User Story: System Types
System Types Management - User Story Document
1. Problem Statement
User Roles Identified:
- Plant Supervisor: Oversees treatment facility operations and monitors system performance parameters
- Utility Administrator: Manages system configuration and maintains system type definitions with monitored parameters
Pain Points by User Role:
Plant Supervisor:
- Fragmented system for tracking different types of infrastructure (intake systems, treatment processes, distribution systems)
- Inconsistent parameter monitoring across different system types leading to incomplete performance analysis
- Difficulty establishing standardized monitoring protocols for different treatment and distribution systems
- Manual tracking of system-specific parameters without proper categorization or historical trending
- Limited ability to correlate system performance with operational efficiency and regulatory compliance
Utility Administrator:
- Time-consuming manual setup of system type configurations and parameter definitions
- Lack of standardized templates for common water utility system types and monitoring parameters
- Difficulty maintaining consistency in system parameter definitions across different operational areas
- Complex process to add new system types and their associated monitored parameters
- Limited ability to customize parameters based on specific utility monitoring requirements
Core Problem:
Water utilities lack a standardized system for managing operational system type definitions with their monitored parameters, leading to inconsistent monitoring protocols, fragmented performance analysis, and inefficient operational oversight across treatment and distribution systems.
2. Who Are the Users Facing the Problem?
Plant Supervisor
- Manages treatment facility operations and system performance monitoring
- Requires standardized system types with proper parameter definitions for effective monitoring
- Needs consistent monitoring protocols across different operational systems
Utility Administrator
- Manages system configuration and master data for operational systems
- Responsible for setting up and maintaining system type definitions with monitoring parameters
- Ensures data consistency across all utility monitoring systems
Both roles should have access to this feature with appropriate permission levels based on their operational responsibilities.
3. Jobs To Be Done
For Plant Supervisor: When I need to monitor treatment and distribution system performance across different operational areas, But I lack standardized system type definitions with proper parameter tracking that makes it difficult to establish consistent monitoring protocols and analyze performance trends, Help me access integrated system type management with standardized parameter definitions and monitoring capabilities, So that I can implement effective monitoring protocols, analyze system performance trends, and make informed operational decisions.
For Utility Administrator: When I need to set up and maintain consistent system type definitions and monitoring parameters across the utility, But I face time-consuming manual processes and lack of standardized templates for system monitoring that create data inconsistencies, Help me configure system types with pre-built templates, easy customization options, and integrated parameter management, So that I can ensure monitoring consistency, reduce setup time for new systems, and maintain standardized operational protocols.
4. Solution
The System Types Management system provides a comprehensive platform for organizing operational systems and their monitoring parameters with the following capability areas:
4.1 System Type Definition and Management
- Pre-configured system types for water utility operations (Intake System, Raw Water Transmission System, Pre-treatment System, Filtration System)
- Custom system type creation with detailed operational descriptions
- Hierarchical organization of system types based on operational workflow
