryMetricImprovementCategoryMetric
Improvement
DescriptionOperationalDescriptionOperational
EfficiencyConfigurationEfficiencyConfiguration
Time75%Time75% reduction in time required to configure SMTP settings through centralized interface and pre-configured
templatesSystemtemplatesSystem
ReliabilityEmailReliabilityEmail Delivery Success
Rate95%Rate95% improvement in email delivery reliability through connection testing and
validationSecurityvalidationSecurity
ComplianceSecurityComplianceSecurity Protocol
Adherence80%Adherence80% improvement in security compliance through standardized authentication and encryption
protocolsErrorprotocolsError
ReductionConfigurationReductionConfiguration
Errors90%Errors90% reduction in email configuration errors through validation and testing
capabilitiesITcapabilitiesIT
ProductivityAdministrativeProductivityAdministrative
Overhead60%Overhead60% reduction in IT administrative time spent on email configuration
managementUsermanagementUser
ExperienceSetupExperienceSetup
Complexity85%Complexity85% reduction in technical complexity for non-IT users configuring email
settingsSupportsettingsSupport
EfficiencyTroubleshootingEfficiencyTroubleshooting
Time70%Time70% faster issue resolution through built-in testing and clear error
messagingCompliancemessagingCompliance
DocumentationAuditDocumentationAudit
Readiness90%Readiness90% improvement in audit preparation time through automated logging and
documentationSystemdocumentationSystem
IntegrationProviderIntegrationProvider
Onboarding50%Onboarding50% faster integration with new email service providers through template-based
configurationBusinessconfigurationBusiness
ContinuityRecoveryContinuityRecovery
Time85%Time85% reduction in email service recovery time during system issues or migrations
12. User Behavior Tracking
System Admin (IT Director) Tracking
smtp_config_createdMetric Category
Events to Track
Properties
Questions Answered
Configuration Management
smtp_config_created,smtp_config_modified,smtp_config_activateduser_id, config_type, provider, security_protocol, timestamp
How frequently are SMTP configurations being created and modified? Which security protocols are most commonly used?
Security Monitoring
tls_enabled,auth_protocol_selected,certificate_validation_enabledencryption_type, auth_method, validation_status, user_role
Are users implementing recommended security practices? Which authentication methods are preferred?
Testing & Validation
connection_test_initiated,connection_test_success,connection_test_failuretest_duration, error_type, retry_attempts, configuration_id
How often are configurations tested before deployment? What are the most common test failure reasons?
Performance Monitoring
smtp_performance_viewed,delivery_metrics_accessed,error_logs_reviewedmetrics_type, time_range, filter_criteria, dashboard_section
How actively are administrators monitoring email performance? Which metrics are most important to users?
Utility Administrator Tracking
Metric Category
Events to Track
Properties
Questions Answered
Configuration Usage
smtp_settings_accessed,provider_template_selected,guided_setup_completedaccess_frequency, template_type, completion_time, user_experience_rating
How often do utility administrators access SMTP settings? Which provider templates are most popular?
User Experience
help_documentation_accessed,error_message_displayed,support_ticket_createdhelp_topic, error_category, resolution_method, user_satisfaction
What areas cause the most confusion for utility administrators? How effective is the guided setup process?
Business Process Integration
notification_config_updated,business_rule_applied,workflow_integration_enablednotification_type, business_process, integration_success, impact_assessment
How are SMTP settings being integrated with business processes? Which notification types require the most configuration?
Collaboration Tracking
it_approval_requested,configuration_shared,collaborative_troubleshootingapproval_type, sharing_method, collaboration_duration, resolution_success
How often do utility administrators need IT support? What types of issues require collaborative resolution?
smtp_settings_accessedSystem Performance Tracking
Metric Category
Events to Track
Properties
Questions Answered
Delivery Performance
email_sent,email_delivered,email_bounced,email_failedrecipient_type, delivery_time, failure_reason, retry_count
What is the overall email delivery success rate? Which types of emails have the highest failure rates?
Configuration Effectiveness
config_deployment_success,config_rollback_initiated,performance_degradation_detectedconfig_version, deployment_method, impact_severity, rollback_reason
How often do configuration changes need to be rolled back? What configuration changes have the biggest impact on performance?
Resource Utilization
connection_pool_usage,timeout_events,retry_attempts_exhaustedconnection_count, timeout_duration, resource_constraint, peak_usage_time
Are connection limits appropriately configured? When do timeout issues occur most frequently?
Security Events
authentication_failure,tls_handshake_failure,suspicious_activity_detectedfailure_type, source_ip, security_protocol, threat_level
Are there security issues with current SMTP configurations? Which authentication methods have the highest failure rates?
email_sent - Test must
- Gmail
- Must