Meter Device Management (MX01US02)
Meter Lifecycle Management User Story Document
1. Problem Statement
Meter Supervisor/Device Manager
- Manual tracking of meter assets leads to inconsistent and incomplete records
- Difficulty monitoring meter performance and identifying issues before they escalate
- Lack of visibility into meter history makes maintenance planning reactive rather than proactive
- Challenge coordinating meter replacements and work orders efficiently
- Limited tools for tracking technical specifications and maintenance history
- Inefficient inventory management of available and deployed meters
- No centralized system for tracking meter consumer allocation history
Core Problem: The utility lacks a centralized, comprehensive meter lifecycle management system that tracks devices from installation through maintenance to replacement, resulting in operational inefficiencies, increased costs, and potential service disruptions.
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
Meter Supervisor/Device Manager: Responsible for managing the utility's meter inventory, specifications, and lifecycle. Oversees meter testing, calibration, and certification processes. Manages meter inventory, replacement programs, and asset maintenance. Ensures regulatory compliance for meter accuracy and performance.
Users who should have access to this feature: The Meter Supervisor/Device Manager role is the primary user, with system administrators having oversight access for configuration and support.
3. Jobs To Be Done
For Meter Supervisor: When I need to track the entire meter inventory in our system, But I lack visibility into meter statuses, locations, and technical specifications, Help me access a centralized inventory management system with detailed meter data, So that I can make informed decisions about procurement, maintenance, and replacement.
For Meter Supervisor: When I need to plan meter replacements, But I don't have clear data on meter age, performance history, and maintenance records, Help me view comprehensive lifecycle data for each meter, So that I can prioritize replacements and optimize asset management.
For Meter Supervisor: When I need to create service orders for meter maintenance, But I struggle with tracking work order status and completion, Help me manage the full work order lifecycle with status updates and documentation, So that I can ensure timely completion of critical maintenance activities.
For Meter Supervisor: When I need to manage meter allocation to consumers, But I struggle with maintaining accurate records of historical assignments and transfers, Help me access a complete allocation history with timestamps and customer details, So that I can ensure accurate billing and resolve customer inquiries.
For Meter Supervisor: When I need to maintain technical compliance of our meter assets, But I lack organized documentation of specifications and certifications, Help me store and retrieve detailed technical data for each meter type, So that I can demonstrate regulatory compliance and make informed procurement decisions.
4. Solution
The Meter Lifecycle Management solution provides a comprehensive platform for tracking, managing, and optimizing utility meters throughout their lifecycle. The solution addresses the identified pain points through these key capabilities:
Meter Inventory Management
- Centralized Meter Registry: All meters tracked in a central database with unique identifiers and searchable attributes
- Status Tracking: Visual indicators for active, maintenance, retired, and unassigned meters
- Batch Operations: Ability to add and manage meters in bulk for efficiency
Individual Meter Tracking
- Detailed Meter Profiles: Comprehensive information page for each meter showing specifications, history, and current status
- Technical Specifications Library: Detailed technical information including certifications, accuracy class, and physical characteristics
- Meter Type Classification: Clear categorization by meter type (manual, photo, smart) with specific attributes for each
Consumer and Location Management