4.2 Parameter Management for System Monitoring
- Configurable monitored parameters for each system type with units of measurement
- Standardized parameter templates for water quality, flow, pressure, and performance metrics
- Custom parameter creation with validation rules and measurement specifications
4.3 Operational System Templates
- Industry-standard system type templates for common water utility operations
- Pre-defined parameter sets for typical monitoring requirements
- Best practice guidance for system monitoring and performance analysis
4.4 Search and Filter Capabilities
- Advanced search across system types and monitored parameters
- Filter by system type for focused management and configuration
- Quick access to related system information and parameter specifications
4.5 Parameter Specification Management
- Detailed parameter definitions with units of measurement and descriptions
- Support for various measurement types (water quality, physical, operational)
- Integration with monitoring systems and data collection platforms
4.6 System Integration and Data Management
- Seamless integration with monitoring platforms and SCADA systems
- Export capabilities for reporting and regulatory compliance
- Data validation and consistency checks across system definitions
4.7 Standardization and Compliance
- Regulatory compliance templates for water quality monitoring
- Standardized naming conventions and parameter specifications
- Audit trails for all system type and parameter changes
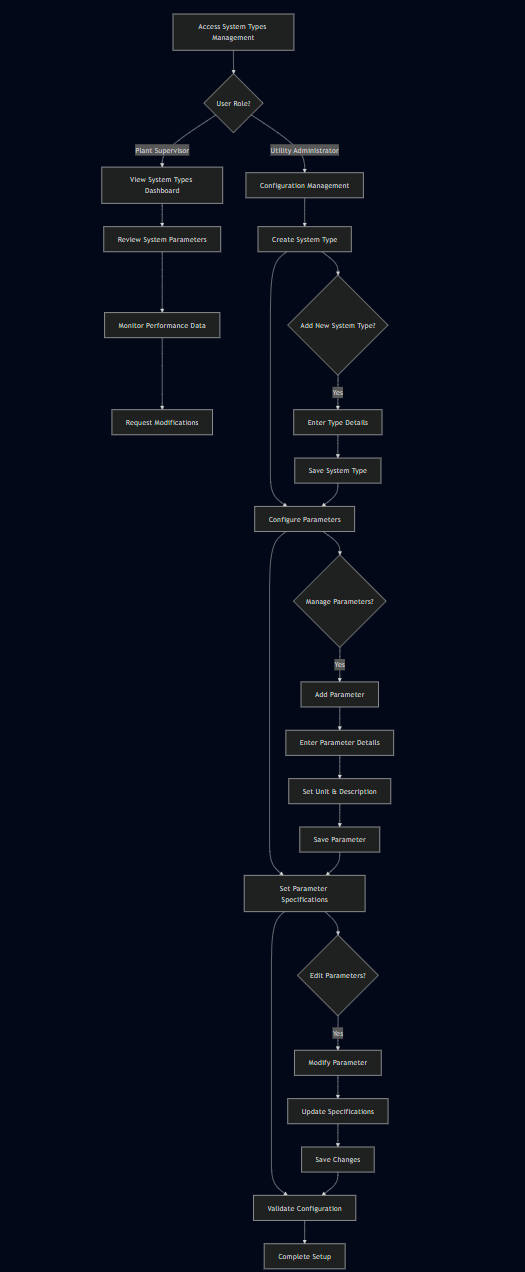
5. Major Steps Involved
Plant Supervisor Flow:
- Access System Types Dashboard
- Navigate to Settings > System Types
- View existing system type definitions and parameter counts
- Review system descriptions and monitoring requirements
- Review System Parameter Configurations
- Expand system types to view monitored parameters
- Review parameter specifications including units and descriptions
- Assess current monitoring coverage and parameter effectiveness
- Monitor System Performance Data
- Access parameter data from integrated monitoring systems
- Analyze trends and performance metrics by system type
- Identify optimization opportunities and operational improvements
- Request System Type Modifications
- Identify gaps in current system monitoring
- Submit requests for new parameters or system types
- Provide operational requirements for monitoring enhancements
- Validate Monitoring Effectiveness
- Review system type utilization and parameter data quality
- Assess monitoring protocol effectiveness
- Recommend improvements for operational oversight
Utility Administrator Flow:
- System Configuration Access
- Log into SMART360 administrative interface
- Navigate to Settings > System Types
- Access system type management dashboard
- Create New System Type
- Click "Add New System Type" button
- Enter system type name and operational description
- Configure system-level settings and monitoring requirements
- Configure Monitored Parameters
- Select specific system type
- Click "Manage Parameters"
- Add new parameters with names, units, and descriptions
- Configure parameter specifications and validation rules
- Set Up Parameter Specifications
- Define parameter names with measurement units
- Enter detailed descriptions for monitoring purposes
- Configure data validation rules and acceptable ranges
- Manage Existing Parameters
- Review and edit existing parameter definitions
- Update parameter specifications as monitoring requirements change
- Remove obsolete parameters with proper validation
- Validate and Test Configuration
- Review complete system type hierarchy
- Test parameter configuration with monitoring systems
- Validate integration with data collection platforms
6. Flow Diagram
7. Business Rules
9. System Types Management
System Types Main Page
Page Header
- Title: "System Types"
- Subtitle: "Define and manage system types and their monitored parameters."
