Data Migration (ONB04US01)
1. Problem Statement
Utilities migrating from legacy systems to SMART360 face significant challenges in data migration and transformation. The process is:
- Time-consuming, taking weeks to migrate critical utility data such as consumer records, meter readings, and billing history.
- Error-prone, leading to data loss, incorrect meter-to-consumer mapping, and inconsistencies in billing and service requests.
- Manually intensive, requiring extensive effort to clean, format, and validate consumption data, payment records, and asset details.
These challenges directly impact key utility operations, including:
- Billing & Revenue Management – Incorrect data leads to overbilling, underbilling, or missing payments, causing financial discrepancies.
- Service Order Execution – Delays in consumer data migration result in service interruptions and slow request processing.
- Meter Data Management – Inaccurate meter readings and historical data errors affect consumption tracking and billing accuracy.
- Asset & Territory Management – Improper mapping of utility assets (transformers, substations, meters) leads to inefficiencies in maintenance and tracking.
Without an efficient migration system, utilities experience:
- Delayed operational readiness, increasing the time required to onboard and serve customers.
- High support dependency, as utility teams spend excessive time manually fixing migration errors.
- Revenue leakage, where incorrect billing data and missing transactions result in financial losses.
An optimized data migration solution for utilities is essential to ensure accurate, efficient, and seamless onboarding into SMART360.
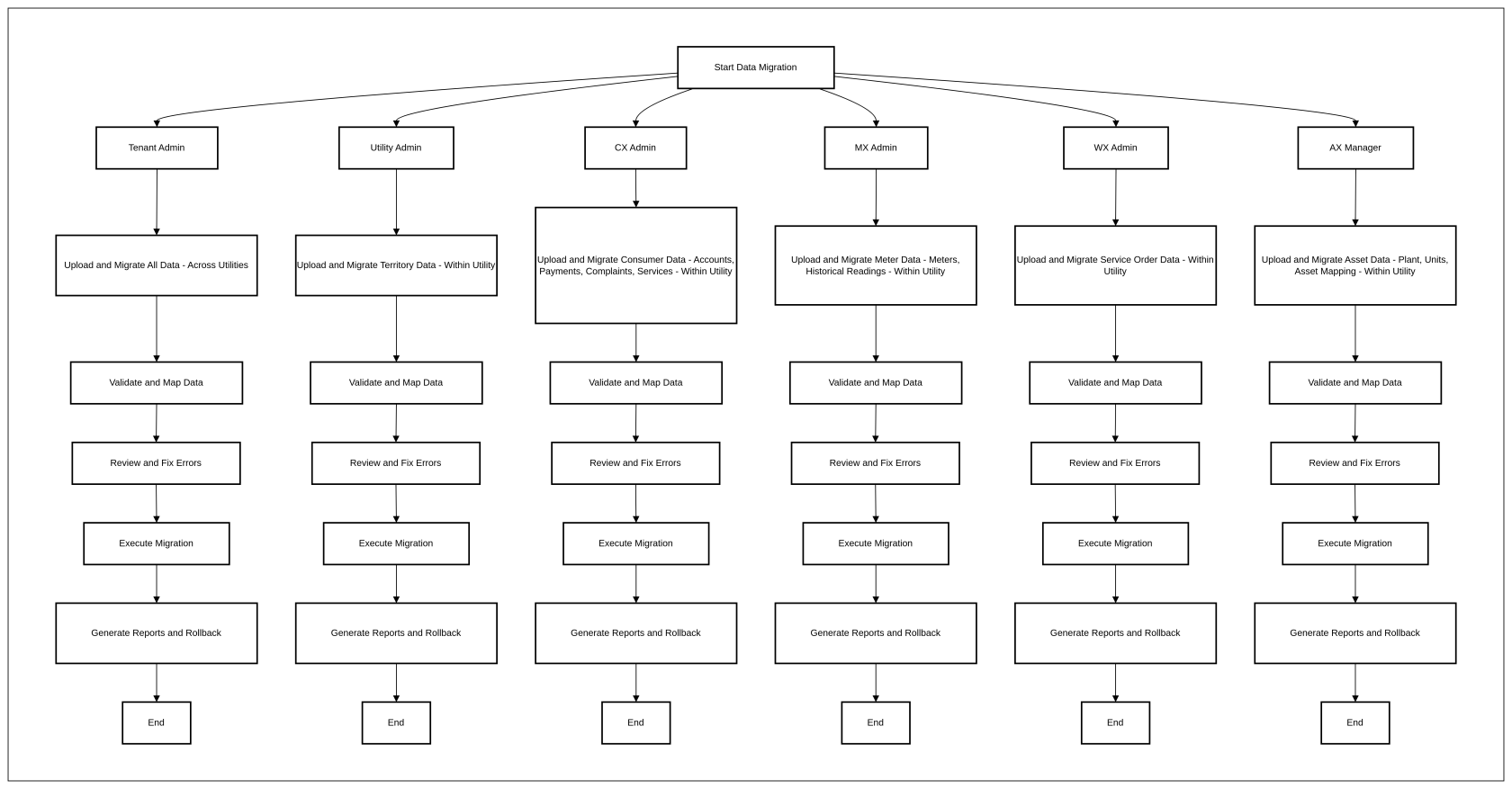
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
- Tenant Admin: Unable to migrate data for specific utility
- Utility Admin: Unable to migrate territory data efficiently, leading to delays in system setup.
- CSO Admin: Struggles with bulk uploads of consumer accounts, payments, complaints, and services, causing payment delays and incorrect account statuses.
- MX Manager: Cannot migrate bulk meter data, historical readings, or update large datasets, leading to errors in consumption tracking and billing.
- WX Admin: Lacks bulk import functionality for service order templates, slowing work order execution.
- AX Admin: Faces inefficiencies in importing plant, unit, and asset data, impacting asset tracking and maintenance scheduling.
These users spend weeks cleaning, transforming, and loading data manually using Postman, Excel, and external tools, creating operational bottlenecks.
User Role Permissions for Data Migration
1. Tenant Admin
- Can upload and migrate all tye of data across all utilities.
- Can manage and view migrations for all utilities.
2. Utility Admin
- Can upload and migrate data only within their assigned utility.
- Can manage and view migrations within their utility within its associated utility.
3. CSO Admin (Consumer Data Management)
- Can upload and migrate consumer related data (accounts, payments, complaints, services) within its associated utility.
- Can manage and View consumer data migrations within its associated utility.
4. MX Manager (Meter Data Management)
- Can upload and migrate meter related data (meters, historical readings) within its associated utility.
- Can manage and view for meter data migrations within its associated utility.
5. BX Manager (Billing Data Management)
- Can upload and migrate Billing related data within its associated utility.
- Can manage and view for Billing data migrations within its associated utility.
6. O&M Manager (Work & Service Orders)
- Can upload and migrate service orders related data within its associated utility.
- Can manage and view service order migrations within its associated utility.
7. AX Admin (Assets & Plant Data)
- Can upload and migrate assets related data within its associated utility.
- Can manage and view asset data migrations within its associated utility.
3. Jobs To Be Done
As a Utility Admin / CSO Admin / MX Manager / BX Manager / O&M Manager / AX Admin, I am responsible for managing vast amounts of consumer, meter, and billing data. Migrating this data from legacy systems to SMART360 has always been a challenge—manual processes are slow, error-prone, and disrupt daily operations.
I need a seamless and intuitive bulk data migration tool that allows me to upload large datasets effortlessly while ensuring accuracy and compliance. The system should accurately and automatically map fields, validate data, and highlight errors before final import, giving me confidence that the data is clean and reliable.
With this solution, I can focus on operations instead of data corrections, reduce migration time, and ensure a smooth transition to SMART360. This will improve efficiency, drive higher adoption, and allow my team to continue working without disruptions.
4. Solution
The AI-Powered Data Migration & Transformation feature introduces:
- AI-Powered Column Mapping – Auto-detects & suggests field mappings with accuracy scores.
- Data Transformation Rules – Standardizes formats, merges/splits columns, and applies regex corrections.
- Live Validation & Error Handling – Detects missing/incorrect data with inline fixing suggestions.
- Smart Auto-Correction & Recommendations – AI-powered anomaly detection and bulk edit options.
- Real-Time Progress & Rollback – Track migration progress, pause, retry, or rollback if needed.
- Post-Migration Reports & Audit Logs – Exportable logs, success/failure reports, and full audit trails.