- Premise Allocation: Track where meters are physically installed with address and geolocation data
- Consumer History: Historical record of all consumers assigned to a particular meter
- Allocation Tracking: Clear visibility of meter reassignments and transfers between premises or consumers
Work Order Management
- Service Order Creation: Ability to create and track different types of meter-related work orders
- Maintenance Scheduling: Plan and schedule regular maintenance activities
- Service History: Track all activities performed on meters from installation through replacement
Consumer Usage Tracking
- Consumption History: Basic log of consumption data for reference
- Historical Data Access: Ability to access past consumption for context
- Consumer History: Track previous customers associated with each meter
Maintenance and Lifecycle Tracking
- Maintenance Records: Document all maintenance activities performed on each meter
- Lifecycle Events: Track key events like installation, calibration, and service activities
- Alert Management: Automated alerts for meters requiring attention based on age, readings, or maintenance schedule
Reporting and Analytics
- Meter Performance Metrics: Track key statistics like days in service and reading quality
- Consumption Reporting: Analyze consumption patterns and trends
- Export Capabilities: Extract data for further analysis and reporting
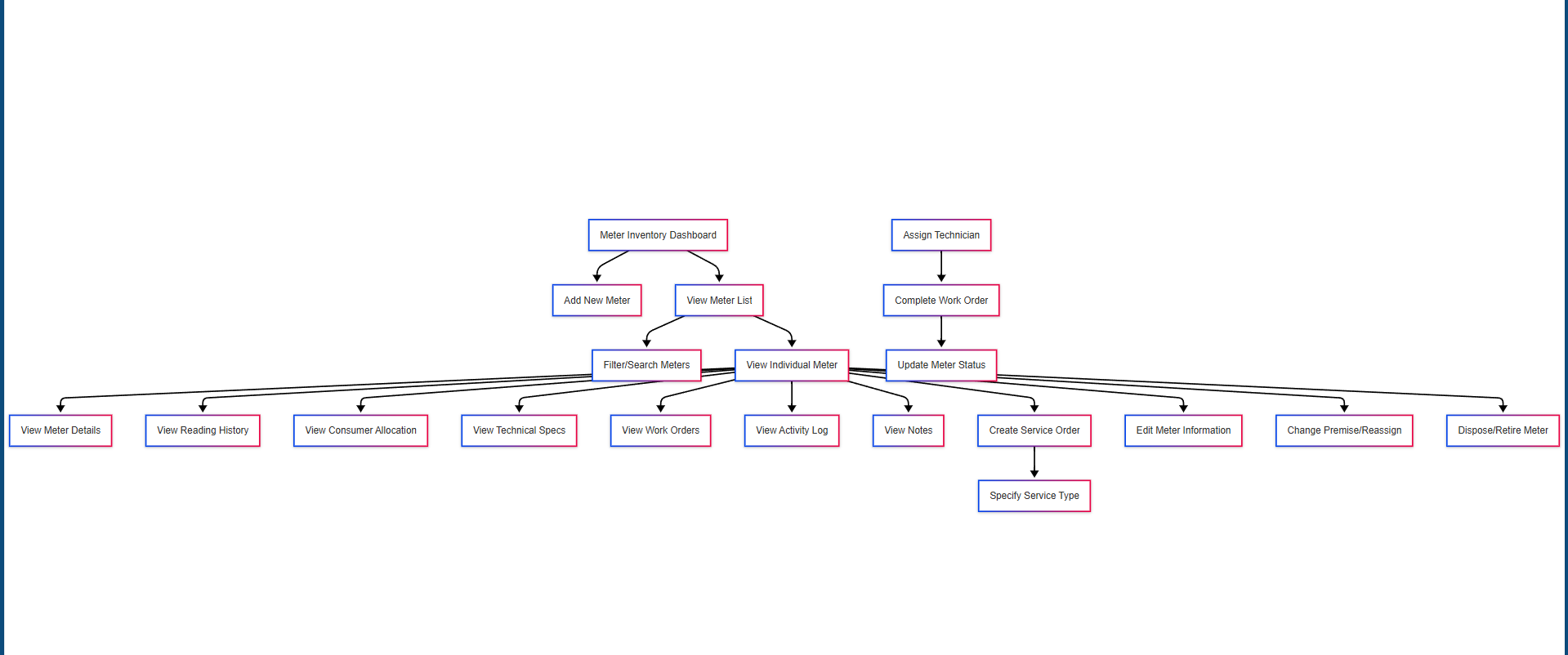
5. Major Steps Involved
For Meter Supervisor
- Access Meter Inventory
- Navigate to the "Meters" section from the main navigation
- View summary metrics of total meters, assigned meters, unassigned meters, under maintenance, and retired meters
- Filter meters by type (Manual, Photo, Smart) using the toggle filters
- Search for specific meters using the search bar
- Add New Meters
- Click "Add Meter" button from the meters list view
- Meter Status (Physical, Assignment, Reading)
- Enter Device Number, Utility Service, Meter Type, Category, and Sub-Category
- Specify installation location details including Premise, Floor, Location
- Add geolocation data (Latitude/Longitude) if available
- Set Installation Date
- Assign to Consumer (optional at this stage)
- Record First Reading if applicable
- Enter Manufacturer Details
- Click "Add Meter" to save or "Add & Next" to continue adding meters
- View Meter Details
- Click on a meter from the list to access its detailed profile
- Review Key Stats (Days in service, Installation date, Alerts, Last maintenance)
- Check Technical Specifications (Basic Info and Technical tabs)
- View Consumer allocation history and premise details
- Monitor reading history and consumption patterns
- Review maintenance and work order history
- Access activity log showing all actions performed on the meter
- Manage Meter Lifecycle
- Identify meters requiring service based on alerts or age
- Click "Service Order" to create maintenance, calibration, or replacement work orders
- Specify Service Type, Replacement Meter (if applicable), Schedule Date, and Reason
- Track work order status and completion through the Work tab
- Update meter status appropriately (Active, Maintenance, Retired)
Additional Meter Supervisor Steps
- Review Consumer Allocation History
- Access the "Allocation" tab for specific meters
- View current and historical consumer assignments
- Check consumer details including account numbers and contact information
- Track premise history and location details for the meter
- Access Technical Documentation
- Navigate to the "Details" tab for technical specifications
- Review certification status and compliance information
- Check physical specifications for replacement planning
- Verify manufacturer details and model information for procurement
- Monitor Meter Status Changes
- Track meter status transitions through the lifecycle
- Document reason codes for status changes
- Maintain history of all status modifications
- Generate reports on meter status distribution across inventory
6. Flow Diagram
7. Business Rules
General Meter Management Rules
- Each meter must have a unique identifier in the system
- Meters must always have one of the following statuses: Active, Maintenance, Inactive, Retired
