Data Migration (ONB01 S01)
User Story: AI-Powered Data Migration & Transformation
1. Problem Statement
Utilities migrating from legacy systems to SMART360 face significant challenges in data migration and transformation. The process is:
- Time-consuming, taking weeks to migrate critical utility data such as consumer records, meter readings, and billing history.
- Error-prone, leading to data loss, incorrect meter-to-consumer mapping, and inconsistencies in billing and service requests.
- Manually intensive, requiring extensive effort to clean, format, and validate consumption data, payment records, and asset details.
These challenges directly impact key utility operations, including:
- Billing & Revenue Management – Incorrect data leads to overbilling, underbilling, or missing payments, causing financial discrepancies.
- Service Order Execution – Delays in consumer data migration result in service interruptions and slow request processing.
- Meter Data Management – Inaccurate meter readings and historical data errors affect consumption tracking and billing accuracy.
- Asset & Territory Management – Improper mapping of utility assets (transformers, substations, meters) leads to inefficiencies in maintenance and tracking.
Without an efficient migration system, utilities experience:
- Delayed operational readiness, increasing the time required to onboard and serve customers.
- High support dependency, as utility teams spend excessive time manually fixing migration errors.
- Revenue leakage, where incorrect billing data and missing transactions result in financial losses.
An optimized data migration solution for utilities is essential to ensure accurate, efficient, and seamless onboarding into SMART360.
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
- Utility Admin: Unable to migrate territory data efficiently, leading to delays in system setup.
- CX Admin: Struggles with bulk uploads of consumer accounts, payments, complaints, and services, causing payment delays and incorrect account statuses.
- MX Admin: Cannot migrate bulk meter data, historical readings, or update large datasets, leading to errors in consumption tracking and billing.
- WX Admin: Lacks bulk import functionality for service order templates, slowing work order execution.
- AX Manager: Faces inefficiencies in importing plant, unit, and asset data, impacting asset tracking and maintenance scheduling.
These users spend weeks cleaning, transforming, and loading data manually using Postman, Excel, and external tools, creating operational bottlenecks.
3. Jobs To Be Done
As a Utility Admin / CX Admin / MX Admin / WX Admin / AX Manager,
I want to migrate bulk data effortlessly while ensuring accuracy,
So that I can focus on operations efficiently with speed, ease of use, high adoption, and seamless data flow.
4. Solution
The AI-Powered Data Migration & Transformation feature introduces:
- AI-Powered Column Mapping – Auto-detects & suggests field mappings with accuracy scores.
- Data Transformation Rules – Standardizes formats, merges/splits columns, and applies regex corrections.
- Live Validation & Error Handling – Detects missing/incorrect data with inline fixing suggestions.
Preview Before Migration– Side-by-side comparison of uploaded vs. processed data.- Smart Auto-Correction & Recommendations – AI-powered anomaly detection and bulk edit options.
- Real-Time Progress & Rollback – Track migration progress, pause, retry, or rollback if needed.
- Post-Migration Reports & Audit Logs – Exportable logs, success/failure reports, and full audit trails.