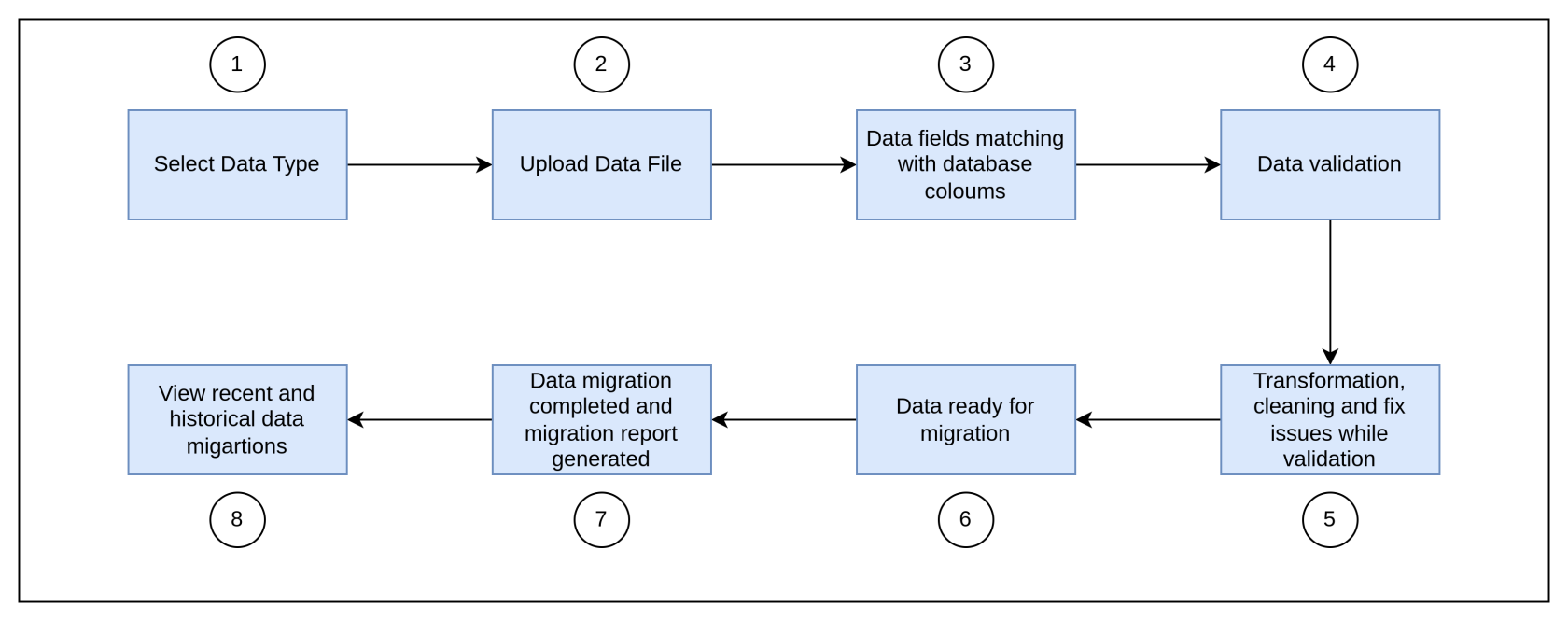
5. Process Flow
6. Major Steps Involved
- User uploads bulk data file (CSV).
- AI-powered column mapping suggests auto-matched fields with manual override.
- Data transformation engine cleans and formats entries (e.g., date standardization, merging duplicate records).
- Live validation detects issues (missing fields, incorrect formats, duplicate entries).
- Inline fixing suggestions are provided for errors.
- Preview step allows users to compare source vs. transformed data.
- User initiates migration, tracking real-time progress.
- Audit logs & post-migration reports confirm success/failures and rollback options.
7. Business Rules
Process Authorization Rules
Upload Process
- The Utility should be selected for the process to begin.
- The system supports AI-powered data upload functionality for seamless integration into the Smart360 system.
- Users can upload data for various data types including:
- Consumers (customer accounts and profiles)
- Meters (meter information and details)
- Meter Data (usage readings and consumption data)
- Service Orders (work orders and service requests)
- Payments (customer payment history and transactions)
- Complaints (customer support tickets and issues)
- Plant (Plant configuration data)
- Unit (Unit configuration data)
- Asset(Asset configuration data)
- User Data (system users and administrative accounts)
- User can enter a migration name, if the name is not added the system will automatically fill it by the file name.
- File upload supports CSV formats
- The system should allow a maximum of 50,000 rows per file upload to ensure performance optimization and prevent system overload.
- The system provides a preview of the uploaded data showing a sample of records (e.g., "Showing 5 of 7052 records").
- Files can be uploaded either through drag-and-drop functionality or by browsing for files.
- User can download the data template file in CSV format
- The template will contain:
- Predefined column headers based on the selected data type.
- Sample data in the first few rows to help users understand the expected format.
- The system displays upload progress with percentage completion indicators.
- Once uploaded, the system displays a confirmation message for successful uploads.
Data Analysis and Mapping
- AI automatically analyzes the file and suggests column mappings between source columns and target Smart360 fields.
- Each suggested mapping is assigned a confidence level (High, Medium, Low) to indicate the reliability of the mapping.
- Each coloum mapping is not madatory.
- File information is displayed showing:
- Filename
- Total columns (e.g., 8)
- Total rows (e.g., 2,426)
- Mapping quality indicators (e.g., 5 High, 2 Medium, 1 Low)
- The system evaluates the uploaded file and assigns confidence levels based on three key factors:
Confidence Level | Criteria | Example |
|---|---|---|
High ✅ | - Exact Name Match between the uploaded field and system field. - Exact Data Type Match (e.g., String → String, Date → Date, Integer → Integer). - Strong Pattern Similarity (e.g., Phone numbers, ZIP codes). | Uploaded File Field:
✅ High confidence because the name matches exactly and the expected data type is correct. |
Medium ⚠️ | - Partial Name Match (e.g., synonyms, abbreviations, slight variations). - Compatible but Different Data Types (e.g., Integer vs. String for an ID field). - Pattern Recognition with Minor Variations (e.g., "Meter No." vs. "Meter ID"). | Uploaded File Field:
⚠️ Medium confidence because "Cust_ID" is a partial match for "Consumer ID", but it's not exact. |
Low ❌ | - No Name Similarity between the uploaded field and system field. - Incompatible Data Types (e.g., Text mapped to Date). - Unrecognized Field Content (e.g., a completely unrelated field). | Uploaded File Field:
❌ Low confidence because "Billing Address" is unrelated to "Consumer ID". |
- Example Scenario
A user uploads a file containing the following columns:
Uploaded Field | System Field (SMART360) | Confidence Level | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| High ✅ | Exact name and data type match. |
|
| Medium ⚠️ | Partial name match, slightly different format. |
|
| Medium ⚠️ | Recognized abbreviation, slightly different spelling. |
|
| Low ❌ | No strong similarity between names. |
|
| Low ❌ | Incorrect field mapping; different meanings. |
- Source columns are mapped to target fields with sample data displayed for reference.
- Users can manually adjust mappings through dropdown selection if the AI suggestion is incorrect.
- The system enforces proper field type mapping (e.g., ensuring Customer ID fields map to appropriate ID fields).
Validation Process
- The system performs data validation after mapping to identify issues requiring attention.
- Validation results are categorized as:
- Valid records (with percentage)
- Warnings (with percentage)
- Errors (with percentage)
- The system specifically identifies and flags:
- Format issues (e.g., "Missing Postal Code format")
- Data inconsistencies (e.g., "Date format inconsistency")
- Unmapped fields (e.g., "Unmapped field: Meter_Type")
- For each issue type, the system shows the number of affected records.
- Users can download a validation report for offline review.
- The system provides detailed information for each issue, including specific records affected.
- A "Fix All Issues" option is available for batch resolution of problems.
Handling Missing Primary Keys for Data Upload
- If the uploaded file does not contain the required primary key for the selected dataset, the system will take action based on the Onboarding (ONB) settings.
Handling Scenarios
1. ONB Has Predefined Prefix & Starting Number
- If the prefix and starting number are already set in ONB, the system will:
- Auto-fill the missing primary key using the predefined prefix and starting number.
- Generate unique primary keys in sequence.
- Show a preview for confirmation before migration.
Example:
- Dataset: Consumer Data
- ONB Settings: Prefix =
CUST, Starting Number =1001 - Generated Keys:
CUST1001,CUST1002,CUST1003… - User Options:
- Confirm the auto-filled primary keys.
- Re-upload the file if the user wants to provide their own primary keys.
2. ONB Does Not Have Predefined Prefix & Starting Number
- If ONB settings do not have a predefined prefix and starting number:
- the system will ask for prefix and starting number
- The system will display a preview before finalization.
- the Prefix and starting name should be set in the num format
Primary Keys Required by Dataset
| Dataset Type | Primary Key Required |
|---|---|
Consumer Data | Customer Number |
Meter Data | Meter Number |
Asset Data | Asset ID, Plant ID, Unit ID |
- Auto-fill when ONB settings exist to ensure seamless migration.
- Prompt user only when ONB settings are missing, reducing unnecessary steps.
- Uniqueness Check: Ensure no duplicate keys are generated.
- Preview & Confirmation: Users must verify generated primary keys before finalizing.
- Re-upload Option: If users want to provide their own primary keys, they can re-upload the file.
Data Correction
- Users can view detailed information about each issue by expanding the issue sections.
- For format issues (e.g., postal codes), the system allows:
- Viewing specific invalid records
- Auto-formatting data to meet system requirements
- For unmapped fields, the system:
- Suggests possible Smart360 mappings
- Allows users to select the appropriate field mapping
- The system tracks correction status, showing:
- Fixed issues (with green checkmarks)
- Remaining issues (with warning or error icons)
- When issues are corrected, the system updates validation statistics (e.g., Valid records percentage increases).
- Auto-format functionality can standardize data formats (e.g., converting postal codes to standard formats).
Error Handling
- Unexpected errors must be flagged for immediate administrator attention
- The system must implement automatic retry logic for transient errors
- Critical errors must halt the migration process until administrator intervention
Error messages must be specific and provide examples for corrections.