- A meter can only be assigned to one consumer and one premise at a time
- Historical consumer and premise allocations must be preserved when a meter is reassigned
- Meter installation date must be recorded and cannot be after the current date
- Meters cannot be permanently deleted from the system, only marked as retired or disposed
- All changes to meter data must be logged with timestamp and user information
- Alert thresholds for meter age and maintenance schedules must be configurable by administrators
- Meter type (Manual, Photo, Smart) must be specified and cannot be changed after creation
- Technical specifications must be recorded for each meter including accuracy class and certification details
Meter Data Management Rules
- Technical specifications must be standardized by meter type and manufacturer
- Historical installation and maintenance data must be preserved for the life of the meter
- Meter status changes must be documented with reason codes and timestamps
- Photographic evidence should be stored for physical meters when available
- Meter records must include certification information and expiration dates
- Technical specifications cannot be modified after initial entry without management approval
- Manufacturer and model information must be selected from pre-approved lists
- Unique serial numbers must be validated at entry to prevent duplication
- Installation dates must be recorded accurately and cannot be after the current date
- Meter location data must follow standardized format and include option for GPS coordinates
Work Order Rules
- All physical changes to a meter require a corresponding work order
- Work orders must include service type, scheduled date, and reason
- Work orders must have one of the following statuses: Pending, In Progress, Completed, Cancelled
- Completed work orders must include completion date and technician information
- Replacement meters must be selected from available inventory before work order creation
- Meter status must be updated automatically based on work order completion
- Calibration work orders must record pre and post calibration readings
- Maintenance records must be associated directly with the meter they apply to
- Work order history must be preserved for the life of the meter
- Standard service types must be predefined in the system (Maintenance, Calibration, Replacement, Investigation)
Consumer and Premise Rules
- A premise can have multiple meters but each meter can only be at one premise
- Consumer reassignment must preserve the historical consumption data for billing purposes
- When a meter is reassigned, a final reading must be recorded for the previous consumer
- Premise location data should include standardized address format plus optional geolocation
- Meter routes and reading cycles must be consistent with geographical organization
- Any change to consumer assignment must be documented with reason and authorization
- Consumer information must include account number and contact details
- Commercial/residential classification must be maintained for each consumer
Error Handling Rules
- Validation failures must provide clear error messages indicating the specific issue
- Critical operations (disposal, reassignment) require confirmation before proceeding
- Duplicate meter numbers must be prevented at the time of entry
- Date inconsistencies (maintenance date before installation) must be flagged
- Invalid meter status transitions must be prevented (e.g., cannot go from Retired to Active)
- Technical specification inconsistencies must be flagged during data entry
- Work orders cannot be completed without all required fields
- Alert notifications must be persistent until acknowledged by an authorized user
- Meters with active alerts cannot be disposed without explicit override authorization
- System must prevent creation of work orders for already retired meters
8. Sample Data
Meter Data
Serial: WM-23456
Type: PHOTO
Status: ACTIVE
Location: 456 Oak Ave, Somewhere
Installed: 2022-05-22
Read Type: Photo Meter
Consumer: Sarah Johnson
Route: S05-DMA01-V-MANASE-B1