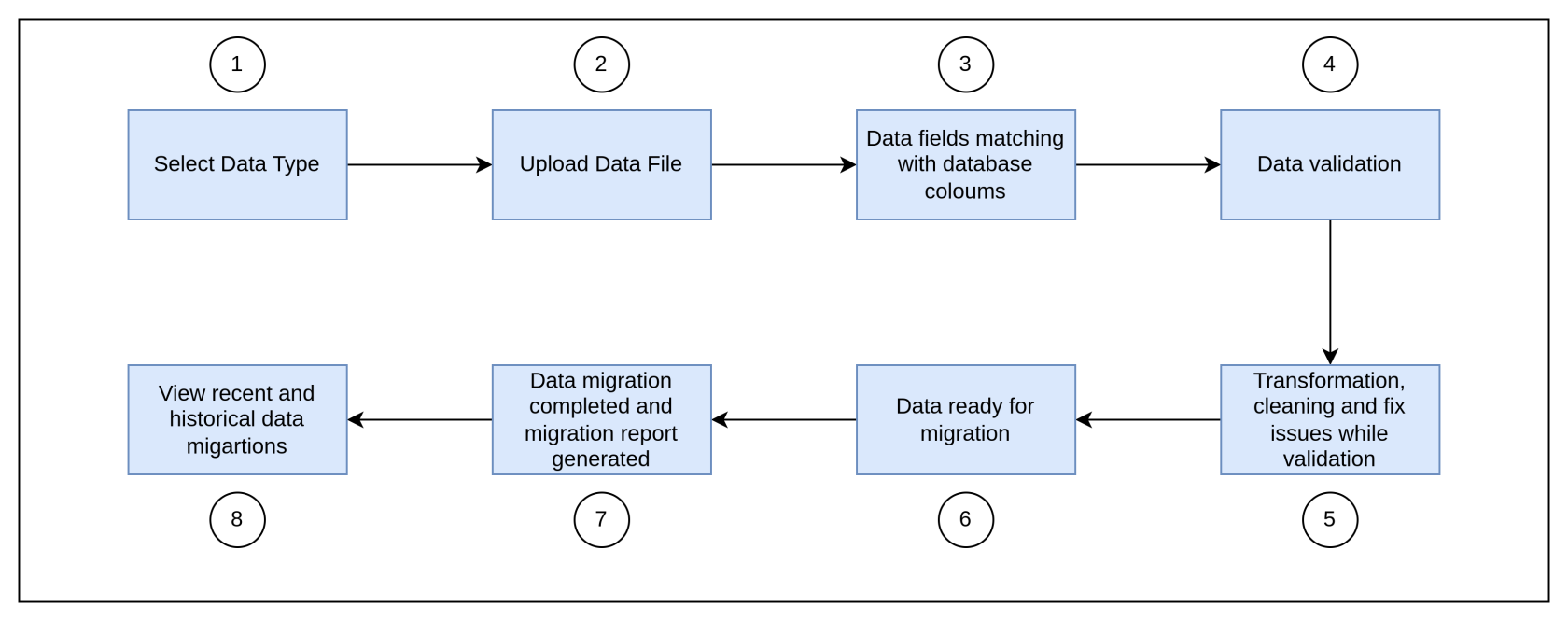
5. Process Flow
6. Major Steps Involved
- User uploads bulk data file (CSV, Excel, JSON, etc.).
- AI-powered column mapping suggests auto-matched fields with manual override.
- Data transformation engine cleans and formats entries (e.g., date standardization, merging duplicate records).
- Live validation detects issues (missing fields, incorrect formats, duplicate entries).
- Inline fixing suggestions are provided for errors.
- Preview step allows users to compare source vs. transformed data.
- User initiates migration, tracking real-time progress.
- Audit logs & post-migration reports confirm success/failures and rollback options.
7. Business Rules
Process Authorization Rules
Upload Process
- The system supports AI-powered data upload functionality for seamless integration into the Smart360 system.
- Users can upload data for various data types including:
- Consumers (customer accounts and profiles)
- Meters (water meter information and details)
- Meter Data (usage readings and consumption data)
- Plans (service plans and rate configurations)
- Tariffs (pricing structures and rate cards)
- Service Orders (work orders and service requests)
- Payments (customer payment history and transactions)
- Complaints (customer support tickets and issues)
- User Data (system users and administrative accounts)
- File upload supports CSV, Excel, and JSON formats with a maximum file size of 20MB.
- Files can be uploaded either through drag-and-drop functionality or by browsing for files.
- The system displays upload progress with percentage completion indicators.
- Once uploaded, the system displays a confirmation message for successful uploads.
Data Analysis and Mapping
- The AI system automatically detects and suggests data types based on file contents (e.g., "Detected: Consumer Data").