✅ Example of Effective Error Handling:
| Error Type | Message | Suggested Fix |
|---|---|---|
Incorrect Format | Date format inconsistent: "Jan 5 2021", "02/03/2024". | Use the standard format: YYYY-MM-DD (e.g., 2024-03-20) . |
Missing Field | Meter ID missing in row 5. Required for meter mapping. | Enter a valid Meter ID before proceeding. |
Duplicate Entry | Meter ID "5001" already exists in the uploaded data (Row 6, Row 12). | Remove duplicates from the uploaded file before re-uploading. |
Overwriting Data | Existing consumer data for Consumer ID "C123" found. | Confirm if data should be updated or kept unchanged. |
Invalid Value | Negative consumption (-250 kWh) in row 12. | Verify meter readings and enter a positive value. |
Mapping Error | Meter ID "M1002" not linked to any consumer account. | Ensure meters are mapped to a valid consumer. |
Unsupported Character | Special characters found in Consumer Name ("John@Doe"). | Remove special characters; use only letters and spaces. |
AI Assistant Integration Rules
- AI assistant must provide real-time updates on migration progress
- Assistant must offer troubleshooting guidance for common error patterns
- AI recommendations must be reviewed by human operators before implementation
- Assistant should suggest optimization strategies based on observed performance
Migration Process
- The system tracks total records to be processed (2897 in total)
- Current progress is displayed both numerically (375 of 2897) and as a percentage (13% Complete)
- The progress bar visually represents completion percentage
- The system maintains counts of successful migrations (367) and errors (8)
- Errors are logged in a separate "Error Log" section with row numbers and error messages
- All migration activity is timestamped [HH:MM PM]
- Log entries show both successful and failed operations
- The system captures the specific row numbers where errors occur
- All errors currently show as "Unexpected error during migration" suggesting generic error handling
Migration Reporting Rules
- Each migration must generate a timestamped report (format: MM/DD/YYYY, HH:MM
AM/PM) - Reports must include total record count, success rate, error rate, and processing time
1. Total Record Count
Definition: The total number of rows processed from the uploaded file.
Formula: Total Record Count=Number of Rows in the Uploaded File\text{Total Record Count} = \text{Number of Rows in the Uploaded File}Total Record Count=Number of Rows in the Uploaded File
Example: If a user uploads a file with 50,000 rows, the Total Record Count = 50,000.
2. Success Rate (%)
Definition: The percentage of records successfully migrated without errors.
Formula: Success Rate=(Successfully Migrated RecordsTotal Record Count)×100\text{Success Rate} = \left( \frac{\text{Successfully Migrated Records}}{\text{Total Record Count}} \right) \times 100Success Rate=(Total Record CountSuccessfully Migrated Records)×100
Example:
Uploaded file: 50,000 rows
Successfully migrated records: 47,500 rows
Success Rate = (47,500 / 50,000) × 100 = 95%
3. Error Rate (%)
Definition: The percentage of records that failed due to validation errors, incorrect field mappings, or missing data.
Formula: Error Rate=(Failed RecordsTotal Record Count)×100\text{Error Rate} = \left( \frac{\text{Failed Records}}{\text{Total Record Count}} \right) \times 100Error Rate=(Total Record CountFailed Records)×100
Example:
Uploaded file: 50,000 rows
Failed records due to errors: 2,500 rows
Error Rate = (2,500 / 50,000) × 100 = 5%
4. Processing Time
Definition: The total time taken to process and migrate the data.
Formula: Processing Time=Migration End Time−Migration Start Time\text{Processing Time} = \text{Migration End Time} - \text{Migration Start Time}Processing Time=Migration End Time−Migration Start Time
Example:
Migration started at 10:00 AM
Migration completed at 10:05 AM
Processing Time = 5 minutes - Success/error distribution must be visually represented with color-coded indicators
- Users must be able to return to the dashboard from the report view
Error Report Generation
- The Error Report is generated when data migration fails for certain records.
- The report is downloadable in Excel (CSV) format.
- Each row in the report corresponds to a record that failed migration.
- The report should clearly indicate why each record was not migrated.
- If no errors are found, the download option is disabled.
- The downloaded CSV must include a detailed message explaining why each data entry failed.
- Show the originnal data entered and then add a error discription coloum.
- The Error report will only include non migrated data with the error message.
Error Report Sample
| Consumer No | Meter No | Premise | Error Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(Blank) | 123456 | 123 Main Street | Consumer No is required and cannot be empty. | |
98765 | ABC123 | user@xyz | 456 Oak Avenue | Meter No must be numeric, but received 'ABC123'. |
12345 | 789012 | user@invalid | 789 Pine Road | Invalid email format. Expected format: xyz@domain.com. |
54321 | 654321 | 321 Birch Lane | Premise not found or not related to the consumer. | |
11223 | 987654 | 852 Cedar Road | Negative balance is not allowed for active accounts. |
Migration History Rules
- The system must maintain a log of all migrations with date and type information
- Migrations must be searchable by name o
- r other parameters
- Migrations must be filterable by:
- Data category, eg: consumer data
- New migrations must be clearly identified in the history
- Migration history must display the most recent migrations at the top
- Migration names must be descriptive of their content when specified by users
- On view for completed migrations, it will redirect to the migration report.
- Below details should be shown for the completed migrations
- Migration name
- Migrated by, name of the user who has perform migration
- Date
- Type
- Status
- Records
- Errors
- Action
Security and Data Management
- The system tracks and allows viewing of upload history.
- The system appears to enforce data quality standards through validation rules.
- The system maintains the relationship between related data entities (e.g., Customer IDs and Meter IDs).
- The system enforces format standards for critical fields like postal codes, dates, and IDs.
- The system allows for error handling and recovery from validation failures.
8. Sample Data Format
9. Acceptance Criteria
- Users can successfully upload bulk data files with 100% accuracy.
- AI-powered field mapping works with accuracy.
- Live validation must detect incorrect/missing data.
- Users can manually correct errors before migration.
- Preview functionality allows comparison between original & processed data.
- Migration progress can be tracked with a real-time status.
- Audit logs provide detailed insights on data corrections.
10. Process Changes
- Eliminates Postman/manual scripts for data import.
- Integrates AI-driven validation before actual migration.
- Replaces manual transformation steps with automated rule-based corrections.
- Reduces dependency on customer support for migration issues.
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Impact Metrics: SMART360 Data Migration Module
| Metric | Before Implementation (Legacy System Challenges) | After Implementation (SMART360 Solution) |
|---|---|---|
Time to Migrate a Single Data Type | 2-4 weeks per data type due to manual validation and cleaning. | Reduced to 1-2 hours with automated validation and transformation. |
Data Errors (Formatting, Duplicates, Missing Fields) | 20-30% of uploaded records required manual fixes. | <5% error rate with structured validation and predefined templates. |
Operational Readiness Delays | Onboarding delayed by 4-6 weeks due to incomplete or incorrect data. | Onboarding within 1 weeks , ensuring a faster go-live. |
Support Dependency for Data Fixes | 100% of migration cases required customer support intervention. | <20% support dependency , as most errors are resolved automatically. |
Billing Inaccuracy Due to Data Issues | Up to 25% of bills generated with incorrect consumption or missing data. | <1% billing errors , ensuring accurate invoicing. |
12. Summary of Business Impact
By implementing the SMART360 Data Migration Module, utilities can expect:
✅ 80% faster data migration
✅ 85% reduction in errors
✅ 60% lower dependency on manual fixes
✅ Faster system onboarding (within weeks instead of months)
✅ Improved billing accuracy, reducing revenue leakage
13. User Behavior Tracking
1. Tenant Admin
Objective: Track Tenant Admins managing data migration across the utilities
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Data Uploads | How frequently bulk data is uploaded | Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether fields are mapped correctly | Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Errors | How many records fail validation | Data Validation |
,
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often records are reviewed before migration | Data Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often data is successfully migrated | Data Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- Are Tenant Admins uploading data efficiently?
- How frequently do mapping errors occur?
- How long does it take to validate and approve data before migration?
2. Utility Admin
Objective: Track Utility Admins managing data migration for their assigned utility.
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Data Uploads | Frequency of data uploads within a utility | Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether fields are mapped correctly | Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Errors | How many records fail validation | Data Validation |
,
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often records are reviewed before migration | Data Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often data is successfully migrated | Data Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- How efficiently are Utility Admins managing data migration?
- Are validation issues slowing down migration?
- How long does the approval process take before migration?
3. CSO Admin (Consumer Data Management)
Objective: Track CSO Admins handling consumer data migration, including accounts, payments, complaints, and services.
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Consumer Data Uploads | Frequency of consumer-related data uploads | Consumer Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether consumer data fields are mapped correctly | Consumer Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Errors | How many consumer records fail validation | Consumer Data Validation |
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often consumer records are reviewed | Consumer Data Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often consumer data is migrated successfully | Consumer Data Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- Are consumer records being uploaded and mapped correctly?
- What is the validation failure rate for consumer data?
- How quickly is consumer data approved and migrated?
4. MX Manager (Meter Data Management)
Objective: Track MX Managers overseeing meter data migration, including readings and meter mapping.