- Breadcrumb: Dashboard > Settings > system-types
Search Field (System Types)
- Field Name: Search
- Placeholder: "Search system types or parameters..."
- Rules:
- Minimum 2 characters required to trigger search
- Search is case-insensitive
- Searches across system type names, descriptions, and parameter names
- Real-time search with 300ms debounce
- Maximum 100 characters allowed
- Special characters allowed: hyphen (-), underscore (_), space, parentheses ()
- Search results highlight matching terms
- Empty search displays all system types
Filter by System Type Dropdown
- Field Name: Filter by System Type
- Default Value: "All System Types"
- Rules:
- Dropdown populates with all existing system type names
- Selection filters the hierarchy view to show only selected type
- "All System Types" option shows complete hierarchy
- Selection persists during session
- Must reset to "All System Types" when system types are added/deleted
Add New System Type Button
System Types Hierarchy Section
System Type Card Display
- Display Requirements:
- System type name displayed as clickable header in blue (
#2563eb) - Parameter count displayed as "{X} parameters" next to type name
- Description shown below type name in gray text
- Expand/collapse functionality with chevron icon
- Edit icon (pencil) on hover for authorized users
- Delete icon (trash) on hover for authorized users
- Three-dot menu for additional actions
- System type name displayed as clickable header in blue (
System Type Examples (from screenshots):
- Intake System: "8 parameters"
- Description: "Raw water collection system that draws water from sources like rivers, lakes, or reservoirs. Monitors water quality at the point of entry."
- Raw Water Transmission System: "3 parameters"
- Description: "Infrastructure that transports raw water from the intake to the treatment plant through pipes, pumps, and storage facilities."
- Pre-treatment System: "7 parameters"
- Description: "Initial treatment processes including coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation to remove large particles and contaminants."
- Filtration System: "7 parameters"
System Type Name
- Rules:
- Required field
- Minimum 3 characters, maximum 50 characters
- Must be unique across all system types (case-insensitive)
- Allowed characters: letters, numbers, spaces, hyphens, ampersands
- Cannot start or end with spaces
- Cannot contain consecutive spaces
- Cannot be only numbers
- Cannot contain special characters: @, #, $, %, ^, *, <, >, ?, |, , /, [, ]
System Type Description
- Rules:
- Required field
- Minimum 10 characters, maximum 500 characters
- Must provide meaningful description of system type purpose
- Cannot be only spaces or special characters
- HTML tags not allowed
- Line breaks preserved in display
Parameter Count Display
- Rules:
- Automatically calculated and displayed
- Format: "{count} parameters" (e.g., "8 parameters", "3 parameters")
- Updates in real-time when parameters are added/removed
- Shows "0 parameters" for empty system types
- Non-editable field
Add New System Type Modal
Modal Header
- Text: "Add New System Type"
- Rules:
- Fixed header text
- Close button (X) in top right corner
System Type Name Field
- Field Label: "System Type Name"
- Placeholder: "Enter system type name..."
- Rules:
- Required field with red asterisk indicator
- Real-time validation with error messages
- Character count indicator showing remaining characters
- Validation error: "System type name must be between 3-50 characters"
- Uniqueness validation: "System type name already exists"
- Invalid character error: "System type name contains invalid characters"
System Type Description Field
- Field Label: "Description"
- Placeholder: "Enter system type description..."