Read Cycle: R06-DMA01-V-LEPATechnical Specifications
Manufacturer: HydroTech
Model: PhotoRead 200
Material: Composite
Connection Size: 3/4 inch
Dimensions: 180 × 110 × 160 mm
Weight: 0.9 kg
Dial Length: 95mm
Dial Count: 6
Max Flow Rate: 15 m³/h
Accuracy: Class C (±1%)
IP Rating: IP67
Certifications: ISO 4064, OIML R49Consumer Allocation
Current Consumer:
Name: John Smith
Account: AccNo1
Period: 2023-05-15 - Present
Contact: +1 555-123-4567
Email: john.smith@example.com
Type: Non-Domestic / Commercial
Address: 123 Main St, Anytown
Previous Consumer:
Name: Maria Rodriguez
Account: AccNo2
Period: 2022-01-10 - 2023-05-14
Contact: +1 555-987-6543
Email: maria.rodriguez@example.com
Type: Domestic / Residential
Address: 123 Main St, AnytownReading History
Date: 2025-03-25
Month: January
Reading: 34 m³
Status: NORMAL
Reader: MX
Validator: kaushal
Date: 2025-02-25
Month: December
Reading: 32.5 m³
Status: NORMAL
Reader: MX
Validator: kaushal
Date: 2025-01-25
Month: November
Reading: 30.2 m³
Status: NORMAL
Reader: MX
Validator: kaushalService History
Type: READING
Date: 2025-03-25
Description: Manual reading recorded: 34
By: kaushal
Type: MAINTENANCE
Date: 2024-12-10
Description: Completed maintenance check
By: John Smith
Type: INSTALLATION
Date: 2022-05-22
Description: Initial installation
By: Mike JohnsonWork Orders
Type: MAINTENANCE
Description: Regular maintenance check
Assigned To: John Smith
Status: COMPLETED
Date: 2024-12-10
Type: CALIBRATION
Description: Annual calibration
Assigned To: Mike Johnson
Status: PENDING
Date: 2025-04-159. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must display a dashboard showing counts of meters by status (Active, Maintenance, Retired, Unassigned)
- The system must allow filtering of meters by type (Manual, Photo, Smart) with accurate counts
- The system must provide a search function to find meters by serial number, consumer name, or location
- The system must display a detailed view of individual meters with tabs for different information categories
- The system must track and display meter technical specifications including manufacturer, model, and physical characteristics
- The system must maintain and display complete consumer allocation history for each meter
- The system must allow users to create service orders with specific types, dates, and reasons
- The system must track meter reading history with validation status and validator information
- The system must display consumption history in both tabular and graphical formats
- The system must maintain a complete activity log of all actions performed on a meter
- The system must allow users to add and view notes associated with each meter
- The system must support work order tracking with status updates and completion records
- The system must allow reassignment of meters to different consumers with historical tracking
- The system must track alert conditions and display the count of active alerts per meter
- The system must support bulk addition of meters through the "Bulk Add Meters" function
- The system must allow editing of meter information while maintaining change history
- The system must display key statistics including days in service, installation date, and maintenance history
- The system must provide export functionality for meter data and consumption history
- The system must prevent invalid state transitions (e.g., from Retired to Active) with appropriate error messages
- The system must require reason documentation for key actions such as meter disposal or status changes
10. Process Changes
Current Process | New Process | Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
Manual tracking of meter inventory in spreadsheets or disconnected systems | Centralized inventory management with real-time status tracking | Reduces inventory reconciliation time by 80% and improves accuracy of meter counts |
Paper-based or verbal work order creation for meter service | Digital work order creation with structured data fields and status tracking | Reduces work order processing time by 60% and eliminates lost or incomplete work orders |