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Meter Data Uploads | Frequency of meter data uploads | Meter Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether meter fields are mapped correctly | Meter Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Errors | How many meter records fail validation | Meter Data Validation |
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often meter readings are reviewed and approved | Meter Readings Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often meter data is migrated successfully | Meter Data Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- Are meter readings being uploaded and mapped correctly?
- How efficiently are errors being resolved?
- What percentage of data is successfully migrated without validation issues?
5. BX Manager (Billing Data Management)
Objective: Track BX Managers handling billing data migration, including rate structures and billing history.
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Billing Data Uploads | Frequency of billing data uploads | Billing Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether billing fields are mapped correctly | Billing Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Errors | How many billing records fail validation | Billing Data Validation |
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often billing records are reviewed and approved | Billing Data Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often billing data is migrated successfully | Billing Data Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- Are billing data uploads happening without major validation errors?
- How efficiently is billing data being reviewed and migrated?
- Are delays in billing approvals affecting migration speed?
6. O&M Manager
Objective: Track O&M Managers handling work order and service order data migration.
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Work Order Data Uploads | Frequency of work order data uploads | Work Order Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether work order fields are mapped correctly | Work Order Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Issues | How many work order records fail validation | Work Order Validation |
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often work orders are reviewed and approved | Work Order Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often work order data is successfully migrated | Work Order Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- Are work order records uploaded correctly?
- How efficiently are work order fields being mapped?
- Are approval delays affecting execution?
7. AX Manager
Objective: Track AX Managers managing asset-related data migration, including plant, unit, and asset details.
| Metric | What it Tells You | Event to Track | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Asset Data Uploads | Frequency of asset-related data uploads | Asset Data Uploaded |
,
,
,
|
Field Mapping Completion | Whether asset fields are mapped correctly | Asset Fields Mapped |
,
,
|
Validation Errors | How many asset records fail validation | Asset Data Validation |
,
,
|
Data Review & Approval | How often asset records are reviewed and approved | Asset Data Approved |
,
,
,
|
Migration Execution | How often asset data is successfully migrated | Asset Data Migrated |
,
,
,
|
Key Insights:
- Are asset records being uploaded and mapped correctly?
- How frequently do mapping errors occur?
- How long does it take for validation and approval before migration?
14. Wireframe
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1MQQYjcWuYSv4zxLWzdrHlI-A2DfqInz3VNRAPcTBt2w/edit?usp=sharing
15. Enhancements in the latest release
Update Data Business rules:
- Data Upload Initial Options:
- Users can either update existing data or upload new data into the system
- Data Type Selection:
- System supports multiple data categories displayyyyy which can be updated
- Each data type has specific attributes and purposes within the utility management system.
- Field Selection Rules:
- Required unique identifier, For example consumer data, customerID
- Users can select which fields to include in their data update, display only the fields which ca be updated.
- multiple fields can be selected and updated
- System allows selective field updates rather than requiring all fields
- CSV Template Usage:
- Users must download the provided template before uploading data
- Templates include the specific headers for the selected fields
- Templates enforce data structure compliance
- Upload Constraints:
- Cannot upload file unless the given file is downloaded
- User will add a migration name same as it is added in the data upload process
- File format must be CSV only for data migration
- After uploading, file it will be same process as normal data upload, excluding the System data mapping tab
Data Upload Business rules:
System Data Mapping:
- Fields Mapping with Data coloum
- Users can select which coloums should be included while data migration process.
- System Data mapping
- This screen will be visible only when system required data is not mapped while mapping coloums. for eg: if plan is required i consumer data and it is ot mapped wile mappig fields then this screenn will be visible, if its mapped then this screen is not needed.
- For each system data missing which is mandatory while uploading the data should be mapped in the System data mapping screen
- Progress tracking shows completion percentage of mapping tasks
- User can mapped the data by selecting the data from the tab section
- Tabs will be as per the non mapped required data
- User can search data across all the coloums using the search bar
- user can use filter to filter the data acress all coloums with the unique coloum values.
- fillter will be multiselect and accordig the data will appear.
- User can update the filtered data
- user can select the desire data and can assigned it to the seleceted data rows
- User can selecet all data together or can select single data.
- Once the data is assigned then it should be tagged with the data row
- Overall progress should be showned.
- All data should be mapped then only user can go on next step
Migration History rules
- The system should maintain the history for data updata
- system should allow data roll back and all actions perform related to the data update and data upload.
- Data rollback can be done within 3 days from data uploaded or data updated
- All transaction data or related data to the roll back data should be delet
UI Rules
- The Icons should be Same which are outline with background icon
- The animations should work as same in the given lovable design.
Wireframe
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1vLa15aRNz4pILjPC7SLVlEaetvCZLGllg2L9TmoF37Y/edit?usp=sharing
Acceptance criteria
- The system must allow users to either update existing data or upload new data into the system
- The system must support multiple data categories that can be updated
- The system must provide specific attributes and purposes for each data type within the utility management system
- The system must require a unique identifier for data updates (e.g., customerID for consumer data)
- The system must allow users to select which fields to include in their data update
- The system must display only the fields which can be updated
- The system must support selection and updating of multiple fields
- The system must allow selective field updates without requiring all fields
- The system must require users to download the provided template before uploading data
- The system must include specific headers for the selected fields in templates
- The system must enforce data structure compliance through templates
- The system must prevent file upload unless the template file is downloaded
- The system must accept only CSV file format for data migration
- The system must follow the same process as normal data upload after file upload, excluding the System data mapping tab
- The system must allow users to select which columns should be included during data migration process
- The system must display System Data mapping screen only when system required data is not mapped while mapping columns
- The system must not show System Data mapping screen if required data is already mapped during field mapping
- The system must require mapping of each mandatory system data missing during upload process
- The system must show progress tracking with completion percentage of mapping tasks
- The system must allow users to map data by selecting from the tab section
- The system must display tabs according to non-mapped required data
- The system must provide search functionality across all columns using the search bar
- The system must provide filter functionality across all columns with unique column values
- The system must support multiselect filters with data appearing according to selections
- The system must allow users to update filtered data
- The system must allow users to select desired data and assign it to selected data rows
- The system must support selection of all data together or single data selection
- The system must tag assigned data with the data row once assignment is complete
- The system must show overall progress
- The system must require all data to be mapped before allowing user to proceed to next step
16. Enhancements in the latest release
1. Business Rules
General Rules
- The system must only accept CSV file format with maximum size of 20MB
- Migration names must be unique and descriptive for tracking purposes
- All mandatory fields specified for each data type must be present in the uploaded file
- File processing must complete within 30 seconds for files under 10MB
File Upload Rules
- The system must validate file format before processing begins
- Processing time must be displayed showing actual time taken (e.g., "9s")
- Row count must be accurately calculated and displayed (e.g., "4,092 rows processed")
- Column count must be automatically detected (e.g., "7 columns found")
- File size must be calculated and displayed in appropriate units (e.g., "0.04 MB")
Data Type Specific Rules
- Consumers: Must include Customer ID, Name, Address, Service Connection
- Consumer Meter Mapping: Must include Customer ID, Meter ID, Connection Date
- Payments: Must include Payment ID, Customer ID, Amount, Payment Date, Payment Method
- Complaints: Must include Complaint ID, Customer ID, Issue Type, Date Reported, Status
Column Mapping Rules
- Target fields marked as "Required" (red indicator) must be mapped to source columns
- Confidence levels must be calculated and displayed: High (Green), Medium (Yellow), Low (Red)
- Source column dropdowns must only show available columns from uploaded file
- Transformation column must default to "No Transformation" for all mappings
Transformation Rules
- No Transformation: Direct mapping with no data modification
- Split: Must specify delimiter and target fields for split operation
- Merge (Concat): Must specify source columns to merge and separator character
- Add Prefix: Must specify prefix text and application conditions
- Add Suffix: Must specify suffix text and application conditions
- Remove Substring: Must specify text to remove and match type
- Uppercase/Lowercase: Must specify application scope (entire text, first letter, etc.)
- Title Case: Must specify word separators and preservation rules
- Trim Whitespace: Must specify trim type (both sides, leading, trailing)
- Find & Replace: Must specify find text, replacement text, and match criteria
Template Management Rules
- Template names must be descriptive and unique within the system
- Templates must capture: Original filename, total mappings count, transformations count
- Usage tracking must increment each time template is applied
- Templates must be associated with specific data types for appropriate reuse
- Template creation date and creator must be tracked for audit purposes
Data Relation Mapping Rules
- Invalid relationships must be flagged and displayed in red (e.g., "Invalid Plan A")
- Valid relationships must be displayed in green (e.g., "Basic Plan", "Premium Plan")
- Bulk assignment functionality must allow selecting multiple records for same relationship
- Search functionality must enable quick location of specific records
- Filter capabilities must allow narrowing records by various criteria
Migration History Rules
- Total Migrations count must reflect all migration processes in the system
- Completed count must show successfully finished migration processes
- Total Records must sum all data records processed across all migrations
- Success Rate must be calculated as percentage of records successfully migrated
- Each migration record must track: Migration Name, Date, Data Category, Status, Total Records, Success Records, Error Records
- Status must accurately reflect: COMPLETED (green), IN PROGRESS (yellow), FAILED (red)
- Success and Error record counts must calculate percentages based on total records
Validation and Error Handling Rules
- High confidence mappings (95%+ confidence) can proceed automatically
- Medium confidence mappings (50-94% confidence) require user review
- Low confidence mappings (<50% confidence) must be manually verified
- Error records must be clearly identified with specific error descriptions
- Success records must be validated against system constraints before import
- All validation errors must provide actionable resolution steps
Progress Tracking Rules
- Overall Progress percentage must be calculated based on completed steps
- Step progress must be clearly indicated (e.g., "3 of 7" steps completed)
- Processing status must show real-time updates during file processing
- Success metrics must be displayed prominently (e.g., "92% (+6%)" completion rate)
Saved Templates Screen Business Rules
Template ID Field:
- Format: Must follow pattern "TPL-XXX" where XXX is a 3-digit sequential number
- Generation: System auto-generates in sequential order (TPL-001, TPL-002, TPL-003, etc.)