- Field Type: Textarea
- Rules:
- Required field with red asterisk indicator
- Character count indicator (10/500)
- Auto-resize textarea based on content
- Validation error: "Description must be between 10-500 characters"
- Cannot contain only whitespace
Add System Type Button
Manage Parameters Section
Manage Parameters Button
Monitored Parameters Display
- Label: "Monitored Parameters:"
- Display Rules:
- Shows parameter names with units in parentheses
- Format: "Parameter Name (Unit), Parameter Name (Unit), and X more..."
- Maximum 5 parameters shown in preview
- "and X more..." shown if more than 5 parameters exist
- Hover tooltip shows all parameters
- Clickable to open parameter management
Example Parameters (from screenshots):
- Intake System Parameters: "Raw Water Turbidity (NTU), Raw Water pH (), Raw Water Temperature (°C/°F), Raw Water Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L), Raw Water Conductivity (μS/cm), and 3 more..."
Manage Parameters Modal
Modal Header
- Text: "Manage Parameters for: [System Type Name]"
- Rules:
- Dynamically shows system type name
- Cannot exceed 80 characters total length
- Close button (X) in top right corner
Add New Parameter Section
Parameter Name Field
- Field Label: "Parameter Name"
- Placeholder: "Enter parameter name..."
- Rules:
- Required field
- Minimum 3 characters, maximum 50 characters
- Must be unique within the system type (case-insensitive)
- Allowed characters: letters, numbers, spaces, hyphens, parentheses
- Cannot start or end with spaces
- Cannot contain consecutive spaces
- Common water quality parameters suggested in dropdown
Unit of Measurement Field
- Field Label: "Unit of Measurement"
- Placeholder: "Enter unit..."
- Rules:
- Optional field
- Maximum 20 characters
- Common units suggested in dropdown: NTU, mg/L, μS/cm, °C, °F, pH, ppm, %
- Custom units allowed
- Cannot contain special characters except forward slash (/), parentheses (), and degree symbol (°)
- Empty unit displays as "()" in parameter list
Parameter Description Field
- Field Label: "Description"
- Placeholder: "Enter parameter description..."
- Field Type: Textarea
- Rules:
- Required field
- Minimum 10 characters, maximum 300 characters
- Cannot contain only whitespace
- Auto-resize textarea
- Character count indicator
Add Parameter Button
Existing Parameters Section
Section Header
- Text: "Existing Parameters"
- Rules:
- Shows count in parentheses: "Existing Parameters (X)"
- Hidden if no existing parameters
Parameter List Items
- Display Format: "[Parameter Name] [Unit]"
- Example: "Raw Water Turbidity NTU"
- Rules:
- Parameter name displayed first
- Unit shown in gray text if provided
- Parameter description below in smaller gray text
- Edit icon (pencil) on hover
- Delete icon (trash) on hover
Example Parameters (from screenshots):
- Raw Water Turbidity: "NTU" - "Monitor and track raw water turbidity levels"
Edit Parameter
- Rules:
- Inline editing with save/cancel options
- Same validation rules as new parameter creation
- Changes save automatically on blur or Enter key
- Escape key cancels editing
- Cannot edit parameter name if data exists in monitoring system
Delete Parameter
- Rules:
- Confirmation dialog: "Are you sure you want to delete this parameter?"
- Cannot delete if parameter has monitoring data
- Error message: "Cannot delete parameter - it contains monitoring data"
- Success message: "Parameter deleted successfully"
8. Sample Data
System Types and Parameters:
Intake System (8 parameters)
├── Description: Raw water collection system that draws water from sources like rivers, lakes, or reservoirs. Monitors water quality at the point of entry.
├── Parameters:
├── Raw Water Turbidity (NTU)
├── Raw Water pH ()
├── Raw Water Temperature (°C/°F)
├── Raw Water Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L)
├── Raw Water Conductivity (μS/cm)
├── Raw Water Alkalinity (mg/L)
├── Raw Water Hardness (mg/L)
└── Flow Rate (L/s)
Raw Water Transmission System (3 parameters)
├── Description: Infrastructure that transports raw water from the intake to the treatment plant through pipes, pumps, and storage facilities.
