Production Architecture Overview
Overview
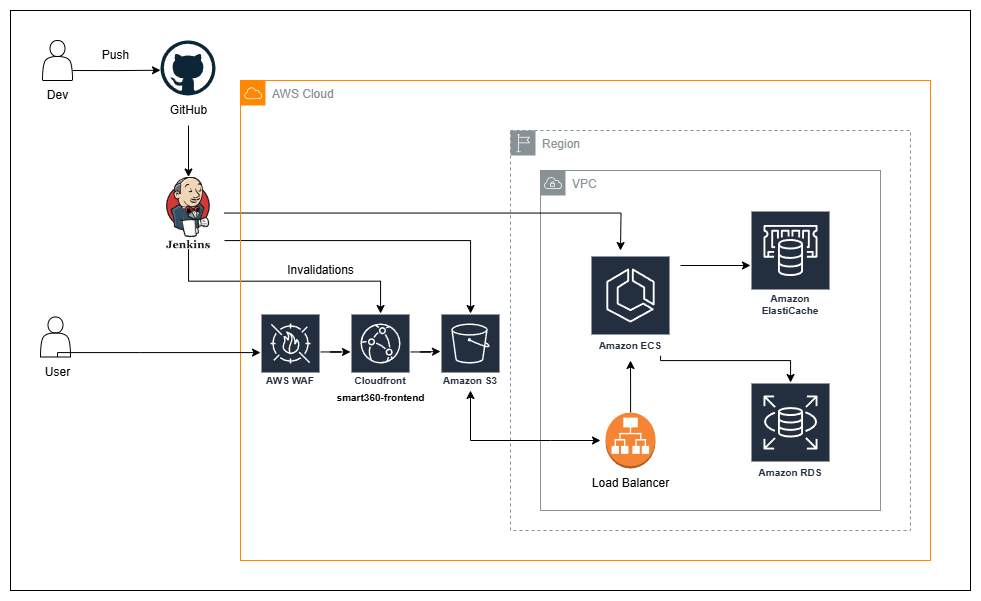
This document provides an overview of the SMART360 product's AWS production architecture deployed in the us-east-1 region. The architecture follows a microservices pattern with a React frontend and Django backend services.
Architecture Components
Frontend Layer
- Technology: React Application
- Hosting: Amazon S3 (Static Website Hosting)
- CDN: Amazon CloudFront
- Security: AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) protecting CloudFront
- Deployment: Automated via Jenkins CI/CD pipeline
Backend Layer
- Technology: Django-based microservices
- Container Orchestration: Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- Compute: 2 x EC2 instances (t3a.xlarge)
- Load Balancing: Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Service Count: 9 microservices currently deployed
- Deployment Strategy: Rolling updates
- Auto Scaling: Enabled (detailed in separate ECS documentation)
Data Layer
- Primary Database: Amazon RDS PostgreSQL 15
- Caching: Amazon ElastiCache Redis (cache.t4g.small)
- Object Storage: Amazon S3 (for static assets and file storage)
AWS Services Used
The SMART360 architecture leverages the following AWS services:
Compute Services
- Amazon EC2: Provides the underlying compute instances for ECS cluster (2 x t3a.xlarge)
- Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service): Container orchestration for microservices deployment and management
Storage Services
- Amazon S3: Static website hosting for React frontend and object storage
- Amazon RDS: Managed PostgreSQL 15 database for persistent data storage
Networking & Content Delivery
- Amazon CloudFront: Global CDN for fast content delivery and caching
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): Distributes incoming traffic across ECS services
- Amazon VPC: Isolated network environment for secure service communication
Caching
- Amazon ElastiCache: Redis caching layer (cache.t4g.small) for improved performance
Security
- AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall): Protects against common web exploits and attacks
Developer Tools & CI/CD
- Amazon ECR: Docker container registry for microservice images (implied for ECS deployments)
Monitoring (Third-party Integration)
- AWS CloudWatch: Default infrastructure monitoring and logging
- Signoz: Primary logging and observability solution [apollo.bynry.com]
Application Stack
- Backend: Python (3.11.4), Django (4.1.9), uwsgi (2.0.26)
- Frontend: React 18
- Source Control: GitHub integration
- Redis : Redis 3.5.3, Elasticache Engine v7.1.0
- DB : Postgres 15
CI/CD Pipeline [Triggered Manually]
- Tool: Jenkins
- Deployment: Manual trigger for each microservice and frontend
- Source Control: GitHub integration
- Deployment Flow:
- Developer pushes code to GitHub
- Manual trigger of Jenkins pipeline
- Build and deployment to respective AWS services
Architecture Flow
User Request → AWS WAF → CloudFront → S3 (React App)
↓
User API Calls → AWS WAF → CloudFront → ALB → ECS Services → RDS/ElastiCacheRequest Flow Details
- Frontend Requests: Users access the React application through CloudFront, which serves static content from S3
- API Requests: API calls from the frontend are routed through the ALB to appropriate ECS microservices
- Data Access: Microservices interact with PostgreSQL RDS for persistent data and Redis ElastiCache for caching
- Security: All web traffic is filtered through AWS WAF before reaching CloudFront
Key Infrastructure Specifications
Component | Specification |
|---|---|
Region | us-east-1 |
ECS Compute | 2 x t3a.xlarge EC2 instances |
Database | RDS PostgreSQL 15 |
Cache | ElastiCache Redis (cache.t4g.small) |
Microservices | 9 services deployed |
Load Balancer | Application Load Balancer (ALB) |
CDN | CloudFront with WAF protection |
ECS Architecture
For detailed information about the ECS microservices deployment, container configurations, service definitions, and scaling policies, please refer to the comprehensive ECS Architecture documentation:
📖 ECS Architecture Documentation
Deployment Process
Frontend Deployment
- Code changes pushed to GitHub
- Manual trigger of Jenkins pipeline for frontend
- React app built and deployed to S3
- CloudFront cache invalidation (if required)
Backend Deployment
- Code changes pushed to GitHub
- Manual trigger of Jenkins pipeline for specific microservice
- Docker image built and pushed to ECR
- ECS service updated with rolling deployment strategy
- Health checks ensure smooth transition
Security Considerations
- WAF Protection: Web Application Firewall filters malicious requests before they reach the application
- HTTPS: All external communications encrypted via CloudFront SSL/TLS
High Availability & Scaling
- Auto Scaling: ECS services are configured with auto-scaling policies
- Load Distribution: ALB distributes traffic across healthy backends (ECS)
- Database: Daily RDS automated backups are enabled
- CDN: CloudFront provides global edge locations for reduced latency
Document Version: 1.0
Last Updated: June 2025
Maintained By: DevOps
Note: This document provides a high-level overview of the overall architecture. For detailed microservices architecture, scaling configurations, and service-specific details, refer to the linked ECS Architecture documentation.

No Comments