- Uniqueness: Must be unique across entire system
- Display: Always displayed in read-only format to users
Template Name Field:
- Length: Minimum 3 characters, maximum 100 characters
- Uniqueness: Must be unique within the same data type category
- Format: Alphanumeric characters, spaces, hyphens, and underscores allowed
- Examples: "Customer Data Import", "Meter Readings", "Payment Records"
- Validation: Cannot contain special characters except hyphens and underscores
Data Type Field:
- Values: Must match predefined system data types (Consumer, Meter Data, Payments, etc.)
- Display: Shows as colored tag/badge for visual categorization
- Validation: Must correspond to actual data categories available in the system
- Consistency: Must match the data type selected during template creation
Created By Field:
- Source: Automatically populated from current logged-in user
- Format: Display user's full name (First Name + Last Name)
- Examples: "John Admin", "Sarah Manager", "Mike Davis"
- Immutable: Cannot be changed after template creation
- Required: Always populated, never empty
Created On Field:
- Format: MM/DD/YYYY (e.g., "1/15/2025", "1/10/2025", "1/5/2025")
- Timezone: System timezone (typically utility's local timezone)
- Auto-population: Automatically set when template is saved
- Immutable: Cannot be modified after creation
- Sorting: Default sort should be by most recent creation date
Usage Field:
- Format: Number followed by "times" text (e.g., "12 times", "8 times", "15 times")
- Calculation: Increments by 1 each time template is successfully applied to a migration
- Initial Value: Starts at "1 times" for newly created templates
- Display: Right-aligned for better readability
- Tracking: Only counts successful applications, not failed attempts
Actions Column:
Table Behavior Rules:
- Pagination: Display standard number of templates per page with pagination controls
- Sorting: Allow sorting by Template ID, Name, Data Type, Created On, Usage
- Filtering: Provide filters for Data Type, Created By, Date Range
- Search: Global search across Template Name and Template ID
- Empty State: Show informative message when no templates exist
- Loading State: Show skeleton/loading animation during data retrieval
Category Tabs (Customer Management, Meter Management, etc.)
- Visual states and selection behavior
- Data type count validation and formatting
- Dynamic calculation requirements
- Display mandatory fields that are required for this data type
- Display the number of entries we have in the system for that specific data type
- On click upload navigate user to the next screen
Processing Statistics Display
Statistics Layout:
- Format: 4-column grid layout with equal spacing
- Alignment: Center-aligned numbers with labels below
- Typography: Large bold numbers with smaller descriptive labels
Rows Processed Statistic:
- Value: "4,092" with comma separator for thousands
- Label: "Rows Processed" in smaller gray text
- Color: Green text color indicating successful processing
- Format: Must use comma separators for numbers ≥1,000
Columns Found Statistic:
- Value: "7" as integer
- Label: "Columns Found" in smaller gray text
- Color: Green text color
- Validation: Must match actual column count detected in uploaded file
File Size Statistic:
- Value: "0.04 MB" with two decimal places
- Label: "File Size" in smaller gray text
- Color: Green text color
- Format: Display in MB with appropriate decimal precision
- Calculation: File size converted from bytes to MB (bytes ÷ 1,048,576)
Processing Time Statistic:
- Value: "9s"
- Label: "Processing Time" in smaller gray text
- Color: Green text color
- Format: Display seconds with "s" suffix
- Precision: Whole seconds for processing times under 60s
Data Preview Section
Section Header:
- Title: "Data Preview (First 5 Rows)"
- Purpose: Clearly indicates limited row display for verification
- Font: Bold header text to distinguish from data content
Preview Table Structure:
- Rows Displayed: Exactly 5 rows of data (excluding header)
- Headers: Must match column names from uploaded CSV file
- Styling: Standard table format with alternating row colors for readability
- Scrolling: Horizontal scroll if columns extend beyond container width
Table Column Data:
- Customer_ID Column: Format "CUST001", "CUST002", etc. - alphanumeric customer identifiers
- Name Column: Full names like "John Smith", "Jane Doe" - proper case formatting
- Address Column: Street addresses like "123 Main St", "456 Oak Ave" - standard address format
- Service_Connection Column: Service codes like "SC001", "SC002" - alphanumeric service identifiers
- Status Column: Status values like "Active", "Inactive", "Pending" - standardized status terms
Data Validation Display:
- Consistency: All displayed data must match exactly what was uploaded
- Format Preservation: Maintain original data formatting from CSV
- Error Indication: No error highlighting in preview (errors handled in later steps)
Navigation Controls
- Position: Bottom left of screen
- Icon: Left-pointing arrow
- Text: "Back"
- Style: Secondary button styling (outline or light background)
- Functionality: Returns to previous file upload step
- Position: Bottom right of screen
- Icon: Right-pointing arrow after text
- Text: "Next: Map Columns"
- Style: Primary blue button
- State: Enabled since file processing completed successfully
- Functionality: Proceeds to column mapping interface
Column Mapping & Transformations Screen Business Rules
Page Header Section
Section Title:
- Text: "Column Mapping & Transformations"
- Icon: Transformation/mapping icon (interconnected arrows or similar)
- Subtitle: "Map your source columns to target fields and configure data transformations"
- Font: Bold header with descriptive subtitle in smaller gray text
Mapping Table Structure
Target Field Column
Field Names:
- Display: System-defined target field names (Customer ID, First Name, Last Name, Email, Phone, Address, City, State, Zip Code)
- Format: Proper case with spaces for readability
- Required Indicator: Red "Required" badge for mandatory fields
- Validation: Target fields must match system schema definitions
Required Field Indicators:
- Customer ID: Shows red "Required" badge
- Visual: Red background badge with white text
- Position: Adjacent to field name
- Purpose: Clearly identifies fields that must be mapped for successful import
Transformation Column
Default State:
- Initial Value: "No..." (indicating "No Transformation")
- Dropdown Icon: Down arrow indicating expandable dropdown
- State: Enabled for all rows
Dropdown Options (when expanded):
- "No Transformation" (default, with checkmark)
- "Split"
- "Merge (Concat)"
- "Add Prefix"
- "Add Suffix"
- "Remove Substring"
- "Uppercase"
- "Lowercase"
- "Title Case"
- "Trim Whitespace"
- "Find & Replace"
Selected Transformation Display:
- Email row shows "Add Prefix" with gear/settings icon
- Format: Transformation name + configuration icon
- Click behavior: Opens transformation configuration popup
Source Column Dropdown
Column Options:
- Must populate from actual uploaded file columns
- Examples shown: "first_name", "last_name", "phone_number", "street_address", "city_name", "state_code", "postal_code"
- Format: Exact column names as they appear in CSV file
- Empty State: Blank dropdown for unmapped fields
- Validation: Only show columns that exist in uploaded file
Dropdown Behavior:
- Single selection per target field
- Disable column options already selected in other rows (to prevent duplicate mappings)
- Show column preview data on hover
Confidence Level Column
Confidence Scoring:
- High Confidence: Green background, "High Confidence" text, 95% score
- Medium Confidence: Yellow/amber background, "Medium Confidence" text, 75% score
- Low Confidence: Red background, "Low Confidence" text, 50% score
Confidence Calculation Rules:
- Based on AI matching algorithm between source and target field names
- High (90-100%): Exact or near-exact name matches
- Medium (60-89%): Partial matches or common patterns
- Low (0-59%): Poor matches or manual mappings
Visual Indicators:
- Color-coded backgrounds for immediate recognition
- Percentage values should be displayed for precision
- Icons optional but recommended for accessibility
File Data Column
Sample Data Display:
- Format: "Sample 1, Sample 2..." indicating multiple sample values
- Content: First few values from the source column
- Truncation: Use ellipsis (...) for longer content
- Purpose: Allows user to verify mapping accuracy
Transformed Data Column
Preview Content:
- Shows result of applied transformation on sample data
- Format: "Sample 1, Sample 2..." matching File Data format
- Real-time Updates: Must update when transformation changes
- No Transformation: Shows identical content to File Data column
Sample Data Column (rightmost)
Additional Samples:
- Extended sample data beyond first preview
- Format: "Sample 1,5" or similar truncated format
- Scrollable: Allow horizontal scroll if more samples needed
- Validation: Help users verify data quality
Transformation Popup Business Rules
No Transformation Popup
Content:
- Title: "No Transformation"
- Message: "Data will be copied directly without any modifications"
- Buttons: "Cancel" and "Apply"
- No additional configuration needed
Sample Data Display:
- Before: Shows original source data
- After: Shows identical data (no changes)
Split Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Delimiter: Text input field
- Placeholder: "Enter delimiter (e.g., comma, semicolon, space)"
- Examples: "," ";" "|" " " or custom string
- Validation: Cannot be empty
- Split into Target Fields: Multi-select dropdown
- Options: All available target fields