├── Parameters:
├── Transmission Pressure (kPa)
├── Flow Velocity (m/s)
└── Pipeline Pressure Loss (kPa/km)
Pre-treatment System (7 parameters)
├── Description: Initial treatment processes including coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation to remove large particles and contaminants.
├── Parameters:
├── Coagulant Dose (mg/L)
├── Flocculant Dose (mg/L)
├── Settling Tank Efficiency (%)
├── Sludge Production Rate (kg/day)
├── Chemical Feed Rate (L/min)
├── Mixing Intensity (rpm)
└── Retention Time (minutes)
Filtration System (7 parameters)
├── Description: Advanced filtration processes for removing fine particles, pathogens, and dissolved contaminants from pre-treated water.
├── Parameters:
├── Filter Bed Depth (m)
├── Filtration Rate (m/h)
├── Backwash Frequency (hours)
├── Filter Efficiency (%)
├── Pressure Drop (kPa)
├── Turbidity Removal (%)
└── Filter Runtime (hours)Sample Parameter Details:
Parameter: Raw Water Turbidity
├── Unit: NTU
├── Description: Monitor and track raw water turbidity levels to assess source water quality and treatment requirements
├── Monitoring Frequency: Continuous
├── Acceptable Range: 0.1 - 100 NTU
├── Regulatory Requirement: Yes
Parameter: Coagulant Dose
├── Unit: mg/L
├── Description: Track chemical coagulant dosing rates for optimal flocculation and particle removal efficiency
├── Monitoring Frequency: Hourly
├── Acceptable Range: 5 - 50 mg/L
├── Regulatory Requirement: No
Parameter: Filter Efficiency
├── Unit: %
├── Description: Monitor filtration system performance through removal efficiency calculations
├── Monitoring Frequency: Daily
├── Acceptable Range: 95 - 99.9%
├── Regulatory Requirement: Yes9. Acceptance Criteria
- The system must display a hierarchical view of system types with parameter counts
- The system must allow creation of new system types with name and description fields
- The system must provide parameter management for each system type with add/edit/delete capabilities
- The system must support parameter configuration with name, unit, and description fields
- The system must validate that system type names are unique across the system
- The system must validate that parameter names are unique within their parent system type
- The system must prevent deletion of system types that have associated monitoring data
- The system must prevent deletion of parameters that contain historical monitoring data
- The system must provide search functionality across system types and parameters
- The system must support filtering by system type in management views
- The system must display parameter counts for each system type
- The system must support various parameter units (NTU, mg/L, °C, %, kPa, etc.)