- The system provides a preview of the uploaded data showing a sample of records (e.g., "Showing 5 of 7052 records").
- AI automatically analyzes the file and suggests column mappings between source columns and target Smart360 fields.
- Each suggested mapping is assigned a confidence level (High, Medium, Low) to indicate the reliability of the mapping.
- File information is displayed showing:
- Filename
- Total columns (e.g., 8)
- Total rows (e.g., 2,426)
- Mapping quality indicators (e.g., 5 High, 2 Medium, 1 Low)
- Source columns are mapped to target fields with sample data displayed for reference.
- Users can manually adjust mappings through dropdown selection if the AI suggestion is incorrect.
- The system enforces proper field type mapping (e.g., ensuring Customer ID fields map to appropriate ID fields).
Validation Process
- The system performs data validation after mapping to identify issues requiring attention.
- Validation results are categorized as:
- Valid records (with percentage)
- Warnings (with percentage)
- Errors (with percentage)
- The system specifically identifies and flags:
- Format issues (e.g., "Missing Postal Code format")
- Data inconsistencies (e.g., "Date format inconsistency")
- Unmapped fields (e.g., "Unmapped field: Meter_Type")
- For each issue type, the system shows the number of affected records.
- Users can download a validation report for offline review.
- The system provides detailed information for each issue, including specific records affected.
- A "Fix All Issues" option is available for batch resolution of problems.
Data Correction
- Users can view detailed information about each issue by expanding the issue sections.
- For format issues (e.g., postal codes), the system allows:
- Viewing specific invalid records
- Auto-formatting data to meet system requirements
- For unmapped fields, the system:
- Suggests possible Smart360 mappings
- Allows users to select the appropriate field mapping
- The system tracks correction status, showing:
- Fixed issues (with green checkmarks)
- Remaining issues (with warning or error icons)
- When issues are corrected, the system updates validation statistics (e.g., Valid records percentage increases).
- Auto-format functionality can standardize data formats (e.g., converting postal codes to standard formats).
Migration Process
- The migration process follows a sequential workflow:
- Upload (choose file)
- Map (define field mapping)
- Validate (fix any issues)
- Migrate (complete process)
- All issues must be resolved before proceeding to the final migration step.
- The system provides navigation options to move between steps (e.g., "Back to Mapping").
- Keyboard shortcuts are available for navigation (e.g., Alt+1, Alt+2, etc.).
- When all issues are resolved, the system displays a "Fix issues to proceed" message with a confirmation that data will be ready for migration.
- The system provides confirmation messages for successful actions (e.g., "Format corrected - All postal codes have been standardized").
- Error messages are displayed when system errors occur during the process.
Pre-Migration Validation
Source data must be validated for completeness and integrity before migration beginsTarget system capacity must be verified to ensure sufficient storage for migrated dataData mapping rules must be established and verified before executionAll personally identifiable information (PII) must be identified and properly secured during migration
Execution Controls
Migrations must follow the established 6-step process (currently showing Step 6: Migration)System must display real-time progress indicators showing percentage complete (currently 34%)Migration logs must capture timestamps and process status for each recordSystem must enforce volume limits of 250 records per batch (85/250 currently processed)Migration processes exceeding 4 hours must trigger automatic notification to system administrators
Error Handling
- All errors must be categorized by error code
- Error descriptions must be logged and displayed in the error log panel
- Unexpected errors must be flagged for immediate administrator attention
- The system must implement automatic retry logic for transient errors
- Critical errors must halt the migration process until administrator intervention
- Detailed Error Codes & Fix Recommendations
Error messages must be specific and provide examples for corrections.