- Validation: Must select at least 2 target fields
- when selected split and selected multiple target filed columns and applied then display the same transformation rule for the other target fileds and do not let user access the those fields unless user changes the original one
Sample Data:
- Before: "John,Smith,Manager"
- After: Shows split result across selected fields
Merge (Concat) Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Columns to merge: Multi-select dropdown of available source columns
- Options: All mapped source columns
- Validation: Must select at least 2 columns
- Separator: Text input
- Examples: " " (space), "," "-" or custom string
- Option: "No separator" checkbox
- When selected, merge in the source column fields display multiple source columns selected
Sample Data:
- Before: Shows selected columns - "John" + "Smith"
- After: "John Smith" (with space separator)
Add Prefix Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Prefix text: Text input (required)
- Apply to: Radio buttons
- "All rows" (default)
- "Non-empty rows only"
- "Rows matching condition"
- Condition dropdown (if "Rows matching condition" selected):
- Contains text, Starts with, Ends with, Equals, Does not contain, Length greater than, Length less than, Matches pattern
- Value input: Text field for condition criteria
Sample Data:
- Before: "john.smith@email.com"
- After: "user_john.smith@email.com" (with "user_" prefix)
Add Suffix Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Suffix text: Text input (required)
- Apply to: Radio buttons (same as prefix)
- Condition options: Same as prefix transformation
Sample Data:
- Before: "john.smith@email.com"
- After: "john.smith@email.com_verified" (with "_verified" suffix)
Remove Substring Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Text to remove: Text input (required)
- Match type: Radio buttons
- "Exact match" (default)
- "Case-insensitive"
- "Regular expression"
Sample Data:
- Before: "Mr. John Smith"
- After: "John Smith" (removing "Mr. ")
Case Transformation Popups (Uppercase/Lowercase)
Uppercase Configuration:
- Apply to: Radio buttons ("Entire text", "First letter only", "First letter of each word")
- Handle special characters: Checkbox for preserving spaces/punctuation
Lowercase Configuration:
- Apply to: Radio buttons ("Entire text", "Keep first letter uppercase")
- Handle special characters: Checkbox
Title Case Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Word separators: Checkboxes (Space, Hyphen, Underscore, Custom)
- Custom separators: Text input (enabled if Custom checked)
- Preserve existing capitals: Checkbox for acronyms/abbreviations
Trim Whitespace Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Trim type: Radio buttons ("Both sides", "Leading only", "Trailing only")
- Also remove: Checkboxes ("Extra spaces between words", "Tabs", "Line breaks")
Find & Replace Transformation Popup
Configuration Fields:
- Find: Text input (required)
- Replace with: Text input (can be empty for removal)
- Match type: Radio buttons ("Exact match", "Case-insensitive", "Regular expression", "Whole words only")
- Replace: Radio buttons ("First occurrence", "All occurrences")
- Preview: Show before/after examples with highlighting
Sample Data:
- Before: "John Smith III"
- After: "John Smith Jr." (replacing "III" with "Jr.")
Field Categorization
Identifiers (IDs, Codes)
consumer_nometer_numberdevice_no
Names / Text
first_namelast_namemeter_makeutility_serviceremarks
email
Phone
contact_numberalternate_contact_number
Address
streetaddress_linebilling_premiseservice_premisepremiseunitzipcodefloorfloor_unit
Dates
connect_datecurrent_reading_dateinstalled_on
Numeric / Balance
opening_balancecurrent_readinglonglatreading_oem
Status / Category
ownershipPlanCategorySub CategoryStatuscategory(meter)sub_category(meter)meter_type
Field Categorization Asset Management
Identifiers (IDs, Codes)
Facility IDSystem/Network IDSerial NumberAsset ID
Names / Text
Asset Name/DescriptionFacility NameSystem NameNetwork NameAsset ClassAsset TypeSystem Type NameNetwork TypeFacility TypeLocationManufacturerNetwork OperatorFacility ManagerService Zone/DivisionDescription/PurposeDescription/NotesParameter NameParameter DescriptionDimension
- Emails in Facilities, systems and networks
Phone
- (None in asset data)
Address
Address/Site Label(facilities/systems/networks/Assets)Location(asset location within facility)
Dates
Installation Year(convert to date)Commissioned DateCommissioned/Planned Date
Numeric / Balance
Useful LifeInstallation CostReplacement CostCurrent ValueLatitudeLongitudeDesign Capacity (MLD)Annual O&M BudgetDesign CapacityCurrent Throughput
Status / Category
Status(assets)Operating StatusOperational StatusDepreciation MethodOperational HoursBackup StatusDesign Capacity UnitCurrent Throughput UnitUnitUnit of Measurement
Asset Relation Tabs
Facility Assignment Tab
Primary Columns:
Asset Name/Description- Asset identifierFacility ID- The facility being validated/assignedLocation- Physical location within facilityAsset Class- For facility compatibility checkingAsset Type- For facility type appropriatenessInstallation Year- For facility timeline contextStatus- Current operational status
Why these columns: Users need to verify that assets belong to the correct facilities and that the asset type is appropriate for that facility's purpose.
System/Network Assignment Tab
Primary Columns:
Asset Name/Description- Asset identifierSystem/Network ID- The system being validated/assignedFacility ID- Parent facility contextAsset Class- System compatibility verificationAsset Type- System-asset type matchingStatus- Operational alignment checking
Why these columns: System assignments must be logical within the facility hierarchy, and asset types must be compatible with system types.
Asset Class Tab
Primary Columns:
Asset Name/Description- Asset identifierAsset Class- The class being validated/assignedAsset Type- Must be compatible with selected classManufacturer- Class-manufacturer relationship contextInstallation Year- Historical classification contextUseful Life- Class-based life expectancy validation
Why these columns: Asset class and type must be compatible combinations, and manufacturer/age context helps validate appropriate classifications.
Asset Type Tab
Primary Columns:
Asset Name/Description- Asset identifierAsset Type- The type being validated/assignedAsset Class- Parent classification for compatibilityManufacturer- Type-manufacturer compatibilitySerial Number- Type-specific identificationInstallation Cost- Type-cost relationship validation
Why these columns: Asset type must align with asset class, and manufacturer/cost information helps validate type assignments.
Status Tab
Primary Columns:
Asset Name/Description- Asset identifierStatus- The status being validated/assignedInstallation Year- Age context for status appropriatenessUseful Life- Life expectancy vs current statusDepreciation Method- Status impact on depreciationReplacement Cost- Status-value relationship
Why these columns: Asset status should align with age, depreciation, and replacement planning considerations.
Manufacturer Tab
Primary Columns:
Asset Name/Description- Asset identifierManufacturer- The manufacturer being validated/assignedAsset Type- Manufacturer-type compatibilitySerial Number- Manufacturer's serial number format validationInstallation Year- Manufacturer's operational periodInstallation Cost- Manufacturer-cost relationship
Why these columns: Manufacturer assignments must be compatible with asset types, and serial numbers should follow manufacturer-specific formats.
Facility Relation Tabs
Facility Type Tab
Primary Columns:
Facility Name- Facility identifierFacility Type- The type being validated/assigned (Treatment Plant, Pumping Station, Storage, Distribution)Design Capacity (MLD)- Capacity alignment with facility typeOperating Status- Type-status compatibilityCommissioned Date- Type evolution contextService Zone/Division- Type-service area appropriateness
Why these columns: Facility type must align with capacity, operational status, and service purpose. Different types have different capacity expectations and service roles.
Operating Status Tab
Primary Columns:
Facility Name- Facility identifierOperating Status- The status being validated/assigned (Active, Inactive, Under Construction, Decommissioned)Commissioned Date- Status-timeline validationDesign Useful Life- Status vs. expected lifespanAnnual O&M Budget- Budget alignment with operational statusFacility Manager- Management assignment for operational facilities
Why these columns: Operating status must be logical given the facility's age, budget allocation, and management assignment. Active facilities should have managers and budgets.
Operational Hours Tab
Primary Columns:
Facility Name- Facility identifierOperational Hours- Hours being validated/assigned (24/7, Business Hours, Custom)Facility Type- Type-hours compatibilityDesign Capacity (MLD)- Capacity utilization vs. hoursService Zone/Division- Service demand vs. operational scheduleOperating Status- Status-hours alignment
Why these columns: Operational hours must match facility type requirements, service demands, and current operational status.
Service Zone/Division Tab
Primary Columns:
Facility Name- Facility identifierService Zone/Division- The zone being validated/assignedFacility Type- Type-service zone compatibilityAddress/Site Label- Geographic context for zone assignmentDesign Capacity (MLD)- Capacity vs. zone size/demandOperating Status- Zone service capability
Why these columns: Service zones must be geographically logical, match facility capacity, and align with facility type and operational capability.