Limited visibility into meter history and maintenance records | Complete digital lifecycle record from installation through retirement | Enables data-driven maintenance scheduling and reduces unnecessary replacements by 25% |
Manual association of meters to consumers and premises | Digital allocation tracking with complete history preservation | Reduces billing errors related to incorrect meter association by 90% |
Isolated reading validation without historical context | Contextual validation with historical consumption patterns and meter specifications | Improves reading accuracy by 40% and reduces estimated readings by 30% |
Reactive approach to meter maintenance based on failures | Proactive maintenance scheduling based on age, usage, and performance metrics | Extends average meter lifespan by 15% and reduces emergency replacements by 40% |
Limited meter performance analysis capabilities | Comprehensive analytics on meter types, ages, and failure patterns | Enables data-driven procurement decisions, reducing inventory costs by 20% |
Disconnected processes between field operations and office administration | Integrated workflow from work order creation through completion and billing | Reduces cross-departmental communication errors by 70% and improves service delivery |
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Metric | Impact |
|---|---|
Meter Management Efficiency | 75% reduction in time spent tracking and managing meter inventory |
Meter Lifespan | 15-20% increase in average meter lifespan through optimized maintenance scheduling |
Reading Accuracy | 40% reduction in reading errors and disputed bills |
Field Service Productivity | 30% increase in completed service orders per technician per day |
Inventory Costs | 20% reduction in inventory carrying costs through improved visibility and planning |
Emergency Replacements | 40% reduction in emergency meter replacements |
Data Quality | 95% improvement in meter data completeness and accuracy |
Regulatory Compliance | 100% audit trail for all meter-related activities |
Consumer Satisfaction | 25% reduction in billing disputes related to meter issues |
Revenue Protection | 15% improvement in identifying potential meter tampering or malfunction |
12. User Behavior Tracking
Meter Supervisor Tracking
Metric | Events | Properties |
|---|---|---|
Inventory Management Efficiency | Meter addition, status updates, bulk operations | Time to complete, number of meters processed, error rate |
Meter Replacement Decision Making | Meter replacement order creation | Age of meter, reason for replacement, time since last maintenance |
Alert Response | Alert view, alert resolution | Alert type, time to resolution, resolution action |
Inventory Planning | Inventory view, filter usage | Filter criteria, search terms, export actions |
Questions Answered:
- How efficiently are meters being added and managed? What is the quality of data entry?
- Are meters being replaced based on optimal criteria? What factors trigger most replacements?
- How quickly are meter alerts addressed? What types of alerts are most common?
- How are supervisors analyzing the meter inventory? What metrics are most important for decision making?
Technical Management Tracking
Metric | Events | Properties |
|---|---|---|
Technical Specification Access | Specification views, documentation access | Meter type, specification category, search patterns |
Certification Management | Certification checks, expiration monitoring | Certification type, expiration proximity, renewal actions |
Documentation Completeness | Document uploads, specification updates | Completion rate, missing fields, documentation types |
Technical Issue Resolution | Technical issue logging, resolution actions | Issue type, resolution time, escalation frequency |
Questions Answered:
- Which technical specifications are most frequently referenced? What documentation gaps exist?
- How effectively are certification renewals being managed before expiration?
- What is the completeness level of technical documentation across meter types?
- What technical issues occur most frequently and how quickly are they resolved?