✅ Example of Effective Error Handling:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Error Type | Message | Suggested Fix |
|---|---|---|
Incorrect Format | Date format inconsistent: "Jan 5 2021", "02/03/2024". | Use the standard format: YYYY-MM-DD (e.g., 2024-03-20) . |
Missing Field | Meter ID missing in row 5. Required for meter mapping. | Enter a valid Meter ID before proceeding. |
Duplicate Entry | Meter ID "5001" already exists in the uploaded data (Row 6, Row 12). | Remove duplicates from the uploaded file before re-uploading. |
Overwriting Data | Existing consumer data for Consumer ID "C123" found. | Confirm if data should be updated or kept unchanged. |
Invalid Value | Negative consumption (-250 kWh) in row 12. | Verify meter readings and enter a positive value. |
Mapping Error | Meter ID "M1002" not linked to any consumer account. | Ensure meters are mapped to a valid consumer. |
Unsupported Character | Special characters found in Consumer Name ("John@Doe"). | Remove special characters; use only letters and spaces. |
Post-Migration Rules
System must verify record counts match between source and destinationReconciliation reports must be generated upon migration completionFailed migrations must generate detailed failure analysis reportsData verification scripts must run automatically upon migration completionAll migration activities must be documented in the system audit log
AI Assistant Integration Rules
- AI assistant must provide real-time updates on migration progress
- Assistant must offer troubleshooting guidance for common error patterns
- AI recommendations must be reviewed by human operators before implementation
- Assistant should suggest optimization strategies based on observed performance
Security and Data Management
- The system tracks and allows viewing of upload history.
- The system appears to enforce data quality standards through validation rules.
- The system maintains the relationship between related data entities (e.g., Customer IDs and Meter IDs).
- The system enforces format standards for critical fields like postal codes, dates, and IDs.
- The system allows for error handling and recovery from validation failures.
8. Sample Data Format
Consumer Meter Data
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Consumer Data
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
9. Acceptance Criteria
- Users can successfully upload bulk data files.
- AI-powered field mapping works with >90% accuracy.
- Live validation must detect incorrect/missing data.
- Users can manually correct errors before migration.
- Preview functionality allows comparison between original & processed data.
- Migration progress can be tracked with a real-time status.
- Audit logs provide detailed insights on data corrections.
- Rollback functionality allows reverting migrations.
10. Process Changes
- Eliminates Postman/manual scripts for data import.
- Integrates AI-driven validation before actual migration.
- Replaces manual transformation steps with automated rule-based corrections.
- Reduces dependency on customer support for migration issues.
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Impact Metrics: SMART360 Data Migration Module
| Metric | Before Implementation (Legacy System Challenges) | After Implementation (SMART360 Solution) |
|---|---|---|
Time to Migrate a Single Data Type | 2-4 weeks per data type due to manual validation and cleaning. | Reduced to 2-5 days with automated validation and transformation. |
Data Errors (Formatting, Duplicates, Missing Fields) | 20-30% of uploaded records required manual fixes. | <5% error rate with structured validation and predefined templates. |
Operational Readiness Delays | Onboarding delayed by 4-6 weeks due to incomplete or incorrect data. | Onboarding within 1-2 weeks , ensuring a faster go-live. |
Support Dependency for Data Fixes | 60-70% of migration cases required customer support intervention. | <20% support dependency , as most errors are resolved automatically. |
Billing Inaccuracy Due to Data Issues | Up to 10% of bills generated with incorrect consumption or missing data. | <1% billing errors , ensuring accurate invoicing. |
Service Order Execution Delay | Orders delayed due to missing consumer or meter data. | Immediate execution with correctly mapped consumer-meter relationships. |
Customer Complaints on Migration Issues | 40% of new utility users reported service issues due to incorrect data. | <10% complaints , as clean data is migrated correctly. |
Financial Loss Due to Incorrect Billing | Revenue leakage from incorrect meter readings and missed payments. | Accurate billing ensures zero revenue loss from data inconsistencies. |
12. Summary of Business Impact
By implementing the SMART360 Data Migration Module, utilities can expect:
✅ 80% faster data migration
✅ 85% reduction in errors
✅ 60% lower dependency on manual fixes
✅ Faster system onboarding (within weeks instead of months)
✅ Improved billing accuracy, reducing revenue leakage