Facility Manager Tab
Primary Columns:
Facility Name- Facility identifierFacility Manager- The manager being validated/assignedOperating Status- Management requirement based on statusFacility Type- Manager expertise alignmentAnnual O&M Budget- Budget management responsibilityDesign Capacity (MLD)- Facility complexity for management assignment
Why these columns: Facility managers should be assigned based on operational status, facility complexity, and budget responsibility requirements.
System Data Relation Tabs
Based on the Systems data fields, here are the relation tabs and their required columns:
Facility Assignment Tab
Primary Columns:
System Name- System identifierFacility ID- The facility being validated/assignedSystem Type- System-facility type compatibilityAddress/Site Label- Geographic alignment with facilityStatus- System status vs facility operational statusDesign Capacity- Capacity alignment with facility capacity
Why these columns: Systems must belong to appropriate facilities, and system types should be compatible with facility types. Geographic and capacity alignment ensures logical facility-system relationships.
System Type Tab
Primary Columns:
System Name- System identifierSystem Type- The type being validated/assignedDesign Capacity- Type-capacity compatibilityCurrent Throughput- Performance alignment with typeCommissioned/Planned Date- Type evolution timelineDescription/Purpose- Type-purpose alignment
Why these columns: System type must align with design capacity, actual performance, and stated purpose. Timeline context helps validate type assignments.
Status Tab
Primary Columns:
System Name- System identifierStatus- The status being validated/assigned (Active, Inactive, Under Construction, Maintenance)Commissioned/Planned Date- Status-timeline validationCurrent Throughput- Performance vs status alignmentOperational Hours- Status-hours compatibilityBackup Status- Status impact on backup requirements
Why these columns: System status must be consistent with commissioning timeline, performance levels, operational schedules, and backup availability.
Backup Status Tab
Primary Columns:
System Name- System identifierBackup Status- The backup status being validated/assigned (Available, Not Available, Partial)System Type- Critical systems require backupStatus- Operational status affects backup needsDesign Capacity- High capacity systems need backupCurrent Throughput- Performance criticality assessment
Why these columns: Backup requirements depend on system criticality (type), operational status, and capacity/throughput levels. Critical systems need backup coverage.
Operational Hours Tab
Primary Columns:
System Name- System identifierOperational Hours- Hours being validated/assigned (24/7, Business Hours, Custom)System Type- Type-hours requirementsStatus- Status-hours alignmentCurrent Throughput- Demand-hours relationshipBackup Status- Hours impact on backup needs
Why these columns: Operational hours must match system type requirements, current status, and performance demands. Backup needs vary with operational schedules.
Network Data Relation Tabs
Facility Assignment Tab
Primary Columns:
Network Name- Network identifierFacility ID- The facility being validated/assignedNetwork Type- Network-facility type compatibilityDesign Capacity- Capacity alignment with facility capacityOperational Status- Network status vs facility operational statusDescription/Notes- Context for facility assignment
Why these columns: Networks must be assigned to appropriate facilities where the network type makes sense for the facility's purpose and capacity requirements.
Network Type Tab
Primary Columns:
Network Name- Network identifierNetwork Type- The type being validated/assigned (Distribution, Transmission, Collection, Communication)Design Capacity- Type-capacity relationship validationFacility ID- Facility context for type appropriatenessNetwork Operator- Operator expertise for network typeBackup Status- Type-specific backup requirements
Why these columns: Network type must align with facility purpose, capacity requirements, and operator capabilities. Different types have different backup and operational requirements.
Operational Status Tab
Primary Columns:
Network Name- Network identifierOperational Status- The status being validated/assigned (Active, Inactive, Under Construction, Maintenance)Network Operator- Status-operator assignment relationshipBackup Status- Status impact on backup requirementsDesign Capacity- Performance expectations vs statusNetwork Type- Critical network types vs status
Why these columns: Operational status must be consistent with operator assignment, backup availability, and performance expectations based on network criticality.
Backup Status Tab
Primary Columns:
Network Name- Network identifierBackup Status- The backup status being validated/assigned (Available, Not Available, Partial)Network Type- Type-specific backup criticalityOperational Status- Status-backup requirement alignmentDesign Capacity- High capacity networks need backupNetwork Operator- Operator backup management capability
Why these columns: Backup requirements vary by network type criticality, operational status, and capacity. Critical networks (transmission, communication) typically require backup coverage.
Network Operator Tab
Primary Columns:
Network Name- Network identifierNetwork Operator- The operator being validated/assignedNetwork Type- Operator expertise alignmentOperational Status- Operator assignment for operational networksDesign Capacity- Operator capability vs network complexityFacility ID- Geographic/organizational operator assignment
Why these columns: Network operators should have appropriate expertise for the network type and capacity, and should be assigned based on operational status and geographic location.
Business Rules for Transformation Restrictions
No Transformation
- Allowed for all field types
- Rule: Default option available for every field, regardless of data type
Split
- Allowed: Names/Text, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Email, Phone, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Only allow splitting for fields where logical subdivision makes sense (e.g., full names, combined addresses, compound status values)
Merge (Concat)
- Allowed: Names/Text only
- Not Allowed: All other types
- Rule: Only allow merging text fields like first_name + last_name; prevent merging IDs, numbers, or structured data
Add Prefix
- Allowed: Names/Text, Phone, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Email, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Allow prefixes for descriptive fields but protect unique identifiers and structured data integrity
Add Suffix
- Allowed: Names/Text, Phone, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Email, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Similar to prefix - allow for descriptive enhancement but protect critical data structures
Remove Substring
- Allowed: Names/Text, Email, Phone, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Allow cleanup of text fields but prevent modification of IDs and precise numeric/date values
Uppercase
- Allowed: Names/Text, Email, Phone, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Standardization allowed for text fields but not for case-sensitive IDs or numeric data
Lowercase
- Allowed: Names/Text, Email, Phone, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Same as uppercase - text standardization only
Title Case
- Allowed: Names/Text, Address only
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Email, Phone, Dates, Numeric/Balance, Status/Category
- Rule: Only for proper nouns and addresses where title case is appropriate; not for technical fields
Trim Whitespace
- Allowed for all field types
- Rule: Data cleanup allowed universally as it doesn't alter content meaning
Find & Replace
- Allowed: Names/Text, Email, Phone, Address, Status/Category
- Not Allowed: Identifiers, Dates, Numeric/Balance
- Rule: Allow pattern replacement in descriptive fields but protect unique identifiers and precise numeric values from corruption
Navigation and Action Buttons
Progress Scroll Bar
Visual Indicator:
- Horizontal scroll bar showing progress through mapping table
- Position: Below main table content
- Behavior: Updates as user scrolls through columns
Back Button
Properties:
- Position: Bottom left
- Icon: Left arrow
- Text: "Back"
- Style: Secondary button (outline or gray)
- Action: Returns to previous step (file upload)
Save as Template Button
Properties:
- Position: Bottom center-right
- Icon: Save/template icon
- Text: "Save as Template"
- Style: Secondary button with icon
- Action: Opens template saving popup
- State: Enabled when valid mappings exist
Data Relation Mapping Button
Properties:
- Position: Bottom right
- Icon: Right arrow or relation icon
- Text: "Data Relation Mapping"
- Style: Primary blue button
- Action: Proceeds to next step
- State: Enabled when all required fields are mapped
Save Template Popup Business Rules
Template Name Field
Input Properties:
- Label: "Template Name"
- Placeholder: "Enter a descriptive name for this template"
- Validation: 3-100 characters, unique name required
- Required: Cannot be empty
Source File Information Section
Display Fields:
- Original File: Shows uploaded filename (e.g., "fortworth_rfp_gap_analysis.csv")
- Total Mappings: Shows count of mapped fields (e.g., "9 fields mapped")
- Transformations: Shows count of applied transformations (e.g., "1 applied")
- Format: Read-only informational display
Mapping Configuration Summary
Scrollable List Display:
- Format: "source_column → Target Field" with confidence percentage
- Examples: "cust_id → Customer ID 95% confidence"
- Transformation Indicator: Purple "add_prefix" tag for transformed fields
- Confidence Color Coding: Green (95%), Yellow (75%), Red (50%)
- Scroll Behavior: Vertical scroll for long lists
Template Benefits Section
Information Display:
- Background: Light blue informational background
- Bullet Points:
- "Reuse this configuration for files with similar column structures"
- "Save time by automatically applying proven mappings and transformations"
- "Ensure consistency across multiple data imports"
- "Reduce errors by using tested mapping configurations"
Template Action Buttons
- Style: Secondary/outline button
- Position: Bottom right, before Save
- Action: Closes popup without saving
- Style: Primary blue button
- Position: Bottom right
- Icon: Save icon
- Action: Saves template and closes popup
- Validation: Requires valid template name
Data Relation Mapping Screen Business Rules
Source Data Section Header
Section Title:
- Text: "Source Data"
- Font: Bold, larger heading text
- Position: Top of main content area
Section Description:
- Text: "Map your source columns to target relationships and configure data connections"
- Font: Smaller gray descriptive text below title
- Purpose: Explains the function of this step
Action Buttons (Top Right)
- Position: Top right, left of Save Template
- Style: Secondary/outline button
- Text: "Clear All"
- Function: Resets all relationship mappings and selections
- Confirmation: Should prompt user before clearing all data
Column Headers For Customer Data Type
Plan Column:
- Header Text: "Plan"
- Purpose: Shows plan assignments for each customer record
- Sort: Should allow sorting by plan type
Category Column:
- Header Text: "Category"
- Purpose: Shows data categorization
- Display: Currently empty in sample data
Sub Category Column:
- Header Text: "Sub Category"
- Purpose: Shows sub-categorization
- Display: Currently empty in sample data
Status Column:
- Header Text: "Status"
- Purpose: Shows record processing status
- Display: Currently empty in sample data
Invalid Records Warning
Warning Message:
- Text: "2 out of 4 rows have invalid plan details"
- Color: Red text indicating errors/issues
- Position: Above the plan assignment dropdown
- Format: "{count} out of {total} rows have invalid {field} details"
- Purpose: Alerts user to data quality issues requiring attention
Select Plan Values Dropdown:
- Position: Right of warning message
- Text: "Select Plan Values"
- Function: Bulk assignment dropdown for plan values
- Options: Should populate with valid plan options from system
- State: Enabled when records are selected
Search and Filter Controls
Search Field:
- Placeholder: "Search records..."