- The system must allow optional unit specifications for qualitative parameters
- The system must provide validation for parameter descriptions and specifications
- The system must maintain audit trails for all system type and parameter changes
- The system must support export of system type data for reporting purposes
- The system must integrate with monitoring systems for parameter data collection
- The system must provide role-based access control for system type management
- The system must display clear error messages for validation failures
- The system must support bulk parameter management operations
10. Process Changes
Process Area | From | To | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
System Monitoring Setup | Manual configuration of monitoring parameters without standardization | Guided system type creation with predefined parameter templates | 60% reduction in setup time, 80% improvement in monitoring consistency |
Parameter Management | Individual parameter setup across different monitoring systems | Centralized parameter management with system type organization | 70% reduction in configuration effort, 90% improvement in parameter standardization |
Operational Reporting | Manual compilation of monitoring data from multiple sources | Automated reporting based on standardized system type parameters | 50% reduction in reporting time, 85% improvement in data accuracy |
System Performance Analysis | Ad-hoc analysis with inconsistent parameter definitions | Systematic analysis using standardized system types and parameters | 40% improvement in analysis efficiency, 75% better trend identification |
Regulatory Compliance | Manual tracking of required parameters across systems | Automated compliance monitoring with system type parameter mapping | 80% reduction in compliance preparation time, 95% improvement in audit readiness |
New System Commissioning | Custom parameter setup for each new system | Template-based commissioning using existing system type definitions | 65% reduction in commissioning time, 90% improvement in monitoring consistency |
Cross-System Coordination | Different parameter naming across operational areas | Unified parameter definitions with consistent naming conventions | 85% reduction in communication errors, 95% improvement in operational coordination |
Performance Optimization | Limited ability to compare systems due to parameter inconsistencies | Comprehensive system comparison using standardized parameter definitions | 70% improvement in optimization insights, 60% better operational decision-making |
11. Impact from Solving This Problem
Impact Category | Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|---|
Operational Efficiency | System monitoring setup time | 60% reduction through standardized templates and pre-configured parameters |
Data Quality | Parameter definition consistency | 90% improvement through enforced standardization and validation rules |
Monitoring Effectiveness | Parameter coverage completeness | 80% improvement through systematic parameter management |
System Performance | Performance analysis accuracy | 75% improvement through standardized parameter definitions and trending |
Resource Utilization | Administrative workload | 70% reduction in parameter configuration and maintenance efforts |
Decision Making | Operational insights quality | 60% improvement through consistent system type organization and analysis |
Compliance Management | Regulatory reporting accuracy | 95% improvement through automated parameter mapping and tracking |
Cross-System Coordination | Operational communication efficiency | 85% improvement through unified parameter terminology |
Performance Optimization | System comparison capability | 70% improvement through standardized parameter benchmarking |
Strategic Planning | System upgrade effectiveness | 65% improvement through comprehensive parameter performance history |
12. User Behavior Tracking
Plant Supervisor Tracking:
Event | Properties | Insights Goal |
|---|---|---|
system_type_performance_viewed | system_type, parameters_accessed, time_spent, performance_period | Understanding which system types require the most operational attention |
parameter_analysis_performed | system_type, parameters_analyzed, analysis_duration, trends_identified | Identifying parameters most critical for operational decision-making |
monitoring_dashboard_accessed | system_types_viewed, parameters_monitored, alert_responses | Tracking operational monitoring patterns and response effectiveness |
system_performance_exported | system_type, parameters_included, export_format, use_case | Understanding reporting needs and most valuable system performance data |
Questions Answered:
- Which system types require the most operational monitoring?
- What parameters are most critical for performance optimization?
- How effectively are monitoring protocols being followed?
- What system performance data is most valuable for operational decisions?
Utility Administrator Tracking:
Event | Properties | Metrics | Insights Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
system_type_created | type_name, creation_time, parameters_count, user_id | Number of new system types per month | Measuring system expansion and monitoring evolution |
parameter_configured | parameter_name, system_type, unit_specified, description_length | Configuration complexity and completeness | Understanding setup patterns and optimization opportunities |
parameter_management_session | system_type, parameters_modified, session_duration, changes_made | Time spent on parameter configuration | Identifying areas where templates or automation could improve efficiency |
system_type_search_performed | search_term, results_found, action_taken, user_context | Search effectiveness and user behavior | Improving search functionality and information architecture |
validation_errors_encountered | error_type, field_name, resolution_time, system_type | Data quality and user experience | Identifying common configuration issues and improving user guidance |
monitoring_integration_tested | system_type, parameters_tested, integration_success, issues_found | Integration effectiveness and reliability | Ensuring seamless connection with monitoring systems |
Questions Answered:
- How effectively are administrators configuring new system types?
- Where do users encounter the most difficulty in parameter setup?
- What are the most common system type configuration patterns?
- How can we streamline the administrative workflow?
- Are parameter definitions comprehensive for monitoring needs?
- What templates or automation would provide the most value?