- Icon: Search/magnifying glass icon
- Position: Left side of filter bar
- Function: Text search across all visible columns
- Behavior: Real-time search as user types
- Text: "Filters"
- Icon: Filter icon
- Style: Secondary button with icon
- Function: Opens advanced filtering options
- Purpose: Allow filtering by specific criteria
Assign to Selected Button:
- Text: "Assign to Selected (0)"
- Background: Blue (primary action color)
- State: Shows count of selected records
- Format: "Assign to Selected ({count})"
- Function: Applies selected plan to checked records
- State: Disabled when no records selected
Bulk Assignment Dropdown:
- Position: Right side of action bar
- Default Text: "Bulk Assignment"
- Function: Select assignment action for multiple records
- Options: Various bulk actions for selected records
Data Table Structure
Selection Column (Checkboxes)
Checkbox Behavior:
- Position: First column, left-most
- Function: Multi-select rows for bulk operations
- Header Checkbox: Select/deselect all visible rows
- Individual Checkboxes: Select specific rows
- State Tracking: Update "Assign to Selected" count dynamically
Consumer No Column
Data Format:
- Pattern: "CON001", "CON002", "CON003", "CON004"
- Format: Alphanumeric consumer identifier
- Sort: Should allow alphanumeric sorting
- Link: Should be clickable to view consumer details
First Name Column
Data Display:
- Examples: "John", "Jane", "Bob", "Alice"
- Format: Proper case names
- Validation: Must be non-empty for valid records
- Edit: Should allow inline editing if permissions allow
Last Name Column
Data Display:
- Examples: "Doe", "Smith", "Johnson", "Williams"
- Format: Proper case surnames
- Validation: Must be non-empty for valid records
- Edit: Should allow inline editing if permissions allow
Billing Premise Column
Data Display:
- Examples: "Main Street", "Oak Avenue", "Pine Road", "Elm Street"
- Format: Street address or location identifier
- Purpose: Identifies billing location for customer
- Validation: Must match valid premise addresses in system
Service Premise Column
Data Display:
- Examples: "Main Street", "Oak Avenue", "Pine Road", "Elm Street"
- Format: Street address or location identifier
- Purpose: Identifies service delivery location
- Note: Often matches Billing Premise but can differ
Plan Column (Critical Field)
Valid Plan Display:
- Examples: "Basic Plan", "Premium Plan"
- Color: Green text indicating valid relationship
- Background: Light green or normal background
- Format: Plan names must match system-defined plans
Invalid Plan Display:
- Examples: "Invalid Plan A", "Invalid Plan B"
- Color: Red text indicating validation error
- Background: Light red or error highlighting
- Format: Shows original imported value with "Invalid" prefix
- Validation: Must be resolved before proceeding
Plan Validation Rules
Valid Plan Criteria:
- Must exist in system's plan master data
- Must be active and available for assignment
- Must match exactly (case-sensitive or normalized)
- Must be compatible with customer type/category
Invalid Plan Handling:
- Display original value with error indication
- Provide dropdown of valid plan options for correction
- Block progression until all invalid relationships resolved
- Show count of invalid records prominently
Plan Assignment Options:
- Dropdown should populate with all active system plans
- Options should be filtered based on customer eligibility
- Should allow bulk assignment to multiple selected records
- Should validate assignments before applying
Navigation Controls
Back to Column Mapping Button:
- Position: Bottom left
- Icon: Left arrow
- Text: "Back to Column Mapping"
- Style: Secondary button
- Function: Returns to previous mapping step
- Behavior: Should preserve current relationship data
Continue to Validation Button:
- Position: Bottom right
- Icon: Right arrow or checkmark
- Text: "Continue to Validation"
- Style: Primary blue button
- State: Disabled if invalid relationships exist
- Function: Proceeds to final validation step
- Validation: Must ensure all required relationships are valid
Data Quality Requirements
Relationship Validation:
- All plan assignments must reference valid system plans
- Customer-premise relationships must be logically valid
- Any required relationship fields must be populated
- Foreign key constraints must be satisfied
Error Prevention:
- Provide real-time validation feedback
- Show available options in dropdowns
- Highlight conflicts immediately
- Prevent progression with unresolved errors
Bulk Operations:
- Support multi-select for efficient data management
- Provide bulk assignment capabilities
- Allow bulk validation and correction
- Enable bulk clear/reset operations
Progress Tracking
Validation Status:
- Track percentage of valid vs invalid relationships
- Show progress toward completion requirements
- Update counts in real-time as corrections are made
- Provide clear indication when ready to proceed
Error Resolution Tracking:
- Count invalid relationships by type
- Track resolution progress
- Highlight priority issues requiring attention
- Show completion criteria clearly
Consumer Template Changes
- Remove
- Ownership
- Approved Date
- Activate Date
- Payment Received
Data Relation Tabs for Meter Data Type
Utility Service Tab
Primary Columns:
meter_number- Unique identifier for trackingutility_service- The service being validated/assignedpremise- Location context for service validationcategory- Service category for groupingsub_category- More specific service classificationcurrent_reading_date- Shows meter activity/status
Why these columns: Users need to see the meter identifier, current service assignment, location, and service categories to make informed utility service relationship decisions.
Meter Type Tab
Primary Columns:
meter_number- Unique identifiermeter_type- The type being validated/assignedutility_service- Service context (different services may require different meter types)current_reading- Indicates if meter is functionalinstalled_on- Installation date for type validationpremise- Location for compatibility checking
Why these columns: Meter type decisions depend on the service type, installation date, and current functionality. Location helps verify compatibility with service requirements.
Meter Make Tab
Primary Columns:
meter_number- Unique identifiermeter_make- The make being validated/assignedmeter_type- Make must be compatible with typedevice_no- Device-specific identifier from manufacturerinstalled_on- Age/vintage informationcurrent_reading_date- Shows if device is operational
Why these columns: Meter make validation requires seeing the relationship between manufacturer, device number, meter type compatibility, and operational status.
2. Sample Data
Before Transformation (Source File):
- customer_id,first_name,last_name,email_address,phone_number,street_address,city_name,state_code,postal_code
- CUST001,John,Smith,john.smith@email.com,555-0123,123 Main St,Springfield,IL,62701
- CUST002,Jane,Doe,jane.doe@email.com,555-0456,456 Oak Ave,Springfield,IL,62702
- CUST003,Bob,Johnson,bob.johnson@email.com,555-0789,789 Pine Rd,Springfield,IL,62703
After Transformation (Target System Format):
- Customer ID: CUST001
- First Name: John
- Last Name: Smith
- Email: john.smith@email.com
- Phone: 555-0123
- Address: 123 Main St
- City: Springfield
- State: IL
- Zip Code: 62701
Template Configuration Sample:
- Template: Customer Data Import
- Source File: customer_data.csv
- Mappings: 9 fields mapped
- Transformations: 1 applied (Email prefix transformation)
- Confidence Levels: 95% Customer ID, 95% First Name, 95% Last Name, 75% Email (with transformation)
3. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must support CSV file uploads up to 20MB in size
- The system must process uploaded files and display row count, column count, file size, and processing time
- The system must provide data preview showing first 5 rows of uploaded data
- The system must automatically suggest field mappings with confidence scores (High/Medium/Low)
- The system must require mapping of all mandatory fields before proceeding
- The system must provide transformation options: No Transformation, Split, Merge, Add Prefix, Add Suffix, Remove Substring, Uppercase, Lowercase, Title Case, Trim Whitespace, Find & Replace
- The system must show real-time preview of transformed data in the "Sample Data" column
- The system must allow saving mapping configurations as reusable templates
- The system must display template information including name, data type, creator, creation date, and usage count
- The system must track migration history with name, date, data category, status, total records, success records, and error records
- The system must calculate and display success rates as percentages
- The system must provide "View Data" action for each completed migration
- The system must validate data relationships and flag invalid connections in red
- The system must enable bulk assignment of relationships to multiple selected records
- The system must provide search and filter capabilities in data relation mapping
- The system must display overall progress percentage throughout the migration process
- The system must show step progression (e.g., "3 of 7" steps completed)
- The system must provide help links for exporting CSV files from Excel
- The system must display mandatory field warnings with specific field requirements
- The system must enable cancellation at any step with confirmation prompts